DATA APPLICATION MANAGEMENT SYSTEM NATIONAL SKILL STANDARD TESTING CENTER IN LOGISTICS SOUTHEAST BANGKOK UNIVERSITY UNDER LEAN CONCEPTUAL
Main Article Content
Abstract
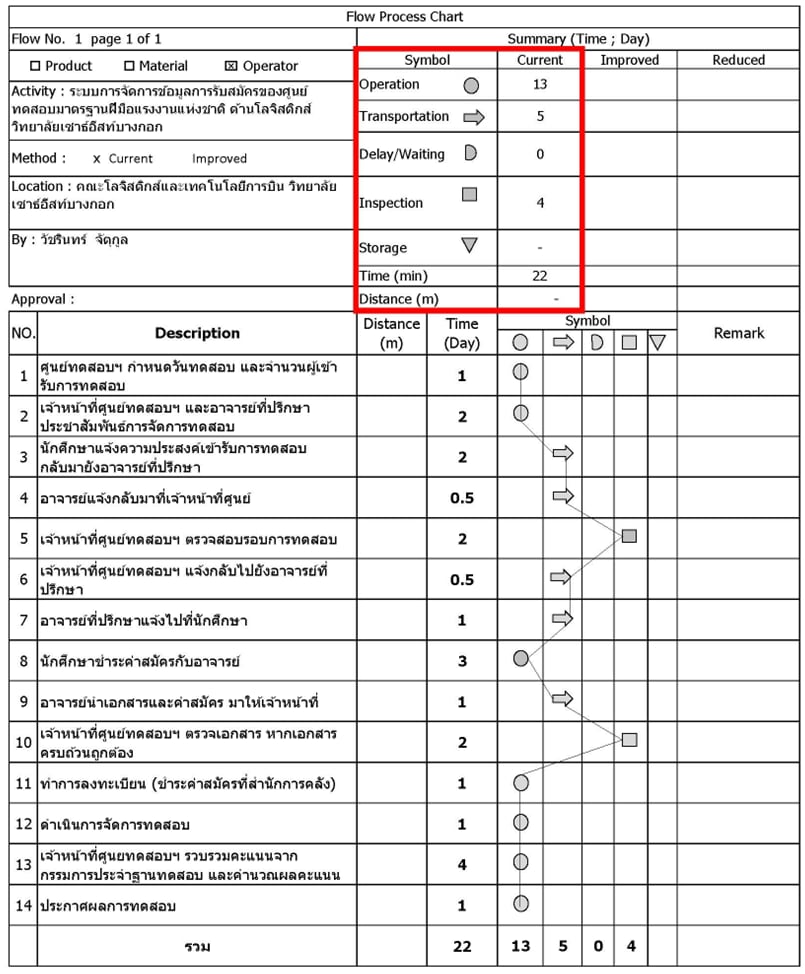
The purposes of this research were 1) to study the recruitment process of the National Skill Standard Testing Center for Logistics. Southeast Bangkok University 2) to develop the admission management system of the testing center and 3) to study the satisfaction level of the admission management system of the testing center. From studying the admissions process of the testing center with process flow chart It was found that the problems arising in the admissions process of the testing center There are complex workflows. This results in wastage, error, and inefficiency with operators. It also affects the satisfaction of candidates taking the test. The researcher therefore analyzed the problems found to determine the cause by questioning techniques. Why-Why-Analysis Then, the researcher developed a system to manage the admissions data of the testing center according to the system development life cycle (SDLC) principle to reduce waste in the testing center's admissions process. And to assess the satisfaction level of the admissions management system of the testing center. The research results showed that Admission process of the testing center from the original period of 22 days, reduced to 12 days, or 45.45 percent of the reduced amount. and satisfaction results of administrators, faculty, and staff on the use of the admissions management system of the testing center the mean was 4.19 and the standard deviation was 0.52 or was in the quality level of satisfaction. Classified by aspects of 1) Functionality the mean was 3.97 and the standard deviation was 0.53 or was in the quality level of high satisfaction. 2) Management and efficiency of the system. The mean was 4.42 and the standard deviation was 0.51 or was in the quality level of satisfaction. 3) System safety. The mean was 3.92 and the standard deviation was 0.58 or was in the quality level of satisfaction. with a mean of 4.54 and a standard deviation of 0.51 or at the highest level of satisfaction quality and 5) information system services. The mean was 4.14 and the standard deviation was 0.51 or was in the quality level of satisfaction. However, the results of the satisfaction of the test applicants on the use of the admissions management system of the testing center the mean was 4.51 and the standard deviation was 0.51 or was in the highest level of satisfaction quality. Classified by aspects of 1) Functionality The mean was 4.52 and the standard deviation was 0.52 or was in the highest satisfaction quality level. 