Sterols and Nutritional Values in Some Macroalgae
Main Article Content
Abstract
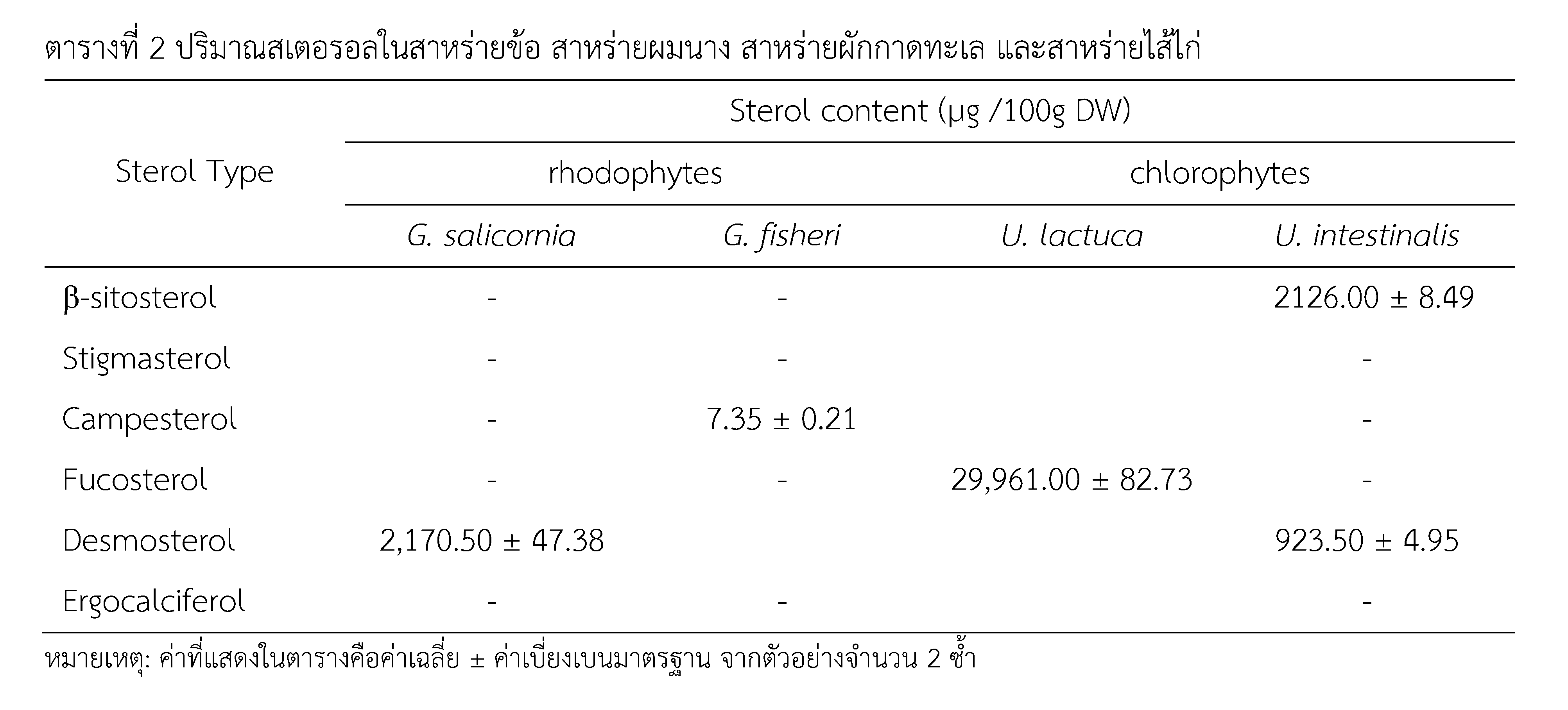
The present investigation evaluated the sterol composition and nutritional value of four macroalgal species, Gracilaria salicornia, G. fisheri, Ulva lactuca, and U. intestinalis. Analysis of sterol extracts revealed distinct profiles for each species in both the types and relative abundances of the sterols identified. A comparative nutritional assessment of the Rhodophyta species indicated that G. salicornia exhibited a superior fatty acid profile, with a greater proportion of unsaturated fatty acids compared to G. fisheri. Notably, the detection of eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) underscores the potential of these species as a source of valuable polyunsaturated fatty acids. Comparative analysis between the two Rhodophyta species, G. salicornia and G. fisheri, showed similar amino acid, protein, and fat contents, but differing mineral compositions, with G. fisheri being richer in calcium and G. salicornia in iron. For the Chlorophyta, U. lactuca exhibited higher levels of unsaturated fatty acids and magnesium compared to U. intestinalis. Their dominant amino acids differed (cysteine in U. lactuca, aspartic acid in U. intestinalis), and all proximate composition parameters (moisture, protein, fat, ash, carbohydrate) were distinct. These findings underscore the nutritional potential of these species for food applications and provide critical data to guide their future commercial cultivation and utilization.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
References
Abidi, S.L. (2001). Review: chromatographic analysis of plant sterols in foods and vegetable oils. Journal of Chromatography A 935(1-2): 173 - 201.
Aguilera-Morales, M., Casas-Valdez, M., Carrillo-Domı́nguez, S., González-Acosta, B. and Pérez-Gil, F. (2005). Chemical composition and microbiological assays of marine algae Enteromorpha spp. as a potential food source. Journal of Food Composition and Analysis 18(1): 79 - 88.
