Noise Prediction of Cylinder Flow using Machine Learning
Main Article Content
Abstract
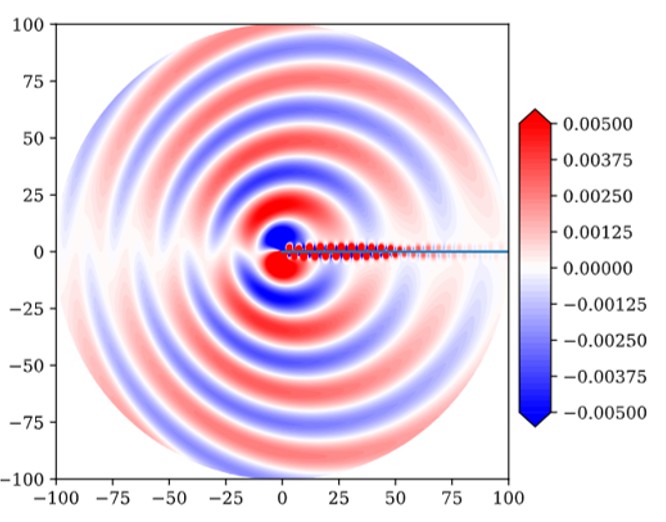
The accurate prediction of aerodynamic noise generated by cylinder flow is a critical challenge in various engineering applications, including automotive and aerospace industries. Traditional Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) methods, such as Direct Numerical Simulation (DNS), often require significant computational resources and time to simulate the complex interactions within flow. This study successfully creates a model using Machine Learning (ML) techniques to predict the pressure fluctuation in flow over a cylinder which provides a faster and equally reliable alternative to conventional methods.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
References
Zhao Q, Chen S, Zhang H. Study on flow-induced noise propagation mechanism of cylinder–airfoil interference model by using large eddy simulation. AIP Advances. 2022;12(6):065310.
Vinuesa R, Brunton SL. Enhancing Computational Fluid Dynamics with Machine Learning. Journal of Computational Physics. 2020;408:109248.
Lighthill M. Aeroacoustic prediction based on large-eddy simulation and the Ffowcs Williams–Hawkings equation. Journal of Fluid Mechanics. 1998;45(3):245-280.
Shiri FM, Perumal T, Mustapha N, Mohamed R. A comprehensive overview and comparative analysis on deep learning models. Journal of Artificial Intelligence. 2024;6(1):301-360.
Yousif MZ, Yu L, Lim HC. Physics-guided deep learning for generating turbulent inflow conditions. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press; 2022.
Mosavi A, Wang J. Efficiency of ML models in flow-induced noise prediction. Computational Mechanics Journal. 2021;16(4):309-322.
Wang Y, Zhang H. Hybrid machine learning with physical constraints for noise prediction. Journal of Applied Fluid Mechanics. 2022;17(6):783-798.
Zhou B, Karniadakis G. Towards efficient CFD through machine learning: A review. Journal of Computational Physics. 2022;454:110901.
Inoue O, Hatakeyama N. Sound generation by a two-dimensional circular cylinder in a uniform flow. Journal of Fluid Mechanics. 2002;471:285–314.
Nagata T, Nonomura T, Takahashi S, Fukuda K. Direct numerical simulation of subsonic, transonic and supersonic flow over an isolated sphere up to a Reynolds number of 1000. Journal of Fluid Mechanics. 2020;900:1-23.
Chung TJ. Applications to Acoustics. In: Computational Fluid Dynamics. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press; 2012.
Anderson JD. Modern Compressible Flow with Historical Perspective. 3rd ed. New York: McGraw-Hill; 2003.
Kim J, Sandberg RD. Efficient parallel CFD methods for turbulent flow simulations on multi-core CPU/GPU clusters. Journal of Computational Physics. 2012;231(12):4355-4374.
Kennedy CA, Carpenter MH, Lewis RM. Low-storage, explicit Runge-Kutta schemes for the compressible Navier-Stokes equations. Applied Numerical Mathematics. 2000;35(3):177-219.
Kim J. High-order compact filters for large eddy simulation. Journal of Computational Physics. 2010;229(20):7751-7762.
Ferziger JH, Perić M. Computational Methods for Fluid Dynamics. 3rd ed. Berlin: Springer; 2002.
James G, Witten D, Hastie T, Tibshirani R. An Introduction to Statistical Learning. 1st ed. New York: Springer; 2013.
Goodfellow I, Bengio Y, Courville A. Deep Learning. 1st ed. Cambridge: MIT Press; 2016.
Murphy KP. Machine Learning: A Probabilistic Perspective. 1st ed. Cambridge: MIT Press; 2012.