Tailoring mechanical, thermophysical and ultrasonic properties of dysprosium monochalcogenides
Main Article Content
Abstract
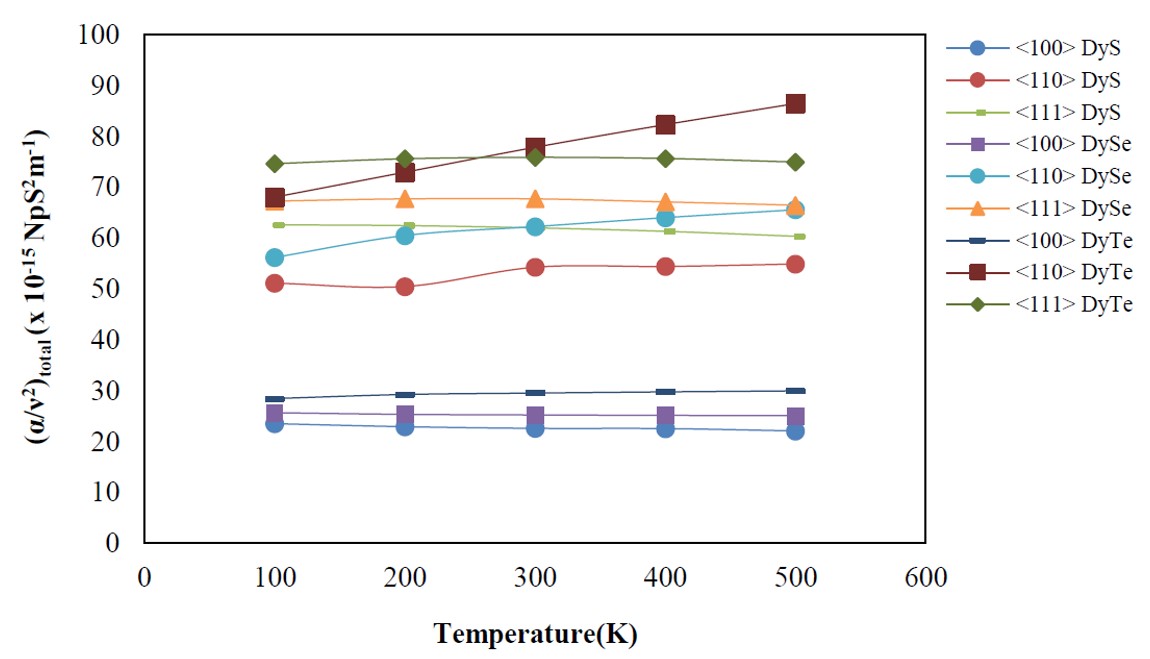
The ultrasonic characteristics of dysprosium monochalcogenides, DyX (X = S, Se and Te) as a function of temperature and crystallographic direction, are studied in present investigation. First, the second- and third-order elastic constants (SOECs and TOECs) have been computed using Coulomb and Born-Mayer potential from 0K to 500K. The mechanical properties have been evaluated with the achieved values of SOECs for finding the intrinsic properties, stability and futuristic performance of DyX. The mechanical stability and elastic moduli follow the order DyS > DySe > DyTe. Supplemental the acoustic velocities including Debye average velocity, thermal relaxation time, Debye temperature and nonlinear parameter have been computed along <100>, <110> and <111> directions in the temperature range 100K to 500K. The Debye average velocity is found to be highest for wave propagating along <110> and polarized along Finally, the ultrasonic attenuation using the modified Mason’s approach has been computed in the temperature regime 100-500K along different crystallographic directions and calculated results predict that Akheiser damping dominates over the thermal attenuation. The obtained results have been analyzed and discussed with the available literature.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
References
Petit L, Szotek Z, Lüders M, Svane A. Rare-earth pnictides and chalcogenides from first-principles. J Phys Condens Matter. 2016;28:223001.
Tripathi SN, Srivastava V, Pawar H, Sanyal SP. First-principles investigation of structural, electronic and mechanical properties of some dysprosium chalcogenides, DyX (X=S, Se and Te). Indian J Phys. 2020;94:1195-201.
Hulliger F, Landolt M, Schmelczer R. Low-temperature behavior of DyS, DySe, HoS and HoSe. In: McCarthy GJ, Silber HB, Rhyne JJ, Kalina FM, editors. The Rare Earths in Modern Science and Technology. Boston: Springer; 1982. p. 455-8.
Schoenes J, Repond P, Hulliger F, Ghosh DB, De SK, Kunes J, et al. Experimental and theoretical investigation of optical properties of dysprosium monopnictides. Phys Rev B. 2003;68(8):085102.
Gaith M. Elastic and mechanical investigation of rare earth monochalcogenides under high pressure. Int Rev Mech Eng. 2020;14(11):693-8.
Bhajanker S, Srivastava V, Sanyal SP. High pressure effect on structural, elastic and thermal properties of DyP and DyAs. J Phys Conf Ser. 2012;377:012079.
Bafekry A, Faraji M, Fadlallah MM, Jappor HR, Hieu NN, Ghergherehchi M, et al. Prediction of two dimensional bismuth-based chalcogenides Bi2X3 (X=S,Se,Te) monolayers with orthorhombic structure: a first-principle study. J Phys D Appl Phys. 2021;54:395103.
Kuroda MA, Jiang Z, Povolotskyi M, Klimeek G, Newns DM, Martyna GJ. Anisotropic strain in SmSe and SmTe: implications for electronic transport. Phys Rev B. 2014;90:245124.
Otero-Díaz LC, Torralvo MJ, Rojas RM. Thermal behaviour and microstructural characterization of γ-Dy2S3. Solid State Ion. 1993;63-65:318-24.