Ahmad, V.U., Memon, A.H., Ali, M.S., Perveen, S. and Shameel, M. (1996). Somalenone, A C26 sterol from the marine red alga Melanothamnus somalensis. Phytochemistry 42(4): 1141 - 1143.
Al Easa, H.A., Kornprobst, J.M. and Rizk, A.M. (1995). Major sterol composition of some algae from Qatar. Phytochemistry 39(2): 373 - 374.
AOAC. (2000). Official methods of analysis of AOAC International. 17th edition. Gaithersburg, M.D., USA: Association of Analytical Communities.
AOAC. (2005). Official methods of analysis of AOAC International. 18th edition. Gaithersburg, M.D., USA: Association of Analytical Communities.
Awad, A.B., von Holtz, R.L., Cone, J.P., Fink, C.S. and Chen, Y.C. (1998). beta-Sitosterol inhibits growth of HT-29 human colon cancer cells by activating the sphingomyelin cycle. Anticancer Research 18(1A): 471 - 473.
Catani, M.V., Gasperi, V., Bisogno, T. and Maccarrone, M. (2018). Essential dietary bioactive lipids in Neuroinflammatory diseases. Antioxidants & Redox Signaling 29(1): 37 - 60. doi: 10.1089/ars.2016.69 58.
Dawczynski, C., Schubert, R. and Jahreis, G. (2007). Amino acids, fatty acids, and dietary fibre in edible seaweed products. Food Chemistry 103(3): 891 - 899.
Derdemezis, C.S., Filippatos, T.D., Mikhailidis, D.P. and Elisaf, M.S. (2010). Review article: effects of plant sterols and stanols beyond low density lipoprotein cholesterol lowering. Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology and Therapeutics 15(2): 120 - 134. doi: 10.1177/1074248409357921.
DMSc. (2003). Compendium of methods for food analysis. Department of Medical sciences (DMSc), National Bureau of Agricultural Commodity and Food Standards (ACFS).
Emekli-Alturfan, E., Kasikci, E. and Yarat, A. (2010). Effects of oleic acid on the tissue factor activity, blood lipids, antioxidant and oxidant parameters of streptozotocin induced diabetic rats fed a high cholesterol diet. Medicinal Chemistry Research 19: 1011 - 1024.
Gamero-Vega, G., Palacios-Palacios, M. and Quitral, V. (2020). Nutritional Composition and Bioactive Compounds of Red Seaweed: A Mini-Review. Journal of Food and Nutrition Research 8(8): 431 - 440.
