Effects of Rice Husk Fiber Treatment on the Polishing Pad from Rice Husk Fiber Mixed with Polyurethane.
Main Article Content
Abstract
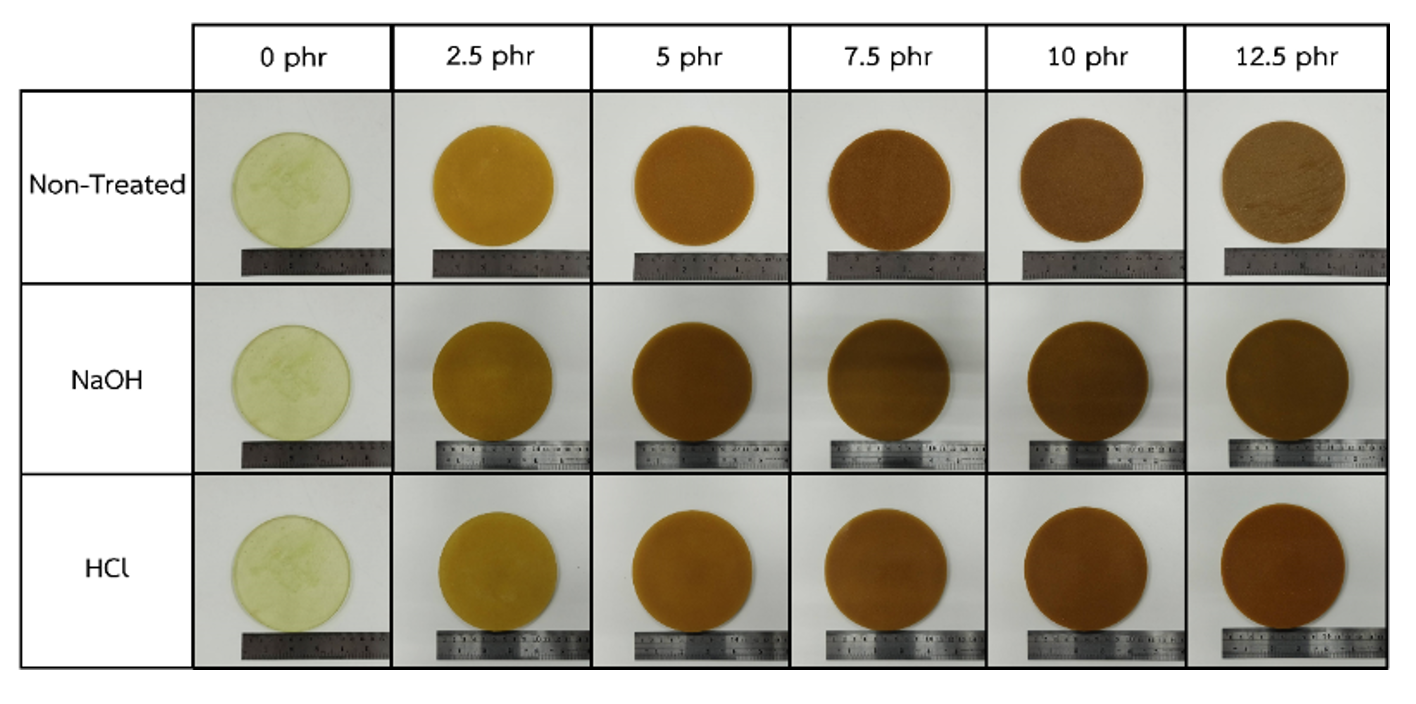
This research aimed to study the effects of treating rice husk fiber with hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide mixed with polyurethane on the properties of polishing pads. Rice husk fibers, sized to 80 mesh, were mixed with polyurethane at ratios of 0, 2.5, 5, 7.5, 10, and 12.5 parts per hundred resin (phr) to create polishing pads with a diameter of 120 mm and thickness of 5 mm for hardness testing. Abrasion resistance was assessed using cylindrical specimens with a diameter of 15 mm and height of 16 mm, while water absorption tests were conducted on 10 g samples of the polishing pads. The results indicated that polyurethane mixed with each type of rice husk treatment could be molded into a polishing pad. The hardness of the pads made from rice husks treated with hydrochloric acid and untreated husks showed no significant difference. However, the polishing pads made from hydrochloric acid-treated rice husks exhibited higher abrasion resistance and lower water absorption compared to those made from untreated husks. In contrast, polishing pads made with sodium hydroxide-treated rice husks demonstrated decreased hardness across all ratios, although their abrasion resistance and water absorption both increased. From the research study, it can be concluded that treating rice husks with hydrochloric acid improved abrasion resistance and reduced water absorption without affecting hardness.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Articles published in Journal of Industrial Technology Ubon Ratchathani Rajabhat University both hard copy and electronically are belonged to the Journal.
