Optimal Organic Loading Rate for Biogas Production System for Soybean Meal Fed Black Soldier Fly Processing Wastewater
Main Article Content
Abstract
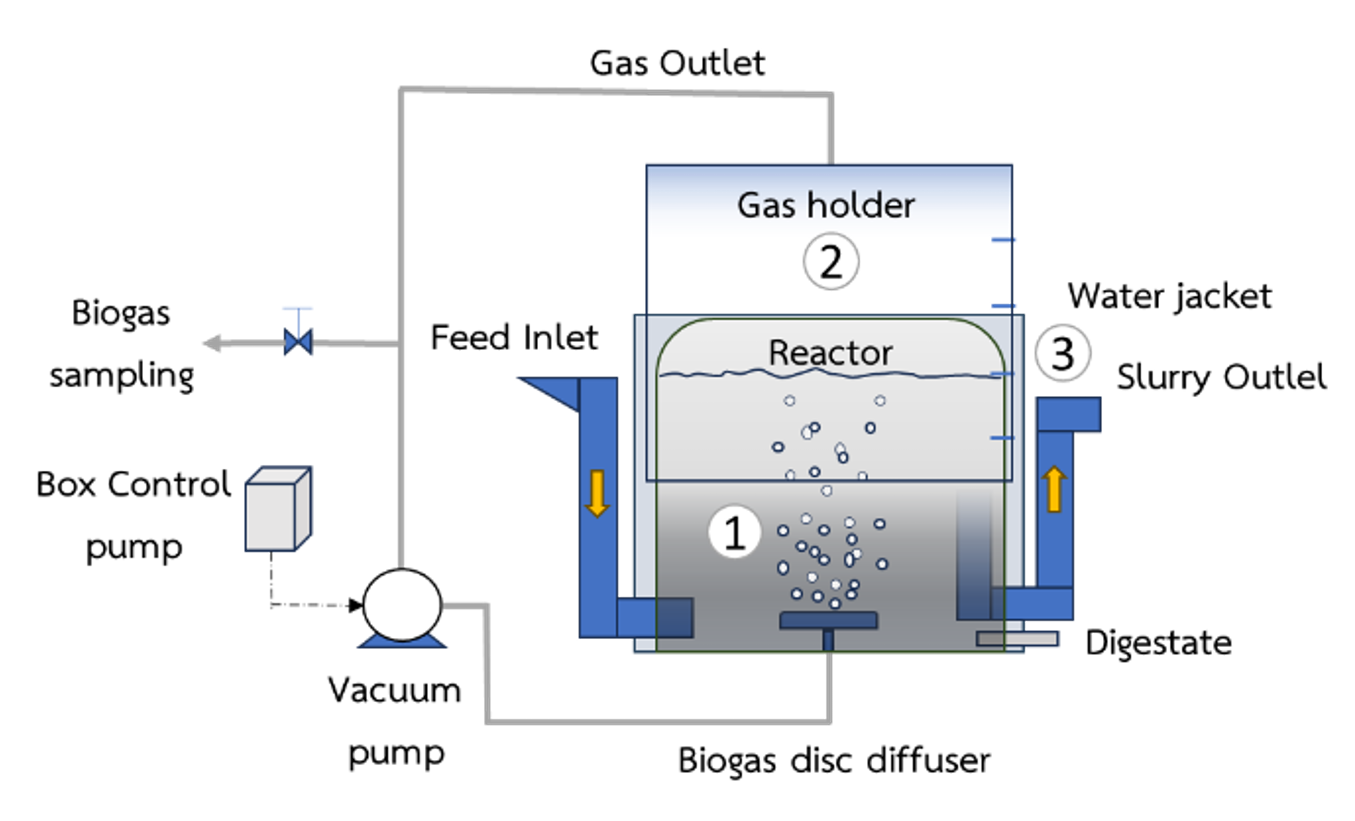
This research was to study the optimum Organic Loading Rate (OLR) for wastewater treatment of the Black Soldier Fly Larvae (BSFL) processing. The inoculum was sludge from the biogas system in a pig farm. The biogas system in this study was a floating drum digester mixed with biogas recirculation. The OLRs were added in the biogas reactor as 1.00, 2.00, and 3.00 kgCOD/m3day, respectively. The hydraulic retention time (HRT) was 20 days. The experiments operated on the ambient temperature. Biogas volume and methane content value were measured during the operations. The result showed that the operation of different OLR 1.00, 2.00, and 3.00 kgCOD/m3day, with mixing could produce average cumulative biogas volume of 1,214.17, 1,716.04, and 1,714.48 Lite, respectively. The average methane content was 66.64%, 69.02%, and 67.22% respectively. The OLR of 2 kgCOD/m3day was the optimum organic loading rate. The COD removal efficiency was 66.29%, the total solid removal was 65.95% and the volatile solid removal was 81.15%. This was the most suitable and efficient condition for treating the BSFL wastewater. It can be further studied in larger biogas systems. It could be possible to decrease the impact of wastewater and water pollution on the environment.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Articles published in Journal of Industrial Technology Ubon Ratchathani Rajabhat University both hard copy and electronically are belonged to the Journal.
