Predicting the Temperature Increase Trend of a Generator Using RNN, GRU, and LSTM Algorithms at Nam Ngum 1 Hydropower Plant in Laos
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.69650/rast.2025.260236Keywords:
Recurrent Neural Network, Long Short-Term Memory, Gated Recurrent Unit, Predictive Maintenance, Generator’s Stator WindingAbstract
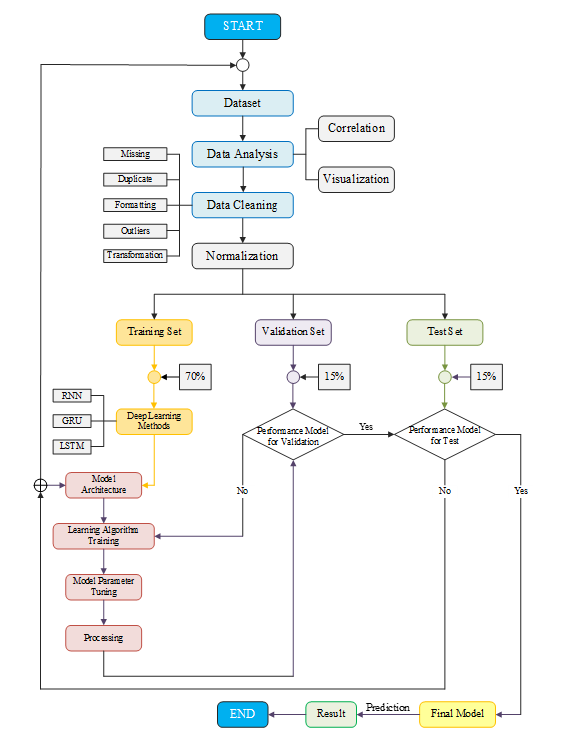
Synchronous generators are integral to the operation of hydropower plants. Stator faults, including short circuits, open circuits, and inter-turn faults, can cause severe performance issues and even catastrophic failures if not identified and mitigated promptly. Traditional generator monitoring methods such as periodic inspections and time-based maintenance often fail to detect subtle or evolving faults. This study proposes an advanced predictive maintenance approach utilizing deep learning techniques to monitor generator health at Nam Ngum-1 (NNG-1) Hydropower Plant in the Lao People’s Democratic Republic (PDR). Accurate temperature forecasting is vital for predictive maintenance, as excessive heat can lead to performance degradation and costly downtime. Using time-series data from the plant’s supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) system, including parameters such as power output, voltage, current, and cooling system temperatures, this research evaluates the models’ ability to capture temporal dependencies critical for precise trend prediction. Among the models tested, the results demonstrate that LSTM, with one hidden layer, achieved the highest accuracy based on MSE, RMSE, MAE, and R-squared, outperforming GRU, which had an R-squared of 98.60%, and RNN, which achieved 97.04%. When implemented with two hidden layers, LSTM maintained its superior performance with an R-squared of 98.34%, compared to GRU's 97.93% and RNN's 92.68%. These results demonstrate LSTM's exceptional capability in capturing both short- and long-term temperature dependencies, making it particularly suitable for predictive maintenance applications. The model's high accuracy in temperature forecasting enables early fault detection, helping to prevent performance degradation and reduce costly downtime in hydropower operations.
References
EDL-Gen. WOLLY OWN BUSINESS, <https://edlgen.com.la/hpp-wholly-owned-business> (2010).
Verginadis, D., Antonino-Daviu, V., Karlis, A. and Danikas, M. Diagnosis of stator faults in synchronous generators: Short review and practical case. in International Conference on Electrical Machines (ICEM). (2020), 2381-4802, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/ICEM49940.2020.9270936.
Li, Y., Han, X., Xu, B. and Wang, Y. A condition-based maintenance approach to an optimal maintenance strategy considering equipment imperfect maintenance model. in 2015 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT). (2015) 1466-1471, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/DRPT.2015.7432469.
Yi, Y., Xuerui, W. and Ke, K., Prediction model and distribution law study of temperature and pressure of the wellbore in drilling in Arctic region, Petroleum Drilling Techniques. 49(3) (2021) 11-20, doi: https://dx.doi.org/10.11911/syztjs.2021047.
Zhang, Q., Jiao, T., Ma, Y., Zhang, Y., Wu, X. and Wu, P. Temperature prediction of generator carbon brush based on LSTM neural network. in 2021 China Automation Congress (CAC). (2021), 5050-5055, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/CAC53003.2021.9728612.
Abumohsen, M., Owda, A., Y. and Owda, M., Electrical load forecasting using LSTM, GRU, and RNN algorithms. Energies. 16 (2023) 2283, doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/en16052283.
Klungsida, N., Maneechot, P., Butploy, N. and Khiewwan, K., Forecasting Energy Consumption from EV Station Charging Using RNN, LSTM, and GRU Neural Network. Journal of Renewable Energy and Smart Grid Technology. 19(1) (2024) 1-6, doi: https://doi.org/10.69650/rast.2024.254636.
Wensheng, L., Kuihua, W., Liang, F., Hao, L., Yanshuo, W. and Can, C. A region-level integrated energy load forecasting method based on CNN-LSTM model with user energy label differentiation. in 2020 5th International Conference on Power and Renewable Energy (ICPRE). (2020), 154-159, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/ICPRE51194.2020.9233226.
Badjan, A., Rashed, G., I., Gony, H. A. I., Bahageel, A. O. M., Hualiang, F. and Shaheen, H., I. Predictive Modelling of Base Station Energy Consumption: Insights and Application of STL- LSTM Networks. in 2024 9th Asia Conference on Power and Electrical Engineering (ACPEE). (2024), 2499-2503, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/ACPEE60788.2024.10532372.
Sciascera, C., Giangrande, P., Papini, L., Gerada, C. and Galea, M., Analytical thermal model for fast stator winding temperature prediction. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics. 64(8) (2017) 6116-6126, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/TIE.2017.2682010.
Qing, S., Rezaniakolaei, A., Rosendahl, L. A. and Gou, X., An analytical model for performance optimization of thermoelectric generator with temperature-dependent materials. IEEEE Access. 6 (2018) 60852-60861, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2874947
Safari, M., Nakharutai, N., Chiawkhun, P. and Phetpradap, P. DEA-RNNs: An Ensemble Approach for Portfolio Selection in the Thailand Stock Market. in Partial Identification in Econometrics and Related Topics. (2024), 453-467, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-59110-5_30.
Plevris, V., Solorzano, G., Bakas, N. and Ben Seghier, M. Investigation of performance metrics in regression analysis and machine learning-based prediction models. in the 8th European Congress on Computational Methods in Applied Sciences and Engineering (ECCOMAS Congress 2022). (2022), 1-25, doi: https://doi.org/10.23967/eccomas.2022.155.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 School of Renewable Energy and Smart Grid Technology (SGtech)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
All copyrights of the above manuscript, including rights to publish in any media, are transferred to the SGtech.
The authors retain the following rights;
1. All proprietary rights other than copyright.
2. Re-use of all or part of the above manuscript in their work.
3. Reproduction of the above manuscript for author’s personal use or for company/institution use provided that
(a) prior permission of SGtech is obtained,
(b) the source and SGtech copyright notice are indicated, and
(c) the copies are not offered for sale.









