Application of 5D building information modeling using Cubicost in estimating construction structure work costs (Case study: Emergency Room and Hemodialysis Building at Waras Wiris Local General Hospital of Boyolali, Indonesia)
Main Article Content
Abstract
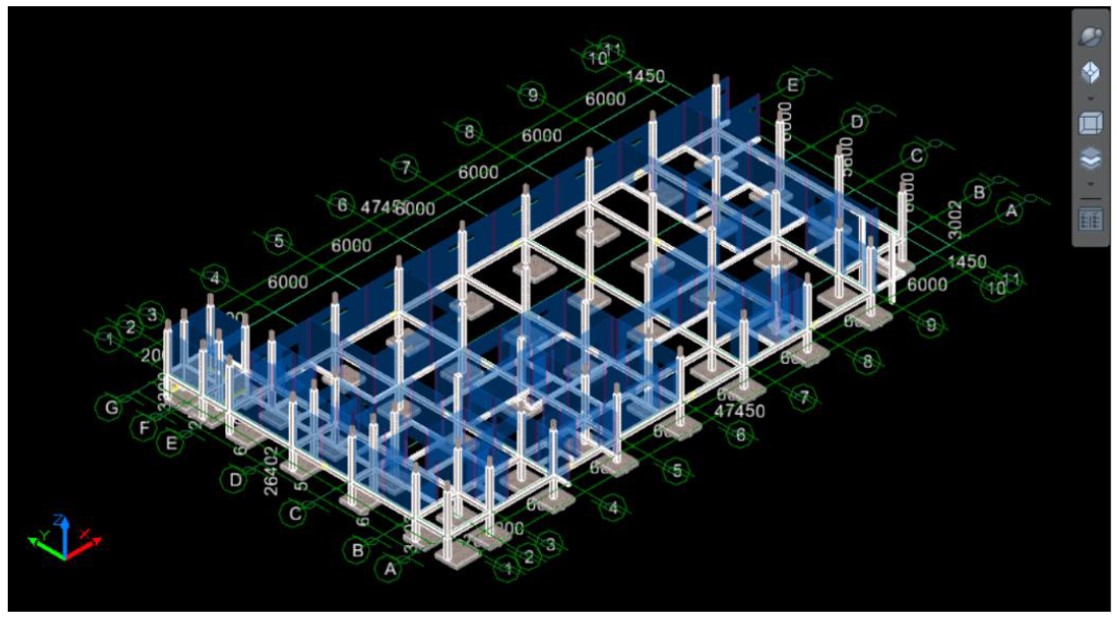
In construction projects, quantity take-off is an important process that must be considered because it will substantially impact the estimate of the overall project cost. The components that make up the structure of a building are very complex, so time inefficiencies and accuracy in calculating the volume of work often occur, which are fatal to construction costs. Therefore, in this study, an analysis of the application of 5D BIM in construction projects was carried out to identify its effectiveness, accuracy, and efficiency in determining the quantity take-off. The 5D BIM application used in this case is 5D BIM Cubicost TAS to determine the quantity take-off of concrete and formwork and 5D BIM Cubicost TRB to determine the quantity take-off of reinforcement in detail. The research method used was a comparative analysis method of the use of 5D BIM and conventional applications. The object of this research was the construction project of the Emergency Room and Hemodialysis Building at Waras Wiris Local General Hospital of Boyolali. The analysis shows that the 5D BIM Cubicost TAS and TRB efficiency in structure work was IDR 220,526,781.12 or 9.254%.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
References
Liu H, Cheng JCP, Gan VJL, Zhou S. A knowledge model-based BIM framework for automatic code-compliant quantity take-off. Autom Constr. 2022;133:104024.