Gressler, V., Yokoya, N.S., Fujii, M.T., Colepicolo, P., Filho, J.M., Torres, R.P. and Pinto, E. (2010). Lipid, fatty acid, protein, amino acid and ash contents in four Brazilian red algae species. Food Chemistry 120(2): 585 - 590.
Goad, L.J. (1978). The sterols of marine invertebrates, composition, biosynthesis and metabolites. In: Scheuer, P.J. (Ed.), Marine Natural Products, Chemical and Biological Perspectives Vol. 2, pp. 75 -172. New York: Academic Press.
Gylling, H., Plat, J., Turley, S., Ginsberg, H.N., Ellegard, L., Jessup, W., Jones, P.J., Lutjohann, D., Maerz, W., Masana, L., Silbernagel, G., Staels, B., Boren, J., Catapano, A.L., De Backer, G., Deanfield, J., Descamps, O.S., Kovanen, P.T., Riccardi, G., Tokgozoglu, L. and Chapman, M.J. (2014). Plant sterols and plant stanols in the management of dyslipidemia and prevention of cardiovascular disease. Atherosclerosis 232(2): 346 - 360.
Hannan, M.A., Sohag, A.A.M., Dash, R., Haque, M.N., Mohibbullah, M., Oktaviani, D.F., Hossain, M.T., Choi, H.J. and Moon, I.S. (2020). Phytosterols of marine algae: Insights into the potential health benefits and molecular pharmacology. Phytomedicine 69(Suppl. 1): 153201.
Hendriks, H.F.J., Weststrate, J.A., van Vliet, T. and Meijer, G.W. (1999). Spreads enriched with three different levels of vegetable oil sterols and the degree of cholesterol lowering in normocholesterolaemic and mildly hypercholesterolaemic subjects. European Journal of Clinical Nutrition 53(4): 319 - 327.
Jiménez, P., Bustamante, A., Echeverría, F., Sambra, V., Rincón-Cervera, M.Á., Farías, C. and Valenzuela, R. (2023). Metabolic Benefits of Phytosterols: Chemical, Nutritional, and Functional Aspects. Food Reviews International 40(9): 1 - 23.
Kapetanovic´, R., Sladic, D., Popo, S., Zlatovic, M., Kljajic, Z. and Gasic, M. J. (2005). Sterol composition of the Adriatic Sea algae Ulva lactuca, Codium dichotomum, Cystoseira adriatica and Fucus virsoides. Journal of Serbian Chemical Society 70(12): 1395 - 1400.
Kazir, M., Abuhassira, Y., Robin, A., Nahor, O., Luo, J., Israel, A., Golberg, A. and Livney, Y.D. (2019). Extraction of proteins from two marine macroalgae, Ulva sp. and Gracilaria sp., for food application, and evaluating digestibility, amino acid composition and antioxidant properties of the protein concentrates. Food Hydrocolloids 87(1): 194 - 203.
Khotimchenko, S.V. (2005). Lipids from the marine alga Gracilaria verrucosa. Chemistry of Natural Compounds 41(3): 285 - 288.
Kris-Etherton, P.M. (1999). Monounsaturated Fatty Acids and Risk of Cardiovascular Disease. Circulation 100(11): 1253 - 1258. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.100.11.1253.
Li, X., Fan, X., Han, L. and Lou, Q. (2002). Fatty acids of some algae from the Bohai Sea. Phytochemistry 59(2): 157 - 161.
Lin, A.S., Engel, S., Smith, B.A., Fairchild, C.R., Aalbersberg, W., Hay, M.E. and Kubanek, J. (2010). Structure and biological evaluation of novel cytotoxic sterol glycosides from the marine red alga Peyssonnelia sp. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry 18(23): 8264 - 8269.