Pokrzywnicki S. Crystal field effects and magnetic properties of Dy2Te3. J Alloys Compd. 1995;225(1-2):163-5.
Khot SD, Malavekar DB, Bagwade PP, Nikam RP, Lokhande CD. Synthesis of reduced graphene oxide (γ GO)/dysprosium selenide (Dy2S3) composite electrode for energy storage; flexible asymmetric super capacitor. J Phys Chem Solids. 2023;179:111419.
Privitera SMS. Synthesis, properties and applications of germanium chalcogenides. Nanomaterials. 2022;12(17):2925.
Ning S, Huang S, Zhang T, Zhang Z, Qi N, Chen Z. Two dimensional β-PdX2 (X= S, Se,Te) monolayers with promising potential for thermoelectric applications. J Phys Chem C. 2022;126(42):17885-93.
Singh D, Yadav RR, Tiwari AK. Ultrasonic attenuation in semiconductors. Indian J Pure Appl Phys. 2002;40:845-9.
Lahourpour F, Boochani A, Parhizgar SS, Elahi SM. Structural, electronic and optical properties of graphene-like nano-layers MOX2 (X: S, Se, Te): DFT study. J Theor Appl Phys. 2019;13:191-201.
Srivastava V, Bhajanker S, Sanyal SP. High pressure effect on structural and mechanical properties of some LnO (Ln = Sm, En, Yb) compounds. Phys B Condens Matter. 2011;406(11):2158-62.
Dantas NS, da Silva AF, Persson C. Electronic band-edge properties of rock salt PbY and SnY(Y=S,Se and Te). Opt Mater. 2008;30(9):1451-60.
Li XH, Xing CH, Cui HL, Zhang RZ. Elastic and acoustical properties of Cr3AlB4 under pressure. J Phys Chem Solids. 2019;126:65-71.
Shafiq M, Arif S, Ahmad I, Asadabadi SJ, Maqbool M, Aliabad HAR. Elastic and mechanical properties of lanthanide monoxides. J Alloys Compd. 2015;618:292-8.
Winey JM, Hmiel A, Gupta YM. Third-order elastic constants of diamond determined from experimental data. J Phys Chem Solids. 2016;93:118-20.
Liu L, Xu G, Wang A, Wu X, Wang R. First-principles investigations on structure stability, elastic properties, anisotropy and Debye temperature of tetragonal LiFeAs and NaFeAs under pressure. J Phys Chem Solids. 2017;104:243-51.
Born M, Mayer JE. Zur Crittertheorie der Ionenkristalle. Zeitschrift für Physik. 1932;75:1-18. (In German)
Singh A, Singh D. Investigation of alkali halide crystals AX (A= Li, Na, K; X= F,Cl, Br) by elastic, mechanical and ultrasonic analysis. Zeitschrift für Naturforschung A. 2023;78(10):947-58.
Bhalla V, Singh D. Mechanical and thermo-physical properties of rare-earth materials. In: Aswal DK, Yadav S, Takatsuji T, Rachakonda P, Kumar H, editors. Hand book of Meterology and Applications. Singapore: Springer; 2022. p. 1-33.
Tripathi S, Agrawal R, Singh D. Non-linear elastic, ultrasonic and thermophysical properties of lead telluride. Int J Thermophys. 2019;40:78.
Singh D, Tripathy C, Paikaray R, Mathur A, Wadhwa S. Behaviour of ultrasonic properties on SnAs, InTe and PbSb. Eng Appl Sci Res. 2019;46(2):98-105.
Akhieser A. On the absorption of sound in solids. J Phys (Moscow). 1939;1(1):277-87.
Bömmel HE, Dransfeld K. Excitation and attenuation of hypersonic waves in quartz. Phys Rev. 1960;117(5):1245-52.
Mason WP. Effect of impurities and phonon processes on the ultrasonic attenuation of germanium, crystal quartz, and silicon. Phys Acoust. 1965;3:235-86.
Tosi MP. Cohesion of ionic solids in the Born model. Solid State Phys. 1964;16:1-120.
Singh D, Pandey DK, Singh DK, Yadav RR. Propagation of ultrasonic waves in neptunium monochalcogenides. Appl Acoust. 2011;72(10):737-41.
Yadav RR, Singh D. Ultrasonic attenuation in lanthanum monochalcogenides. J Phys Soc Jpn. 2001;70:1825-32.
Yadav RR, Singh D. Effect of thermal conductivity on ultrasonic attenuation in praseodymium monochalcogenides. Acoust Phys. 2003;49:595-604.
Bala J, Singh D. Elastic and ultrasonic properties of fermium monopnictides. Eng Appl Sci Res. 2020;47(2):182-9.
Cousins CSG. New relation between elastic constants of different orders under central force interactions. J Phys C: Solid State Phys. 1971;4:1117.
Pugh SF. XCII. Relations between the elastic moduli and the plastic properties of polycrystalline pure metals. Lond Edinb Dubl Phil Mag. 1954;45(367):823-43.
Pettifor DG. Theoretical predictions of structure and related properties of intermetallic. Mater Sci Technol. 1992;8(4):345-9.
Watt JP. Elastic properties of polycrystalline minerals: comparison of theory and experiment. Phys Chem Minerals. 1988;15:579-87.
Gray DE. American Institute of Physics Handbook, 3rd ed. New York: McGraw–Hill; 1972.
Singh A, Singh D. Influence of temperature and orientation on elastic, mechanical, thermophysical and ultrasonic properties of platinum group metal carbides. Johnson Matthey Technol Rev. 2024;68(1):49-59.