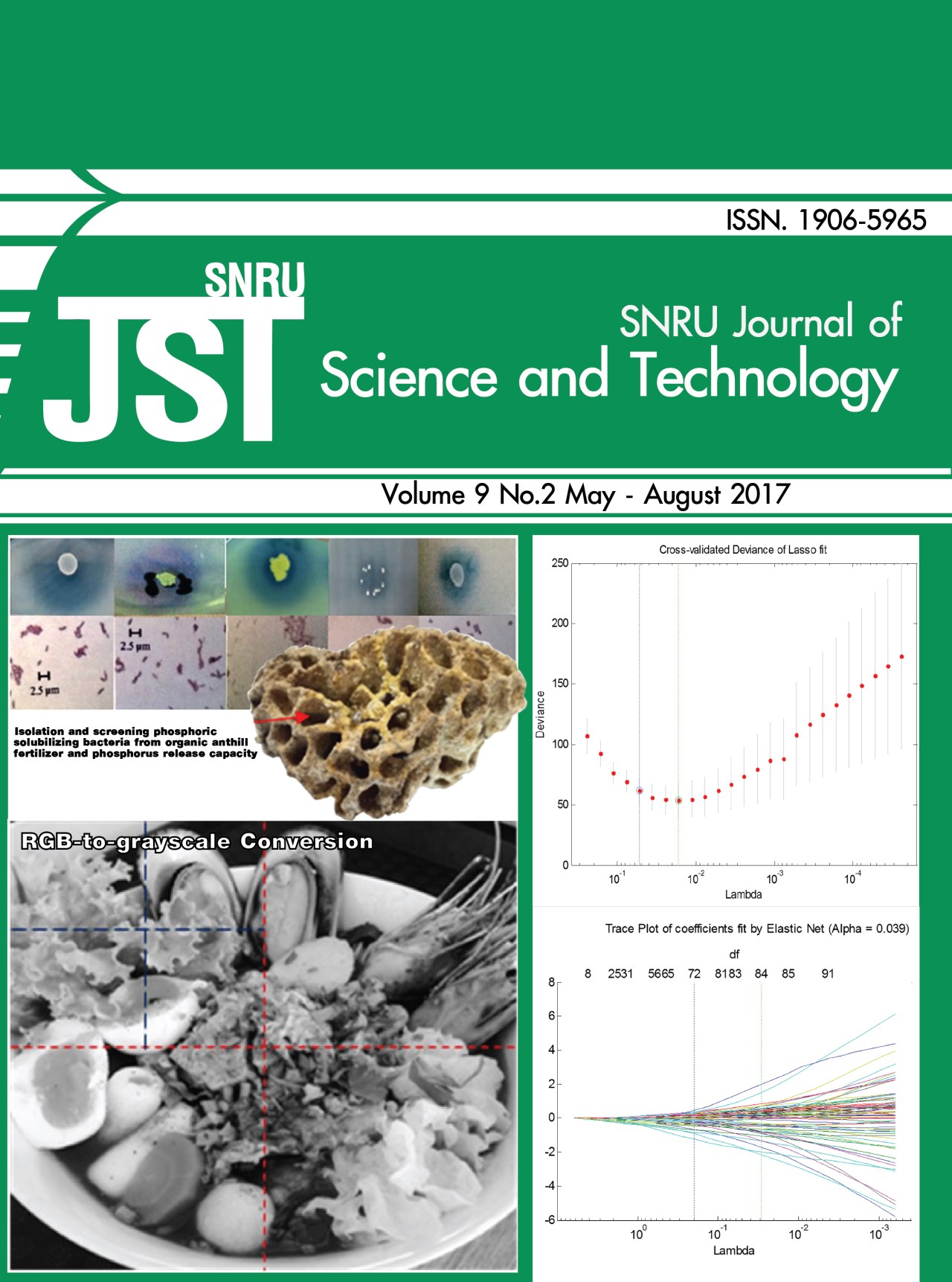
Isolation and screening phosphoric solubilizing bacteria from organic anthill fertilizer and phosphorus release capacity
Keywords:
Screening, Phosphate solubilizing bacteria, Phasphate fertilizer, AnthillAbstract
Phosphate solubilizing bacteria (PSB) play role in solubilizatiion and
mineralization of inorganic phosphate in soil to soluble organic phosphate (P).
The organic P is available to plant growth. It is also a major microorganism in
P biofertilizer. This work was to investigate the occurrence of PSB from liquid
organic anthill fertilizer and theircapacity for releasing soluble phosphate.
Population of total bacteria and PSB was estimated by using plate count
method. The result indicated that the population of total bacteria and PSB
ranged from 240 x 105 – 950 x 105 CFU g–1 and 0.32 x 105 – 16.0 x 105 CFU g–1
soil on plate count agar and Pikovskaya (PVK) agar medium, respectively.
Twenty five PSB showed diversity of different colony morphology on PVK agar medium.
Preliminary test on efficiency of soluble phosphate production observed from
hydrolytic capacity (HC) calculating from ration of diameter of clear zone and colony.
Their HC ranged 1 – 4.60. Five PSB isolates such as 2-2A, 2-7, 3-5, 8-2A and 8-4
were selected as high efficiency of PSB from value of HC at 4.60, 3.40, 3.40, 3 and 2.90
respectively. They were tested releasing soluble phosphate in PVK broth supplement
with FePO4, AlPO4, and Ca3(PO4)2. The result revealed that 2-2A isolates plays highest of
soluble phosphate concentration in broth supplement with FePO4,
AlPO4, and Ca3(PO4)2 at 4.80, 6.30 and 8.20 mg mL–1 respectively.