Mechanical and thermophysical analysis of B2 structured ferromagnetic materials
Main Article Content
Abstract
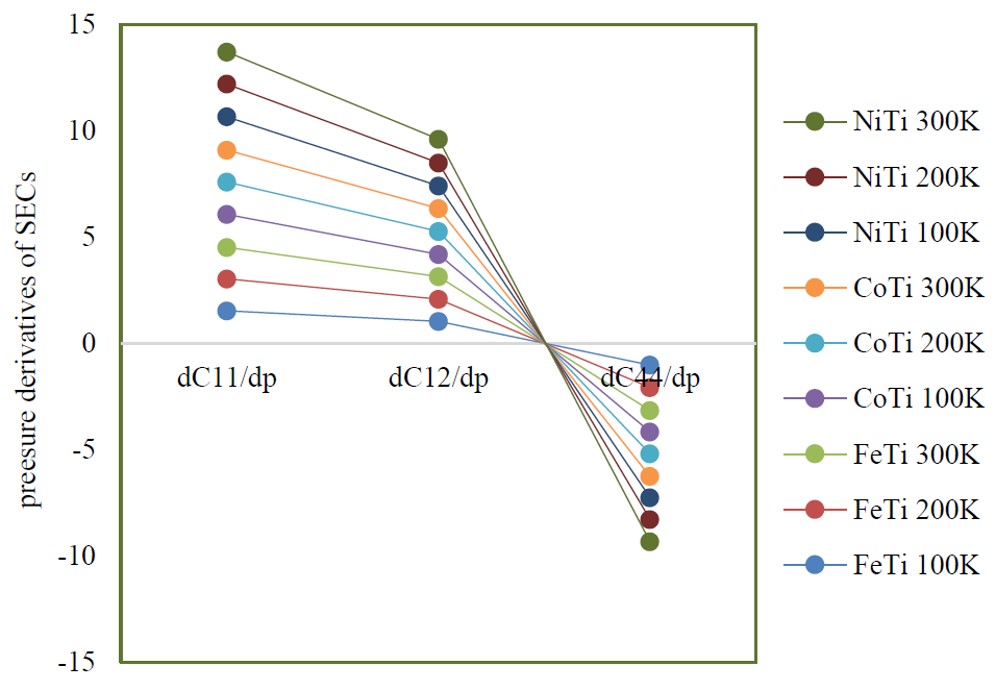
The temperature dependent thermophysical, mechanical and ultrasonic properties of B2 structured ferromagnetic materials MTi (M: Fe, Co, Ni) have been evaluated in present study. The Coulomb and Born-Mayer potential model has been applied to calculate second and third order elastic constants in the temperature range 0-300K. The values of second order elastic constants have been used to find the mechanical and thermophysical properties. The chosen materials have been found ductile as the value of Pugh’s indicator for MTi has been found greater than 1.75. The FeTi has been found more stable than CoTi and NiTi. The mechanical constants have been found highest for FeTi. Again, the values of elastic stiffness constants have been used to compute the ultrasonic velocities, Debye average velocities, Debye temperatures, thermal conductivities and Grüneisen parameters along <100>, <110> and <111> directions for the longitudinal and shear modes of wave propagation. The ultrasonic velocities have been observed more for longitudinal mode than shear mode. The ultrasonic velocities and Debye temperatures are found to be highest along <100> direction for all chosen materials. Hence <100> direction would be most suitable for the wave propagation in case of MTi. The obtained values of elastic, mechanical, thermophysical and ultrasonic properties have been compared with existing literatures and discussed.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
References
Zhang L, Chen H, Wang Z, Ma L, Tang P. Theoretical predictions of structure, mechanics, dislocation and electronics properties of FeTi alloy at high pressure. Metals. 2023;13(9):1547.
Wollmershauser JA, Neil CJ, Agnew SR. Mechanisms of ductility in CoTi and CoZr B2 Intermetallics. Metall Mater Trans A. 2010;41:1217-29.
Kaneno Y, Takasugi T, Hanada S. Tensile property and fracture behaviour of hot-rolled CoTi intermetallic compound. Mater Sci Eng A. 2001;302(2):215-21.
Koroteev YM, Lipnitskii AG, Chulkov EV, Silkin VM. The (110) surface electronic structure of FeTi, CoTi and NiTi. Surf Sci. 2002;507-510:199-206.
Bihlmayer G, Eibler R, Neckel A. Elastic properties of B2-NiTi and B2-PdTi. Phys Rev B. 1994;50(18):13113-7.
Brill TM, Mittelbach S, Assmus W, Mullner M, Luthi B. Elastic properties of NiTi. J Phys: Condens Matter. 1991;3:9621.
Haskins JB, Lawson JW. Finite temperature properties of NiTi from first principles simulations: structure, mechanics and thermodynamics. J Appl Phys. 2017;121(20):205103.
