AI-Driven mobile application for enhancing efficiency and preserving herbal knowledge
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.55674/cs.v18i1.262604Keywords:
Artificial intelligence, Mobile application, Herbal knowledge, Multimedia learning, Community developmentAbstract
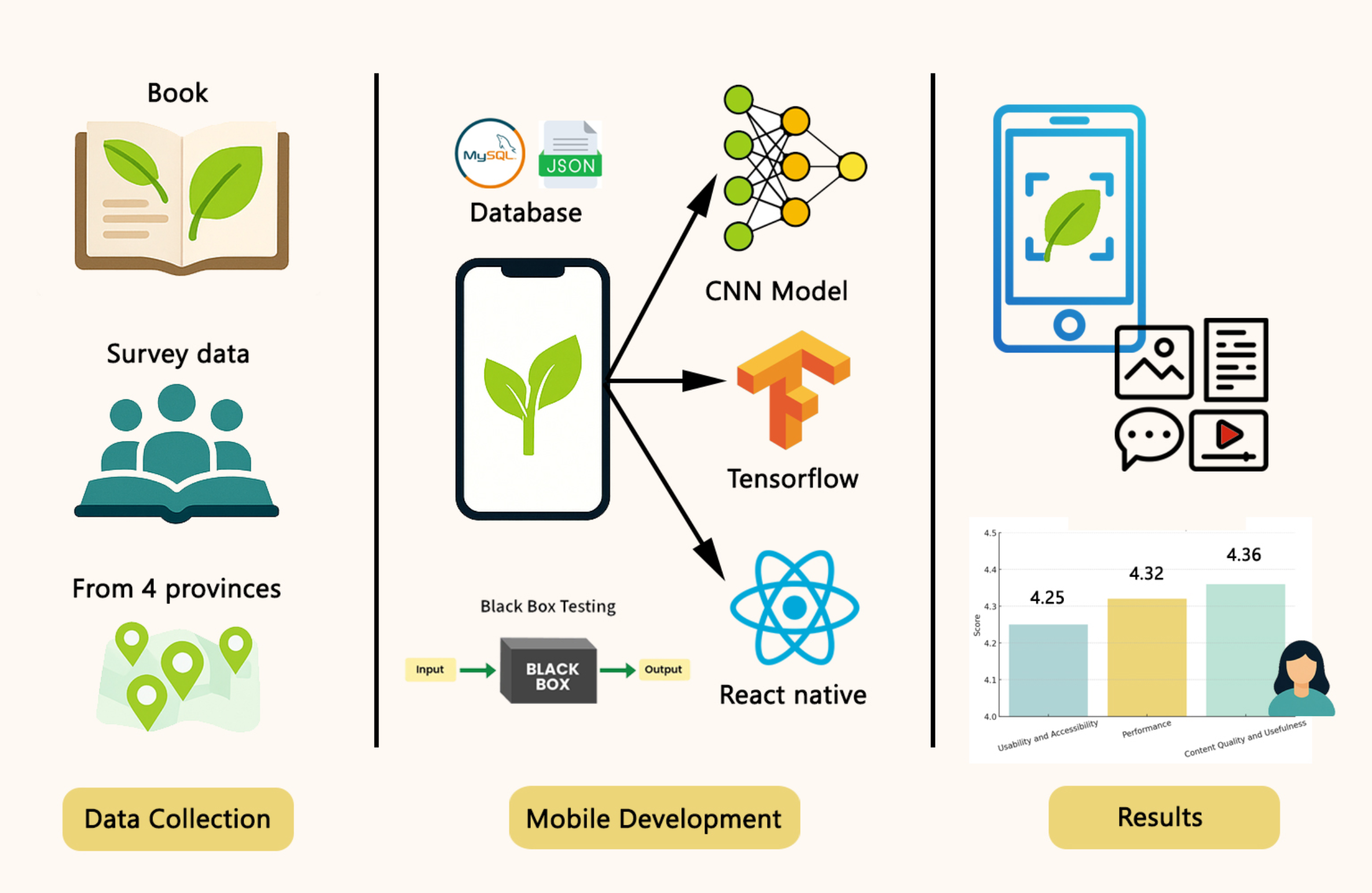
Traditional Thai medicine and local herbal knowledge are important local wisdom heritages, yet there are still limitations in access and methods of knowledge transfer. Therefore, this research aims to develop a mobile application for herbal information search by photographs. This application collects 30 ancient herbal medicine recipes from 4 provinces in the lower northeastern region, namely Surin, Buriram, Chaiyaphum, and Nakhon Ratchasima. The application is developed by using Extreme Programming approach which applies Convolutional neural network (CNN: DenseNet201) model on TensorFlow. The model is trained with 4,211 herbal images covering 30 species, with an accuracy of 92%. The system includes a function that allows users to add new herbal data, which must be validated by 5 users. In addition, there is a learning media on herbal medicine recipes in multimedia format developed according to the ADDIE Model process. The test results from a sample group of 100 people who passed the purposive sampling criteria, who must have had experience using herbal medicine at least 5 times and have basic knowledge of information technology. The evaluation results found that there was the highest level of satisfaction in all 3 areas: usability and accessibility (=4.25, SD=0.66), system efficiency (
=4.32, SD=0.71), and content quality (
=4.36, SD=0.71). The results of relationship analysis between basic factors and satisfaction levels revealed that the service area was the only factor that had a statistically significant effect on overall satisfaction (p < 0.05). The results of the research demonstrated that the application of artificial intelligence in combination with multimedia learning media in the application was possible to increase the perception of herbal information. This study demonstrates creative science by integrating traditional herbal knowledge with modern mobile application technology, resulting in a practical and culturally relevant tool developed in the Thai language.
GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
HIGHLIGHTS
- Innovative Integration of AI and Herbal Knowledge, The study introduces an AI-driven mobile application using Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN).
- Multimedia-Based Collaborative Learning Platform, The application combines image and video infographics based on traditional Thai herbal wisdom.
- Community-Centered Data Contribution System, The system allows users to verify and add new herbal data.
- Strong Evaluation Results Across Multiple Dimensions, Satisfaction surveys from 100 participants across four provinces indicated high ratings in usability, performance, and content quality (Mean > 4.25 in all aspects), reflecting the app’s effectiveness and relevance.
References
Ayamuang, T., Rukkachart, N., Sukkasem, P., & Sompeewong, P. (2025). The study and development of Thai traditional medicine knowledge through the application of local wisdom: Extracting substances from Aloe Vera for strawberry coating. International Journal of Education & Literacy Studies, 13(2), 675–684.
Ayele, A. H., Seid, A., Mekonnen, A. B., Adnew, W. W., & Yemata, G. (2024). Ethnobotanical study of the traditional use of medicinal plants used for treating human diseases in selected districts of West Gojjam zone, Amhara Region, Ethiopia. Phytomedicine Plus, 4(3), 100620.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phyplu.2024.100620
Saensouk, P., Ragsasilp, A., Thawara, N., Boonma, T., Appamaraka, S., Sengthong, A., Daovisan, H., Setyawan, A. D., & Saensouk, S. (2024). Ethnobotanical study of Acanthaceae family in Kantarawichai District, Maha Sarakham Province, Thailand. Biodiversitas Journal of Biological Diversity, 25(8), Article 250829. https://doi.org/10.13057/biodiv/d250829
Sansila, P. S., Senglek, N., & Thanatuskitti, P. (2024). Analysis of Thai herbal recipes in Isan palm leaf scripture: A case study of the 1st palm leaf chapter of folk healer Pim Kaewwiset. Journal of Humanities and Social Sciences Mahasarakham University, 31(1), 23–34.
Suknoo, S., Tikham, S., Srichaipor, N., & Khaminkrua, U. (2022). Wisdom and knowledge of folk healers for medicinal plants utilization: A study of folk healers in Tumbon Chompoo Subdistrict, Noenmaprang District, Pitsanulok Province. Journal of MCU Peace Studies, 10(7), 2920–2935.
Mal, P., & Saikia, N. (2025). Cultural persistence in health-seeking behaviour: A mixed-method study of traditional healing practices among Garo tribal women in Meghalaya, India. Journal of Biosocial Science, 57(2), 201–220. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0021932025000094
Sangngern, P., & Wongsathit, U. (2024). Thai Traditional Medical Texts of Phitsanulok Province: The Study of Manuscripts and Essences [Master’s thesis]. Silpakorn University. http://ithesis-ir.su.ac.th/dspace/handle/123456789/5051
Sama, A., Awae, M., Sangkhaphan, S., Thongjan, P., Totayong, J., Amornsak, P., & Intasaro, S. (2025). The development of a mobile application for Tok Bidan local herbal medicine formulary learning hub, in Narathiwat Province. Interdisciplinary Academic Journal of Faculty of Management Science, 2(1), 27–45.
