แนวทางการใช้ปัญญาประดิษฐ์เชิงสร้างสรรค์สำหรับฟิสิกส์ศึกษา: กรณีศึกษา มจธ. (ราชบุรี)
Main Article Content
บทคัดย่อ
การพัฒนาอย่างรวดเร็วของปัญญาประดิษฐ์เชิงสร้างสรรค์ (Generative AI หรือ Gen-AI) ได้เปิดโอกาสใหม่ในการส่งเสริมการเรียนการสอนในสาขาวิชาต่าง ๆ รวมถึงฟิสิกส์ระดับอุดมศึกษา บทความนี้มุ่งทบทวนการประยุกต์ใช้ Gen-AI ในการเรียนการสอนฟิสิกส์ ณ มหาวิทยาลัยเทคโนโลยีพระจอมเกล้าธนบุรี (มจธ.) พื้นที่การศึกษาราชบุรี โดยเน้นในสองประเด็นหลัก ได้แก่ (1) การพัฒนาทักษะการให้เหตุผลเชิงฟิสิกส์ผ่านการแก้ปัญหาแบบมีแนวทางและการอธิบายด้วยตนเอง และ (2) ความเป็นไปได้ในการใช้ Gen-AI เป็นเครื่องมือประเมินผลการเรียนอัตโนมัติแบบออฟไลน์ เพื่อสะท้อนผลการเรียนรู้อย่างรวดเร็วและลดภาระงานของผู้สอน บทความยังกล่าวถึงความท้าทายที่สำคัญในการจัดการเรียนการสอน ความเป็นส่วนตัวของข้อมูล และความเข้ากันได้ของภาษา โดยเฉพาะในบริบทของการเรียนการสอนด้วยภาษาไทย มีการประเมินเบื้องต้นของการใช้โมเดลภาษาแบบโอเพ่นซอร์ส โดยแสดงให้เห็นถึงศักยภาพและข้อจำกัดในปัจจุบัน ผลการทบทวนบ่งชี้ว่า หากมีการบูรณาการอย่างดี Gen-AI สามารถมีบทบาทในการเปลี่ยนแปลงการศึกษาวิชาฟิสิกส์ โดยส่งเสริมความเข้าใจที่ลึกซึ้ง และสนับสนุนสภาพแวดล้อมการเรียนรู้ที่ปรับให้เหมาะกับแต่ละบุคคลในระดับที่ขยายได้
Article Details

อนุญาตภายใต้เงื่อนไข Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
เอกสารอ้างอิง
Catrambone, R., and Holyoak, K. J. (1989) Overcoming Contextual Limitations on Problem-Solving Transfer. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning Memory and Cognition 15(6): 1147 - 1156.
Chi, M.T.H., Feltovich, P.J. and Glaser, R. (1981) Categorization and representation of physics problems by experts and novices. Cognitive Science 5(2): 121 – 152.
Chi, M.T.H. and VanLehn, K.A. (1991) The Content of Physics Self-Explanations. The Journal of the Learning Science 1(1): 69 – 105.
Doucette, D., Clark, R. and Singh, C. (2020) Professional development combining cognitive apprenticeship and expectancy-value theories improves lab teaching assistants' instructional views and practices. Physical Review Physics Education Research 16(2): 020102. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevPhysEducRes.16. 020102.
Gjerde, V., Paulsen, V.H., Holst, B. and Kolst, S.D. (2022). Problem solving in basic physics: Effective self-explanations based on four elements with support from retrieval practice. Physical Review Physics Education Research 18(1): 010136. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevPhysEducRes.18.010136.