2) Management and efficiency of the system. The mean was 4.49 and the standard deviation was 0.51 or was in the quality level of high satisfaction. The mean was 4.53 and the standard deviation was 0.51 or was in the highest satisfaction quality level. with a mean of 4.50 and a standard deviation of 0.51 or at the highest level of satisfaction quality and 5) information system services. The mean was 4.51 and the standard deviation was 0.53 or was in the highest level of satisfaction quality.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
เนื้อหาและข่อมูลในบทความที่ลงตีพิมพ์ในวารสารวิชาการ เทคโนโลยี พลังงาน และสิ่งแวดล้อม บัณฑิตวิทยาลัย วิทยาลัยเทคโนโลยีสยาม ถือเป็นข้อคิดเห็นและความรับผิดชอบของผู้เขียนบทความโดยตรง ซึ่งกองบรรณาธิการวารสารไม่จำเป็นต้องเห็นด้วย หรือว่าร่วมรับผิดชอบใด ๆ
บทความ ข้อมูล เนื้อหา รูปภาพ ฯลฯ ที่ได้รับการตีพิมพ์ในวารสารวิชาการ เทคโนโลยี พลังงาน และสิ่งแวดล้อม บัณฑิตวิทยาลัย วิทยาลัยเทคโนโลยีสยาม ถือเป็นลิขสิทธิ์ของวารสารวิชาการ เทคโนโลยี พลังงาน และสิ่งแวดล้อม บัณฑิตวิทยาลัย วิทยาลัยเทคโนโลยีสยาม หากบุคคล หรือหน่วยงานใดต้องการนำทั้งหมด หรือส่วนหนึ่งส่วนใดไปเผยแพร่ต่อ หรือเพื่อกระทำการใด ๆ จะต้องได้รับอนุญาต เป็นลายลักษณ์อักษรจากวารสารวิชาการ เทคโนโลยี พลังงาน และสิ่งแวดล้อม บัณฑิตวิทยาลัย วิทยาลัยเทคโนโลยีสยาม เท่านั้น
References
พระราชบัญญัติส่งเสริมการพัฒนาฝีมือแรงงาน พ.ศ. 2545. (2557, 16 กรกฎาคม). ราชกิจจานุเบกษา. เล่ม 131 ตอนพิเศษ 131 ง. หน้า 182-221.
คณะโลจิสติกส์และเทคโนโลยีการบิน วิทยาลัยเซาธ์อีสท์บางกอก. (2561). รายงานการประเมินตนเอง (Self Assessment Report) ประจําปีการศึกษา 2561.
Montgomery D.C. Introduction to Statistical Quality Control. New York: John Wiley & Sons Inc, 2005; 364–413.
Yamane, Taro. (1976). Statistics: An introductory analysis (2nd ed.). New York: Harper and Row.
วันชัย ริจิรวนิช, การศึกษาการทำงาน หลักการและกรณีศึกษา, สำนักพิมพ์แห่งจุฬาลงกรณ์มหาวิทยาลัย,กรุงเทพฯ, หน้า 335-380, 2548.
Surus Tangphaitoon. (2014). 7 Waste Reduction by Kaizen for Production Improvement. 1st Edition. Nonthaburi. (In Thai).
Kittikorn Chantarasenar. (2019). “Why Why Analysis” [Online]. Available: https://leantpm.co /2019/03/02/ why-why-analysis. [Accessed: Apr. 6, 2022].
พัฒนา พรหมณี, ยุพิน พิทยาวัฒนชัย และจีระศักดิ์ ทัพผา. (2563). “แนวคิดเกี่ยวกับความพึงพอใจและการสร้างแบบสอบถามความพึงพอใจในงาน.” วารสารวิชาการสมาคมสถาบันอุดมศึกษาเอกชนแห่งประเทศไทย (สสอท.). 26(1) : 59-66.
Likert, R. N. (1970). A technique for the measurement of attitude. Attitude Measurement. Chicago:Ronal McNally & Company
โอภาส เอี่ยมสิริวงศ์. (2555). การวิเคราะห์และออกแบบระบบ. กรุงเทพ : ซีเอ็ดยูเคชั่น.
สมพร กระออมแก้ว, กิตติ์ดนัย สกุลวรเกียรติ์ และ ณปภัช วรรณตรง. (2564). “ระบบจองรถเพื่อการเกษตรออนไลน์”. วารสารวิทยาศาสตร์และเทคโนโลยี. 5(1) : 25-35.
อัชณี ซาอุรัมย์. (2564). “การพัฒนาระบบการรับสมัครฝึกอบรมออนไลน์ของสถาบันนวัตกรรมเทคโนโลยีไทย-ฝรั่งเศส มหาวิทยาลัยเทคโนโลยีพระจอมเกล้าพระนครเหนือ”. วารสารวิชาการครุศาสตร์อุตสาหกรรม พระจอมเกล้าพระนครเหนือ. 12(1):70-81.