Zhang, Z., Yang, M., Pan, Q., Jin, X., Wang, G., Zhao, Y., & Hu, Y. (2025). Identification of tea plant cultivars based on canopy images using deep learning methods. Scientia Horticulturae, 339, 113908. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2024.113908
Singh, K. K., Gajbhiye, N., & Mishra, G. S. (2025). Exploring Multi-Stage Deep Convolutional Neural Network for Medicinal Plant Disease Diagnosis. Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Deep Learning, Artificial Intelligence and Robotics (ICDLAIR 2024), 193, 88–101. https://doi.org/10.2991/978-94-6463-740-3_9
Kunlerd, A., Ritthiron, A., Nabumroong, B., Luangmaneerote, S., Chaiwachirakhampon, A., & Kaewyotha, J. (2025). A New Data Preprocessing Framework to Enhance the Accuracy of Herbal Plants Classification Using Deep Learning. Journal of Applied Data Sciences, 6(3), 1723–1740. https://doi.org/10.47738/jads.v6i3.733
Polthip, K., & Suphatto (Chaichanram), P. B. (2020). A Shared Cultural Identity of Nakhon-Chaiya-Bu-Rin Provincial Cluster. Ratanabuth Journal, 2(3), 1–8.
Heredia, A. S., García-Chitiva, M. del P., Camacho-Zúñiga, C., Mirabal, L. F. M., & Vázquez-Villegas, P. (2025). Remediation of mathematics knowledge in engineering students through an AI-based self-study educational intervention. 2025 IEEE Global Engineering Education Conference (EDUCON), 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1109/EDUCON62633.2025.11016455
Khan, A., Afridi, A. H., Khan, M. K., & Ahmad, P. (2025). Examining predictors of perceived usefulness of learning management system from the perspectives of distance learning students: An application of the information success model. Asian Association of Open Universities Journal, 20(1), 54–67. https://doi.org/10.1108/AAOUJ-01-2024-0009
Yu, J. (2025). The Impact of Six Visual Factors on Users’ Cultural Participation Intentions in a Virtual Museum Environment: The Mediating Effect of Satisfaction. In M. Rauterberg (Ed.), Culture and Computing. HCII 2025 (Vol. 15800, pp. 375–403). Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-93160-4_24
Aljehani, A., & Qureshi, M. R. (2025). Agile Method: Challenges and Adaptations for Complex Project Environments. International Journal of Information Engineering and Electronic Business (IJIEEB), 17(3), 84–98. https://doi.org/10.5815/ijieeb.2025.03.06
Mannari, C., Sportelli, M., Meesala, H., Okoye, O. F., & Ferrari, A. (2025). End-user requirements modelling: An experience report from digital agriculture. In Requirements Engineering: Foundation for Software Quality (pp. 386–392). Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-88531-0_22
Xu, F., & Correia, A.-P. (2024). Adopting distributed pair programming as an effective team learning activity: A systematic review. Journal of Computing in Higher Education, 36(2), 320–349. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12528-023-09356-3
Li, B., Soachalerm, A., & Tongdecharoen, W. (2024). Effects of Marathon Competition on Economic Aspects in Guangzhou City. International Journal of Social and Administrative Sciences Research (IJSASR), 4(5), 371–382.
Alhazmi, K. (2024). The effect of multimedia on vocabulary learning and retention. World Journal of English Language, 14(6), 390–399. https://doi.org/10.5430/wjel.v14n6p390
Mahdi, H. S., Mohsen, M. A., & Almanea, M. (2024). Multimedia glosses and second language vocabulary learning: A second-round meta-analysis. Acta Psychologica, 248, 104341. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actpsy.2024.104341
Popoola, O. A., Adama, H. E., Okeke, C. D., & Akinoso, A. E. (2024). Conceptualizing agile development in digital transformations: Theoretical foundations and practical applications. Engineering Science & Technology Journal, 5(4), 1524–1541. https://doi.org/10.51594/estj.v5i4.1080
Barros, L., Tam, C., & Varajão, J. (2024). Agile software development projects–Unveiling the human-related critical success factors. Information and Software Technology, 170, 107432. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.infsof.2024.107432
Dagan, A., Guy, I., & Novgorodov, S. (2023). Shop by image: Characterizing visual search in e-commerce. Information Retrieval Journal, 26(2). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10791-023-09418-1
Hashmi, A. (2024). A Hybrid Approach to Fashion Product Recommendation and Classification: Leveraging Transfer Learning and ANNOY. Proceedings of the 2024 2nd International Conference on Self Sustainable Artificial Intelligence Systems (ICSSAS), 635–641. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICSSAS64001.2024.10760516

Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Creative Science

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.








