Characterization of particulate matters emitted from biomass combustion using electron microscopy and energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy
Main Article Content
Abstract
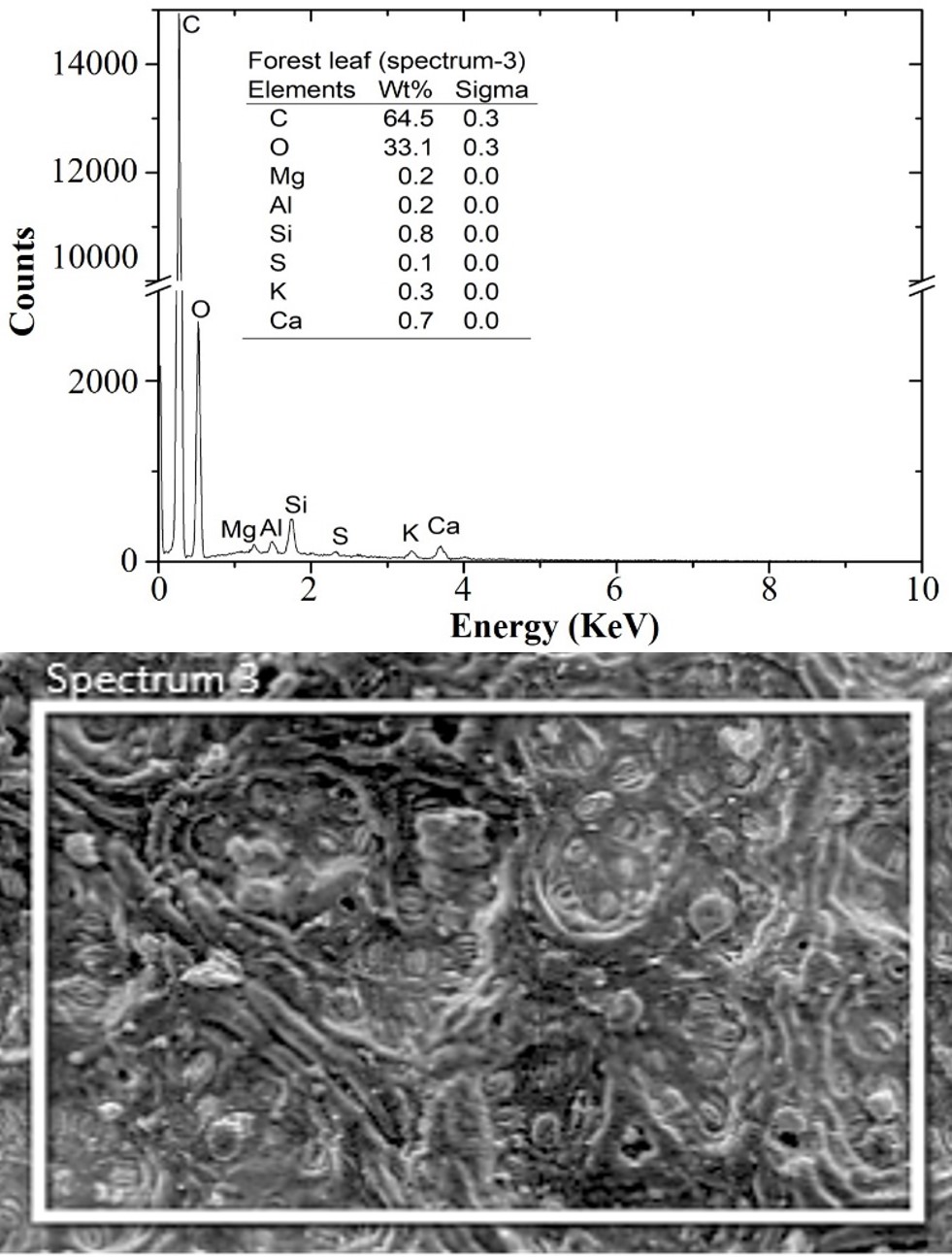
Particulate Matters (PMs) emitted from biomass combustion including open burning of biomass agricultural residues, and forest fires must be reduced to protect both human health and the environment. The physical characteristics of morphology, elemental composition and nanostructure of particulate matters generated from biomass combustion were successfully investigated by using electron microscopy and energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS) analysis with Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) and Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM), and thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) was used to analyze the oxidation kinetics of particulate matters. Before biomass burning, it was found that about 65% of carbon fraction in biomass raw material while 95% of carbon fraction in soot and 84% in ash particles after burning. The average diameter size of single primary particles is approximately 36 nm. Nanostructure of the single primary particle of biomass soot is mainly composed of curve line carbon crystallites while metallic ash nanoparticle is composed of straight-line hatch patterns. The inter-planar spacing of fringes of biomass soot and ash crystallites is 0.36 nm and 0.28 nm, respectively. This article aims to study the different nanostructure of biomass forest leaves residual ash and soot such as agglomerated particles, primary particle's measurement using TEM image analysis.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
References
Simoneit, Bernd R.T. Biomass burning-A review of organic tracers for smoke from incomplete combustion, Applied Geochemistry, Vol. 17, 2002, pp. 129-162.