References
X. Chu, M. Li, G. Wang, K. Wang, R. Shang, Z. Wang, and L. Li, “Evaluation of the Low Inclusion of Full-Fatted Hermetia illucens Larvae Meal for Layer Chickens: Growth Performance, Nutrient Digestibility, and Gut Health,” Frontiers in Veterinary Science, vol. 7, pp. 1–7, Nov. 2020, doi: 10.3389/fvets.2020.585843.
Department of Internal Trade (DIT), “Oil crops and animal feed materials,” (in Thai), Department of Internal Trade, 2020. Accessed: Jan. 10, 2023. [Online]. Available: https://agri.dit.go.th/index.php/home.
Kung Krabaen Bay Royal Development Study Center, “Black Soldier Fly larvae (BSFL) for protein from animal feed,” (in Thai), Kung Krabaen Bay Royal Development Study Center, Chanthaburi, Thailand, 2022. Accessed: Jan. 6, 2023. [Online]. Available: https://www4.fisheries.go.th/doffile/fkey/ref556.
P. Kritthiraput, K. Sasujit, P. Pintana, C. Sawatdeenarunat, and R. Nirunsin, “Biogas Production of Wastewater From Black Soldier Fly Larvae Washing Process,” (in Thai), M.S. thesis, Dept. Renew. Ener. Eng., Maejo Univ., Chiang Mai, Thailand, 2023.
P. Bulak, K. Proc, M. Pawłowska, A. Kasprzycka, W. Berus, and A. Bieganowski, “Biogas generation from insects breeding post production wastes,” Journal of Cleaner Production, vol. 244, pp. 1-8, Jan. 2020, doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.118777.
Y. Yu, “Research on soybean protein wastewater treatment by the integrated two-phase anaerobic reactor,” Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences, vol. 22, pp. 526-531, Sep. 2015, doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2015.01.006.
C. Rico, J. L. Rico, I. Tejero, N. Munoz, and B. Gomez, “Anaerobic digestion of the liquid fraction of dairy manure in Pilot plant for biogas production: Residual methane yield of digestate,” Journal of Waste Management, vol. 31, pp. 2167–2173, Sep.-Oct. 2011, doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2011.04.018.
P. Sutarut, S. Chobboon, N. Vitjitsombroon, and A. Dechana, “The Development of Biogas Generating Tank from Organic Waste,” (in Thai), Songkhla Rajabhat Univ. Songkhla, Thailand, Sep. 2017, [Online]. Available: http://oservice.skru.ac.th/ebook/lesson.asp?title_code=1457
B. Ruffino, S. Fiore, C. Roati, G. Campo, D. Novarino, and M. Zanetti, “Scale effect of anaerobic digestion tests in fed-batch and semi-continuous mode for the technical and economic feasibility of a full scale digester,” Bioresource Technology, vol. 182, pp. 302-313, Apr. 2015, doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2015.02.021.
U. Bergamo, G. Viccione, S. Coppola, A. Landi, A. Meda, and C. Gualtieri, “Analysis of Anaerobic Digester Mixing: Comparison of Long Shafted Paddle Mixing vs Gas Mixing,” Water Science and Technology, vol. 81, no. 7, pp. 1406–1419, May 2020, doi: 10.2166/wst.2020.248.
Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 22nd ed., American Public Health Association (APHA), American Water Works Association (AWWA) and Water Environment Federation (WEF), Washington, DC, 2012.
S. Vinardell, S. Astals, K. Koch, J. Mata-Alvarez, and J. Dosta, “Co-digestion of sewage sludge and food waste in a wastewater treatment plant based on mainstream anaerobic membrane bioreactor technology: A techno-economic evaluation,” Bioresource Technology, vol. 330, pp. 1-11, Jun. 2021, doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2021.124978.
K. Latha, R. Velraj, P. Shanmugam, and S. Sivanesan, “Mixing strategies of high solids anaerobic co-digestion using food waste with sewage sludge for enhanced biogas production,” Journal of Cleaner Production, vol. 210, pp. 388-400, Feb. 2019, doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.10.219.
M. J. Kim and S. H. Kim, “Conditions of lag-phase reduction during anaerobic digestion of protein for high-efficiency biogas production,” Biomass and Bioenergy, vol. 143, Dec. 2020, doi: 10.1016/j.biombioe.2020.105813.
S. Pongsak, T. Porndonand, C. Piasai, N. Boontian, and M. Padri, “Organic loading Rate for Maximum Biogas Production from Dairy Cattle Manure Wastewater at Suranaree University of Technology,” (in Thai), KKU Research Journal, vol. 20, no. 3, pp. 74-85, Jul-Sep. 2020, [Online]. Available: https://ph02.tci-thaijo.org/index.php/gskku/article/view/192936.
Y. Fransiscus and T. L. Simangunsong, “Anaerobic Digestion of Industrial Tempeh Wastewater with Sludge from Cow Manure Biogas Digester as Inoculum: Effect of F/M Ratio on the Methane Production,” International Journal of Advances in Science Engineering and Information Technology, vol. 11, no. 3, pp. 1007-1013, Jun. 2021, doi: 10.18517/ijaseit.11.3.11846.
M. T. Zinare, A. Dutta, and S. A. Jabasingh, “Start-up of a pilot scale anaerobic reactor for the biogas production from the pineapple processing industries of Belgium,” Renewable Energy, vol. 134, pp. 241-246, Apr. 2019, doi: 10.1016/j.renene.2018.11.058.
S. Pilli, A. K. Pandey, A. Katiyar, K. Pandey, and R. D. Tyagi, “Chapter 2 Pre-treatment Technologies to Enhance Anaerobic Digestion,” in Sustainable Sewage sludge Management Resource. Efficiency: IntechOpen, vol. 23, Jul. 2020, doi: 10.5772/intechopen.93236.
S. Ali, B. Hua, J. J. Huang, R. L. Droste, Q Zhou, W. Zhao, and L. Chen, “Effect of different initial low pH conditions on biogas production, composition, and shift in the aceticlastic methanogenic population,” Bioresource Technology, vol. 289, Oct. 2019, doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2019.121579.
P. Latifi, M. Karrabi, and S. Danesh, “Anaerobic co-digestion of poultry slaughterhouse wastes with sewage sludge in batch-mode bioreactors (effect of inoculum-substrate ratio and total solids),” Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, vol. 107, pp. 288–296, Jun. 2019, doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2019.03.015.
S. Saipa, T. Cheunbarn, N. Homduang, J. Chanathaworn, and R. Nirunsin, “The Study of the Mixing Duration Time and Recirculation Rate Effect to Biogas Production from Sweet Corn Waste by Dry Fermentation Process,” (in Thai), Chiang Rai Rajabhat University Journal, vol. 18, no. 87, pp. 87-105.
X. Chen, Z. Weizhu, L. Gongsong, S Qi, I. Muhammad, W. Yiqi, R. Luotong, and C. Chen, “Anaerobic biodegradation of soybean-process wastewater: Operation strategy and sludge bed characteristics of a high-performance Spiral Symmetric Stream Anaerobic Bioreactor,” Water Research, vol. 197, Jun. 2021, doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2021.117095.