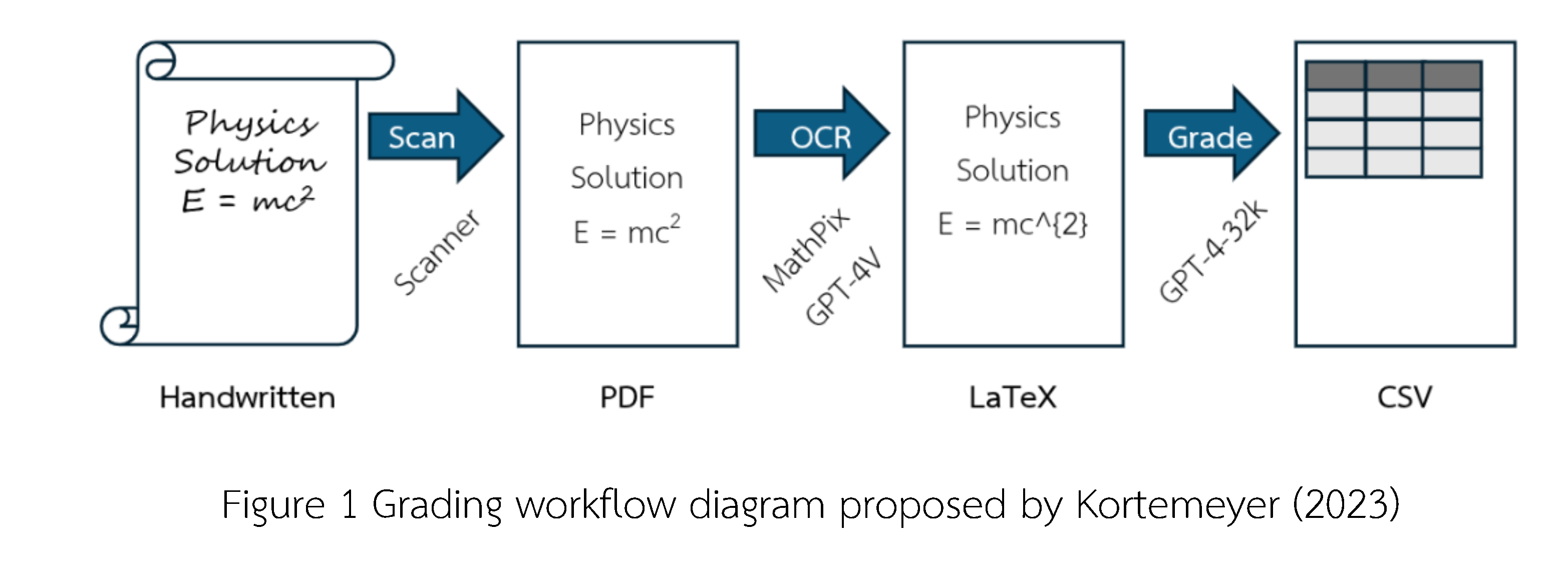
Kortemeyer, G. (2023). Toward AI grading of student problem solutions in introductory physics: a feasibility study. Physical Review Physics Education Research 19: 020163.
Kortemeyer, G., Nöhl, J. and Onishchuk, D. (2024). Grading assistance for a handwritten thermodynamics exam using artificial intelligence: An exploratory study. Physical Review Physics Education Research 20: 020144
Larkin, J., McDermott, J., Simon, D.P. and Simon, H.A. (1980) Expert and Novice Performance in Solving Physics Problems. Science 208(4450): 1335 - 1342
Lin, S. and Singh, C. (2010) Using Analogy to Solve a Three-Step Physics Problem. AIP Conference Proceedings 1289: 29 -32. doi: 10.1063/1.3515228.
Lyamuremye, A., Niyonzima, F.N., Mukiza, J., Twagilimana, I., Nyirahabimana, P., Nsengimana, T., Habiyaremye, J.D., Habimana, O. and Nsabayezu, E. (2024) Utilization of artificial intelligence and machine learning in chemistry education: a critical review. Discover Education 3: 95. doi: 10.1007/s44217-024-00197-5.
Mohamed, M.Z.B., Hidayat, R., Suhaizi, N.N.B., Sabri, N.B.M., Mahmud, M.K.H.B. and Baharuddin, S.N.B. (2022). Artificial intelligence in Mathematics education: A systematic literature review. International Electronic Journal of Mathematics Education 17(3): em0694.
Pipatanakul, K., Jirabovonvisut, P., Manakul, P., Sripaisarnmongkol, S., Patomwong, R., Chokchainant, P. and Tharnpipitchai, K. (2023) Typhoon: Thai Large Language Models. arXiv: 2312.13951. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2312.13951.
Phasook, P., Pranee, J., Saeoung, A., Kerdthaisnog, K., Sukhantharat, K., Chuangkrud, P., Damrongrat, C., Kongyoung, S. (2024). Pathumma-llm-text-1.0.0. Source: https://huggingface.co/nectec/Pathumm a-llm-text-1.0.0. Retrieved date 08 April 2025.
Reinhard, A., Felleson, A., Turner, P.C. and Green, M. (2010) Assessing the impact of metacognitive postreflection exercises on problem-solving skillfulness. Physical Review Physics Education Research 18: 010109. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevPhysEducRes.18.010109.
Soankwan, C., Emarat, N., Arayathanitkul, K., and Chitaree, R. (2007) International Newsletter on Physics Education. Physics Education in Thailand. Source: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/2 37462232_Physics_Education_in_Thailand. Retrieved date 10 April 2025.
Usak, M. (2024). Artificial intelligence in Biology education. Journal of Baltic Science Education 23(5): 806 - 808.
Wink, R. and Bonivento, W.M. (2023). Artificial Intelligence: New Challenges and Opportunities in Physics Education. In: Streit-Bianchi, M., Michelini, M., Bonivento, W., Tuveri, M. New Challenges and Opportunities in Physics Education, Challenges in Physics Education. Springer, Cham. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-37387-9_27