Comparison of different automated sinkhole extraction methods and its distribution on Karst topography
Keywords:
Sinkhole, Comparison, Automated Sinkhole Extraction, Spatial DistributionAbstract
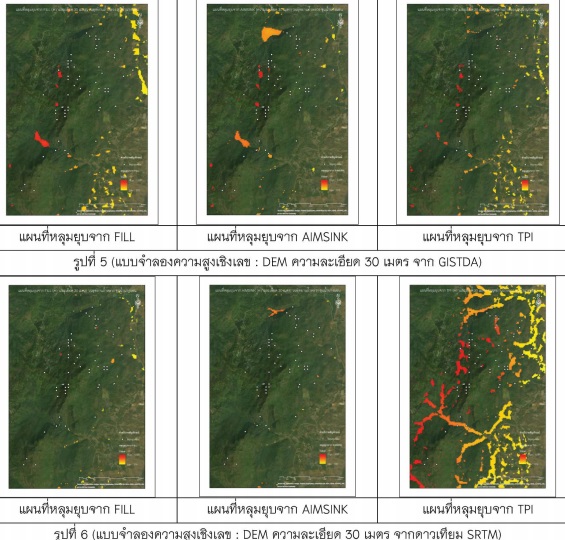
The purpose of this study is to explore and apply the comparison automated sinkhole extraction from Digital Elevation Model. The method is divided into 3 include Automated Identification Model for Sinkhole (AIMSINK), Fill sink method (FILL) and Automated generation of depressions by Topographic Position Index (TPI). Then analyze the distribution of sinkhole from Nearest Neighbor Index on Karst Topology include study area 1 is Tham Luang Forest Park at Chiang Rai province and study area 2 is Royal Agricultural Station Angkhang at Chiang Mai province. These results showed on study area 1 AIMSINK FILL and TPI have positional accuracy 87 percent, 71 percent, and 64 percent respectively. Analyze the distribution of sinkhole FILL (0.73) matched real sinkhole in study area 1 (0.73) and TPI (0.61) has a value close to real sinkhole in study area 2 (0.63). These results indicate that TPI sinkhole small and the groove area is included, AIMSINK suitable for automatic sinkhole extraction but there are limits if the actual area is the syncline therefore FILL most suitable for extraction large area sinkholes on Karst Topology.