Mathematical model of thin-layer drying of long pepper
Keywords:
ANN modeling, Long pepper, Thin-layer dryingAbstract
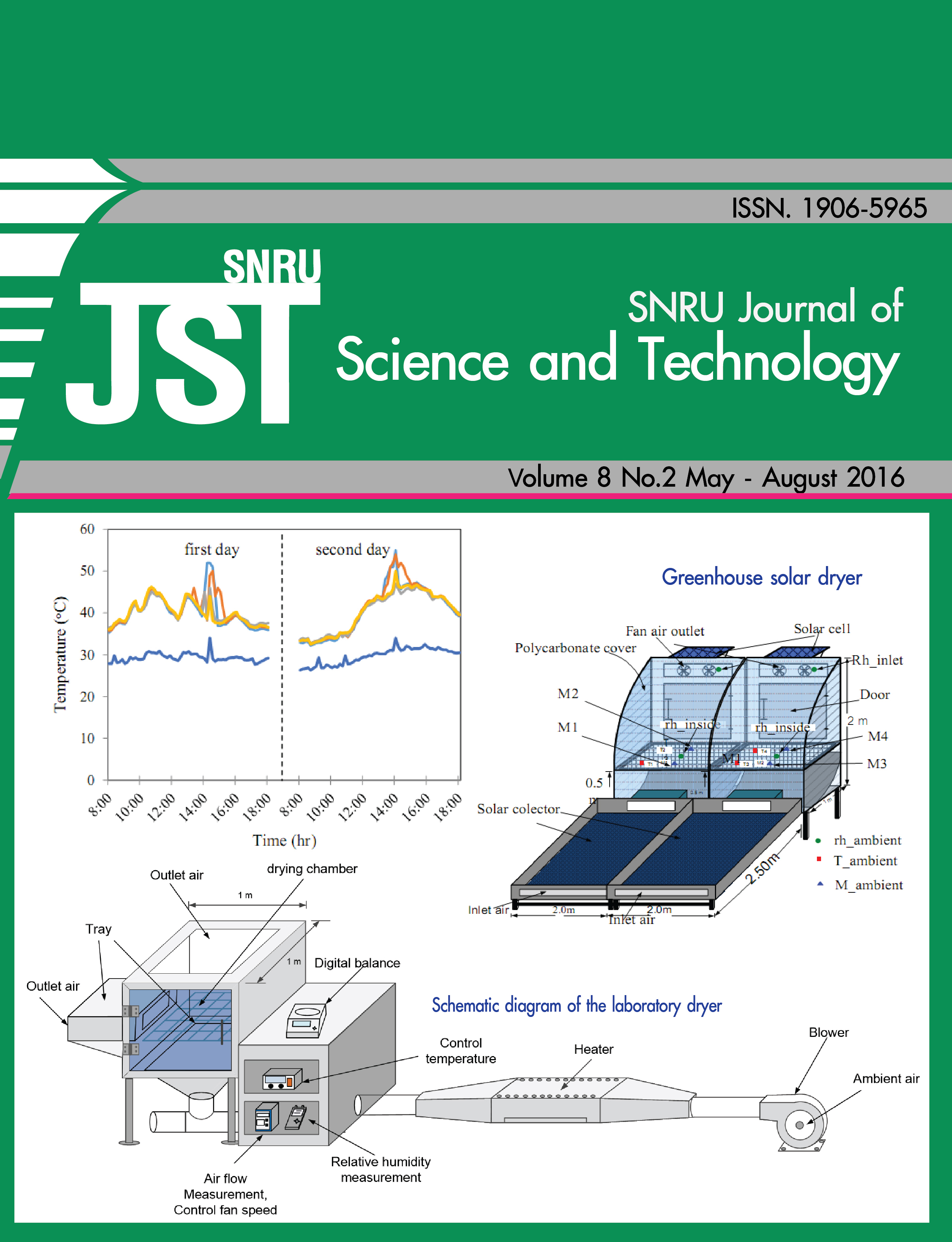
This article presents the thin-layer drying of long peppers, which was conducted under controlled conditions of temperature by using a convective air dryer. The 1000 g of long peppers that the initial moisture content of 550% (d.b.) were dried for the temperature of 40, 50 and 60°C, with the air flow velocity of 0.4, 0.7, 1 and 1.3 m s-1 until its final moisture content reach to 15% (d.b.). Besides the effects of drying air temperature and velocity, seven different thin-layer models were fitted to the experimental data of long peppers. The drying parameters of long peppers were found to be a function of drying air temperature. The Modified Handerson and Pabis model were revealed to be the best and it was followed by the Two-term model. Moisture diffusivities of long peppers have been determined experimentally and moisture diffusivities were found to increase with the increasing in drying air temperature. Moisture diffusivities of long peppers can be explained using an Arrhenius-type equation. A multilayer artificial neural network model was developed to predict the performance of this dryer. The predictive power of the model was found to be high after it was adequately trained. The Modified Handerson and Pabis model was found to be the best, followed by the two term model. The value of R2 of the Modified Handerson and Pabis model was 0.9982-0.9996, indicating good fit and RMSE were also good (0.28-0.71%). This study will be useful to optimize drying process parameters for commercial production of dried long pepper.