Lopes, G., Sousa, C., Bernardo, J., Andrade, P.B., Valentão, P., Ferreres, F. and Mouga, T. (2011). Sterol profiles in 18 macroalgae of the Portuguese coast. Journal of Phycology 47(5): 1210 - 1218. doi: 10.1111/j. 1529-8817.2011.01028.x
Lopes, G., Sousa, C., Valentão, P. and Andrade, P.B. (2013). Sterols in Algae and Health. In Bioactive Compounds from Marine Foods. USA: John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 173 - 191.
MaCartain, P., Gill, C.I.R., Brooks, M., Campbell, R. and Rowland, I.R. (2007). Nutritional value of edible seaweeds. Nutrition Reviews 65(12): 535 - 543.
Marinho-Soriano, E. Camara, M.R., Cabral, T.M. and Carneiro, M.A.A. (2007). Preliminary evaluation of the seaweed Gracilaria cervicornis (Rhodophyta) as a partial substitute for the industrial feeds used in shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) farming. Aquaculture Research 38(2): 182 - 187.
Marrion, O., Fleurence, J., Schwertz, A., Guant, J.L., Mamelouk, L., Ksouri, J. and Villaume, C. (2005). Evaluation of protein in vitro digestibility of Palmaria palmata and Gracilaria verrucosa. Journal of Applied Phycology 17(2): 99 - 102.
Mazzuca, M. and Balzaretti, V. (2003). Fatty acids, sterols and other steroids from seeds of Patagonian Prosopis species. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture 83(10): 1072 - 1075.
McDermid, K.J. and Stuercke, B. (2003). Nutritional composition of edible Hawaiian seaweeds. Journal of Applied Psychology 15(6): 513 - 524.
Miettinen, T. A., Puska, P., Gylling, H., Vanhanen, H. and Vartiainen, E. (1995). Reduction of Serum Cholesterol with Sitostanol-Ester Margarine in a Mildly Hypercholesterolemic Population. New England Journal of Medicine 333(20): 1308 - 1312. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199511163332002.
Moreau, R.A., Powell, M.J. and Hicks, K.B. (1996). Extraction and quantitative analysis of oil from commercial corn fiber. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry 44(8): 2149 - 2154.
Munda, I.M. (1977). Differences in amino acid composition of estuarine and marine fucoids. Aquatic Botany 3(1): 273 - 280.
Murakami, K., Yamaguchi, Y., Noda, K., Fujii, T., Shinohara, N., Ushirokawa, T., Sugawa-Katayama, Y. and Katayama, M. (2011). Seasonal variation in the chemical composition of a marine brown alga, Sargassum horneri (Turner) C. Agardh. Journal of Food Composition and Analysis 24(2): 231 - 236.
Okano, M., Fukamiya, N., Mizui, F. and Aratani, T. (1982). Seasonal variation of sterol, hydrocarbon, and fatty acid fractions in Cladophora densa HARVEY. Bulletin of the Japanese Society of Scientific Fisheries 48(6): 815 - 819.
Ortiz, J., Romero, N., Robert, P., Araya, J., Lopez-Hernández, J., Bozzo, C., Navarrete, E., A., Osorio, A. and Rios, A. (2006). Dietary fiber, amino acid, fatty acid and tocopherol contents of the edible seaweeds Ulva lactuca and Durvillaea antarctica. Food Chemistry 99(1): 98 - 104.
Paiva, L., Lima, E., Neto, A.I., Marcone, M. and Baptista, J. (2017). Nutritional and functional bioactivity value of selected Azorean macroalgae: Ulva compressa, Ulva rigida, Gelidium microdon, and Pterocladiella capillacea. Journal of Food Science 82(7): 1757 - 1764.
Plat, J., Baumgartner, S., Vanmierlo, T., Lutjohann, D., Calkins, K.L., Burrin, D.G., Guthrie, G., Thijs, C., Te Velde, A.A., Vreugdenhil, A.C.E., Sverdlov, R., Garssen, J., Wouters, K., Trautwein, E.A., Wolfs, T.G., van Gorp, C., Mulder, M.T., Riksen, N.P., Groen, A.K. and Mensink, R.P. (2019). Plant-based sterols and stanols in health & disease: “Consequences of human development in a plant-based environment?”. Progress in Lipid Research 74(1): 87 - 102.