Zhu LF, Friák M, Udyansky A, Ma D, Schlieter A, Kühn U, et al. Ab initio-based study of finite-temperature structural, elastic and thermodynamic properties of FeTi. Intermetallics. 2014;45:11-7.
Yu F, Liu Y. First-principles calculations of structural, mechanical and electronic properties of the B2-phase NiTi shape-memory alloy under high pressure. Computation. 2019;7(4):57.
Matsushita M, Tajima I, Abe M, Tokuyama H. Experimental study of porosity and effective thermal conductivity in packed bed of nano-structured FeTi for usage in hydrogen storage tanks. Int J Hydrogen Energy. 2019;44(41):23239-48.
Cheng D, Zhao S, Wang S, Ye H. First-principles study of elastic properties and electronic structure of NiTi, CoTi and FeTi. Philos Mag A. 2001;81(6):1625-32.
Lu W, Li C, Yi J, Li K. Stability and elastic properties of B2 CoX (X= Ti, Zr and Hf) intermetallic compounds as a function of pressure. Philos Mag. 2018;98(3):203-18.
Zadorozhnyy VY, Klyamkin SN, Kaloshkin SD, Skakov YA. Production of intermetallic compound of FeTi by means of mechanical-chemical synthesis and its interaction with hydrogen. Inorg Mater Appl Res. 2010;1:41-5.
Tessier P, Schulz R, Ström-Olsen JO. Elastic stress in composite FeTi hydrogen storage materials. J Mater Res. 1998;13(6):1538-47.
Benyelloul K, Bouhadda Y, Bououdina M, Faraoun HI, Aourag H, Seddik L. The effect of hydrogen on the mechanical properties of FeTi for hydrogen storage applications. Int J Hydrogen Energy. 2014;39(24):12667-75.
Padhee SP, Roy A, Pati S. Mechanical insights into efficient reversible hydrogen storage in ferrotitanium. Int J Hydrogen Energy. 2021;46(1):906-21.
Born M, Mayer JE. Zur Crittertheorie der Ionenkristalle. Zeitschrift für Physik. 1932; 75:1-18. (In German)
Brugger K. Thermodynamic definition of higher order coefficients. Phys Rev. 1964;133(6A):A1611-2.
Ghate PB. Third order elastic constants of alkali halide crystals. Phys Rev. 1965;139(5A):A1666-74.
Yadav RR, Pandey DK. Size dependent acoustical properties of bcc metal. Acta Phys Pol A. 2005;107(6):933-46.
Bala J, Singh SP, Verma AK, Singh DK, Singh D. Elastic, mechanical and ultrasonic studies of boron monopnictides in two different structural phases. Indian J Phys. 2022;96:3191-200.
Singh D, Pandey DK. Ultrasonic investigation in intermetallics. Pramana. 2009;72(2):389-98.
Morelli DT, Slack GA. High lattice thermal conductivity solids. In: Shinde SL, Goela JS, editors. High Thermal Conductivity Materials. New York: Springer; 2006. p. 37-68.
Mason WP. Effect of impurities phonons process on the ultrasonic attenuation of germanium crystal quartz and silicon. In: Mason WP, editor. Physical Acoustics: Principle and Methods, Vol. 3, Part B. New York: Academic press; 1965. p. 235-86.
Gray DE. American Institute of Physics Handbook. 3rd ed. New York: Mc Graw–Hill; 1972.
Acharya N, Fatima B, Chouhan SS, Sanyal SP. First principles study on structural, elastic and thermal properties of equiatomic MTi (M=Fe, Co, Ni). Chem Mater Res. 2013;3(8):22-30.
Tosi MP. Cohesion of ionic solids in the Born model. Solid State Phys. 1964;16:1-120.
Born M, Huang K. Dynamical theory of crystal lattices. Oxford; Clarendon Press; 1954.
Cousin CSG. New relations between elastic constants of different orders under central force interactions. J Phys C Solid State Phys. 1971;4:1117.
Tripathi S, Agrawal R, Singh D. Nonlinear elastic, ultrasonic and thermophysical properties of lead telluride. Int J Thermophys. 2019;40:78.
Pugh SF. XCII. Relations between the elastic moduli and the plastic properties of polycrystalline pure metals. Lond Edinb Dublin Philos Mag J Sci. 1954;45:823-43.
Watt JP. Elastic properties of polycrystalline minerals: comparison of theory and experiment. Phy Chem Minerals. 1988;15:579-87.
Terada Y, Nakata J, Mohri T, Suzuki T. A method for seeking high thermal conductivity compounds. Intermetallics. 1998;6(6):479-85.
Yadav RR, Singh D. Ultrasonic attenuation in lanthanum monochalcogenides. J Phys Soc Jpn. 2001;70(6):1825-32.