References
P. Suriyothin “LED: a Bright and Colourful Light Source … that Needs to Be Verified,” Academic Journal of Architecture. Chulalongkorn University, vol. 60, pp. 11-24, 2011. (in Thai)
B. Zhang, H. Lei, and Y. Chen, “Preparation of Ag2O modified silica abrasives and their chemical mechanical polishing performances on sapphire,” Friction, vol. 5, no. 4, 2017.
S. Dai, H. Lei and J. Fu, “Preparation of SiC/SiO2 Hard Core–Soft Shell Abrasive and Its CMP Behavior on Sapphire Substrate,” Journal of Electronic Materials, vol. 49, no. 2, pp. 1301–1307, 2020. doi: 10.1007/s11664-019-07683-9.
H. Lei, L. Q. Huang, and Q. Gu, “Synthesis of Zn-doped colloidal SiO2 abrasives and their applications in sapphire chemical mechanical polishing slurry,” Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics, vol. 28, no. 2, 2017, doi: 10.1007/s10854-016-5650-7
M. Bahr, Y. Sampurno, R. Han, and A. Philipossian, “Slurry injection schemes on the extent of slurry mixing and availability during chemical mechanical planarization,” Micromachines, vol. 8, no. 6, 2017, doi: 10.3390/mi8060170.
S. Chansatarpornkul, P. Khajornrungruang, and K. Suzuki, “Study on organic fibers in the polishing pad for sapphire chemical mechanical polishing,” in JSPE Autumn Conference, Sep. 4-6, 2019, pp.18-19.
N. Bun-athuek, S. Boripatkosol, A. Rattanapan, P. Kajornrungruang, K. Suzuki, and T. Somthong, “Natural fiber-based polishing pad for chemical mechanical polishing of sapphire substrate,” Journal of Science and Technology: for Local Development, vol. 1, pp. 99-116, 2022. (in Thai)
S. Janepittaya, “Where are Thai rice exports in the world market in an era when 'India-Vietnam' are still strong,” Bangkokbiznews Accessed: Jul. 24, 2023. [Online]. Available: https://www.bangkokbiznews
.com/ business/1080192
I. B. Ugheoke and O. Mamat, “A critical assessment and new research directions of rice husk silica processing methods and properties,” Maejo International Journal of Science and Technology, vol. 6, no. 3, 2012.
M. Ketsuwan, N. Bun-athuek, N. Sukhawipat, S. Boripatkosol, and C. Parung, “Study on mechanical properties of rice husk fiber-based polishing pad for chemical mechanical polishing of sapphire substrate,” in 1st International Conference on Robotics, Engineering, Science, and Technology, Pattaya, Thailand, Feb. 16, 2024.
U. Boonsom, S. Boripatkosol, A. Rattanapan, N. Bun-athuek, and P. Boonsong, “Utilization of rice husk fiber and water hyacinth fiber forming polishing pad for sapphire chemical mechanical polishing (CMP),” KKU Research Journal: Graduate Studies,Vol. 22, No. 4, 2022. (in Thai)
N. Stephen, J. O. Akindapo, and D. K. Garba, “Development of a military helmet using coconut fiber reinforced polymer matrix composite,” European Journal of Engineering and Technology, Vol. 3, No. 7, pp. 55-65, 2015.
K. Yongmalwong and I. Jangchud, “Improving Abrasion Resistance of Natural Rubber by Blending with Linear Low Density Polyethylene (LLDPE): Effects of Compatibilizers,” in The 9th KU KPS National Conference, Nakhon Pathom, Thailand, Dec. 6-7, 2012.
J. A. Halip, S. H. Lee, P. M. Tahir, L. T. Chuan, M. A. Selimin, and H. A. Saffian, “Chemical Treatments of Rice Husk for Polymer Composites,” Biointerface Research in Applied Chemistry, Vol. 11, Issue 4, pp. 12425-12433, 2021. doi.org/10.33263/BRIAC114. 1242512433
K. A. Chanda, A. Hazra, M. P. Kumar, S. Neogi, and S. Neogi, “Chemical Treatments of Rice Husk Filler and Jute Fiber for the Use in Green Composites,” Fibers and Polymers, 16(4), 902-910, 2015. doi: 10.1007/s12221-015-0902-3
J. T. Librea, F. D. Dacanay, Z. Z. Martin, and L. L. Diaz, “Effect of Water and Acid Pre-treatment on the Physicochemical Properties of Rice Husk for Silica Extraction,” in Materials Science and Engineering Conference Series, Apr. 19–20, 2019, doi:10.1088/1757-899X/540/1/ 012007
O. A. Battista, “Hydrolysis and Crystallization of Cellulose,” Industrial & Engineering Chemistry, Vol. 42, No. 3, pp. 502-507, 1950.