Kamil AA, Raflis. Comparison of quality and time cost control using conventional methods and BIM methods. Proceedings of Young Intellectuals Seminar#1, Innovations in Science, Technology, and Art in the Planning and Design of the Built Environment; 2019 Apr 11; Trisakti University, Indonesia. p. 27-33. (In Indonesian)
Umam FN, Erizal, Putra H. Improving the cost efficiency of multi-storey building construction with 5D building information modeling (BIM) Application. Teras J. 2022;12(1):245-56. (In Indonesian)
Christopher Dwi BA, Wasono DS, Hermawan, Dwi Hatmoko JU. Preliminary study of the efficiency of using 5D-BIM on material volume and cost estimation in construction projects (case study of 2-storey residential house). 15th National Conference on Civil Engineering; 2021 Oct 21-22; Semarang, Indonesia. p. 292-301. (In Indonesian)
Perdana AS, Indrayadi M, Pratiwi R. Identification of construction material waste in building construction projects (case study: UNTAN Pontianak rector’s office house). JeLAST. 2018;5(2):1-9. (In Indonesian)
Glodon Company. UNS BIM Implementation Plan. Jakarta: Glodon Indonesia; 2022. (In Indonesian)
Changsaar C, Abidin NI, Khoso AR, Luenhui L, Yaoli X, Hunchuen G. Optimising energy performance of an eco-home using building information modelling (BIM). Innov Infrastruct Solut. 2022;7:140.
Sattineni A, Bradford RH. Estimating with BIM: a survey of US construction companies. Proceedings of the 28th ISARC; 2011 Jun 29 - Jul 2; Seoul, Korea. p. 564-9.
Sacks R, Eastman C, Lee G, Teicholz P. BIM handbook: a guide to building information modeling for owners, designers, engineers, contractors, and facility managers. 3rd Ed. United States: John Wiley & Sons; 2018.
Nadeem A, Wong AKD, Wong FKW. Bill of quantities with 3D views using building information modeling. Arab J Sci Eng. 2015;40:2465-77.
Khosakitchalert C, Yabuki N, Fukuda T. Automated modifcation of compound elements for accurate BIM-based quantity takeoff. Autom Constr. 2020;113:103142.
Choi J, Kim H, Kim I. Open BIM-based quantity take-off system for schematic estimation of building frame in early design stage. J Comput Des Eng. 2015;2(1):16-25.
Herzanita A, Anggraini RP. Comparison of building structure cost estimation between autodesk revit software and Cubicost. Constr Mater J. 2023;5(1):1-11. (In Indonesian)
Putro SH, Febriyuni AP. Calculation of the quantity of work to take off the structure using Glodon Cubicost and autodesk revit on the Surakarta air force hospital project (location: TA2023TKBG11-28) [thesis]. Semarang: Politeknik Pekerjaan Umum Semarang; 2023. (In Indonesian)
Hatmoko JUD, Fundra Y, Wibowo MA, Zhabrinna. Investigating building information modelling (BIM) adoption in Indonesia construction industry. MATEC Web Conf. 2019;258:02006.
Sartika I, Rachmat A, Sugiri T. Implementation of BIM QS in the upper structure planning of the construction project of the mother and child service center building RSUP Hasan Sadikin Bandung. Sistem Infrastruktur Teknik Sipil. 2023;3(1):59-71. (In Indonesian)
Zaini N, Ahmad Zaini A, Tamjehi SD, Razali AW, Gui HC. Implementation of building information modeling (BIM) in Sarawak construction industry: a review. IOP Conf Ser: Earth Environ Sci. 2020;498:012091.
Husin AE, Meisaroh M, Rahmawati DI, Kussumardianadewi BD. Improvement of cost performance based on BIM quantity take-off hospital structure work. Research Square. 2020:1-14.
Lhara Sari O, Yulianto Nugroho T. Analysis of take off quantity with BIM approach and pareto diagram on structural works of prosecutor's office building in Balikpapan City. 2023;10(2):553-63. (In Indonesian)
Aini Osman N, Suhaida SK, Abdul Razak N. Assessing the BIM software application in quantity surveying practice. INTI J. 2019;10:1-6.
Sugiyono. Quantitative research methods. Bandung: Alfabeta; 2018. (In Indonesian)