Myung, C.L. and Park, S. Exhaust nanoparticle emissions from internal combustion engines: A review, International Journal of Automotive Technology, Vol. 13(1), 2012, pp. 9-22.
Myung, C.L., Ko, A. and Park, S. Review on characterization of nanoparticle emissions and pm morphology from internal combustion engines: Part 1, International Journal of Automotive Technology, Vol. 15(2), 2014, pp. 203-218.
Kittelson, D.B. Engines and nanoparticles: A review, Journal of Aerosol Science, Vol. 29(5-6), 1998, pp. 575-588.
Karin, P., Boonsakda, J., Siricholathum, K., Saenkhumvong, E., Charoenphonphanich, C. and Hanamura, K. Morphology and oxidation kinetics of CI engine's biodiesel particulate matters on cordierite diesel particulate filters using TGA, International Journal of Automotive Technology, Vol. 18(1), 2017, pp. 31-40.
Karin, P., Oki, H., Hanamura, K. and Charoenphonphanich, C. Nanostructures and oxidation kinetics of diesel particulate matters, Journal of Research and Applications in Mechanical Engineering, Vol. 1(2), 2012, pp. 3-8.
Karin, P., Borhanipour, M., Songsaengchan, Y., Laosuwan, S., Charoenphonphanich, C., Chollacoop, N., et al. Oxidation kinetics of small CI engine's biodiesel particulate matter, International Journal of Automotive Technology, Vol. 16(2), 2015, pp. 211-219.
Koko, P., Karin, P., Charoenphonphanich, C., Chollacoop, N. and Hanamura, K. Impact of engine oil additives on nanostructure and oxidation kinetics of diesel and synthetic biodiesel particulate matters using electron microscopy, JSAE-20199226, SAE 2019-01-2351, pp. 1-8.
Pasukphun, N. Environmental health burden of open burning in Northern Thailand: A review, PSRU Journal of Science and Technology, Vol. 3(3), 2018, pp. 11-28.
WHO. Public health, Social and environmental determinants of health department, Burden of disease from ambient and household air pollution, World Health Organization, USA, URL: https://www.who.int/phe/health-topics/outdoorair/database, accessed on 2019, 2012.
Vichit-Vadakan, N. and Vajanapoom, N. Health impact from air pollution in Thailand: Current and future challenges. Environmental Health Perspectives, Vol. 119(5), 2011, pp. A197-A198.
Amaral, S.S., de Carvalho Jr, J.A., Martins Costa, M.A., and Pinheiro, C. Particulate matter emission factors for biomass combustion: A review, Atmosphere, , Vol. 7(11), 2016, pp. 1-25.
Junpen, A., Garivait, S. and Bonnet, S. Estimating emissions from forest fires in Thailand using MODIS active fire product and country specific data, Asia-Pacific Journal of Atmospheric Sciences, Vol. 49(3), 2013, pp. 389-400.
Khamkaew, C., Chantara, S. and Wiriya, W. Atmospheric PM2.5 and its elemental composition from near source and receptor sites during open burning season in Chiang Mai, Thailand, International Journal of Environmental Science and Development, Vol. 7(6), 2016, pp. 436-440.
Kiatwattanacharoen, S., Prapamonto, T., Singharat, S., Chantara, S. and Thavornyutikarn, P. Exploring the sources of PM10 burning-season haze in Northern Thailand using nuclear analytical techniques, Chiang Mai University Journal of Natural Sciences, Vol. 16(4), 2017, pp. 307-325.