Rao, V.A. and Janezic, S.A. (1992). The role of dietary phytosterol in colon carcinogenesis. Nutrition and Cancer 18(1): 43 - 52. doi: 10.1080/01635589209514203.
Renaud, S.M. and Luong-Van, J.T. (2006). Seasonal variation in the chemical composition of tropical Australian marine macroalgae. Journal of Applied Phycology 18(1): 381 - 387.
Sarwar, G., Botting, H.G. and Peace, R.W. (1988). Complete amino acid analysis in hydrolysates of foods and feces by liquid chromatography of precolumn phenylisothiocyanate derivatives. Journal Association of Official Analytical Chemistry 71(6): 1172 - 1175.
Shahzad, N., Khan, W., Md, S., Ali, A., Saluja, S.S., Sharma, S., Al-Allaf, F.A., Abduljaleel, Z., Ibrahim, I.A.A., Abdel-Wahab, A.F., Afify, M.A. and Al-Ghamdi, S.S. (2017). Phytosterols as a natural anticancer agent: current status and future perspective. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 88(Suppl. 1): 786 - 794.
Sheu, J.H., Wang, G.U., Sung, P.J., Chiu, Y.H. and Duh, C.Y. (1997). Cytotoxic Sterols from the Formosan Brown Alga Turbinaria ornate. Planta Medica 63(6): 571 - 572.
Stefanov, K., Dimitrov, K., Dimitrova-Konaklieva, S., Kirisheva, I. and Popov, S. (1996). Lipid and sterol composition of the freshwater alga Spirogyra crassa (L.) Kutz (Chlorophyta). Archiv für Hydrobiologie 135(4): 523 - 527.
U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. (1996) Test Methods for Evaluating Solid Waste, Physical/Chemical Methods, Method 6010B, Inductively Coupled Plasma-Atomic Emission Spectrometry, in publication SW 846,. Office of Solid Waste.
Vieira, E.F., Soares, C., Machado, S., Correia, M., Ramalhosa, M.J., Oliva-teles, M.T., Paula Carvalho, A., Domingues, V.F., Antunes, F., Oliveira, T.A.C., Morais, S. and Delerue-Matos, C. (2018). Seaweeds from the Portuguese coast as a source of proteinaceous material: Total and free amino acid composition profile. Food Chemistry 269(15): 264 - 275. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.06.145.
Wachter, G.A., Franzblau, S.G., Montenegro, G., Hoffmann, J.J., Maiese, W.M. and Timmermann, B.N. (2001). Inhibition of Mycobacterium tuberculosis growth by saringosterol from Lessonia nigrescens. Journal of Natural Products 64(11): 1463 - 1464.
Wahbeh, M.I. (1997). Amino acid and fatty acid profiles of four species of macroalgae from Aqaba and their suitability for use in fish diets. Aquaculture 159(1-2): 101 - 109.
Wells, M.L., Potin, P., Craigie, J.S., Raven, J.A., Merchant, S.S., Helliwell, K.E., Smith, A.G., Camire, M.E. and Brawley, S.H. (2017). Algae as nutritional and functional food sources: Revisiting our understanding. Journal of Applied Phycology 29(2): 949 - 982. doi: 10.1007/s10811-016-0974-5.
Wen, X., Peng, C., Zhou, H., Lin, Z., Lin, G., Chen, S. and Li, P. (2006). Nutritional composition and assessment of Gracilaria lemaneiformis Bory. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology 48(9): 1047 - 1053.
Yuan, Y.V. and Walsh, N.A. (2006). Antioxidative and antiproliferative activities of extracts from a variety of edible seaweeds. Food and Chemical Toxicology 44(7): 1144 - 1150. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2006.02.002.