Study of Car Audio Waste Management as a Waste Management Guideline According to the Draft Electrical and Electronic Equipment Waste Management Legislation
Main Article Content
Abstract
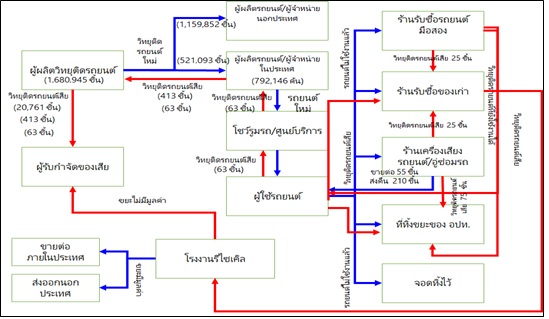
The Problems in management of electrical and electronic waste products exist all over the world because of the manufacturing and innovating to meet the needs and for the convenience of users. However, in Thailand, there is no law that directly applies to the management of these waste products. The relevant agencies are trying to draw up a legislation to enforce the disposal of these electrical and electronic equipment waste products to reduce the impact of toxic substances contamination to environment and public health. In this research, the management of car radio waste products was studied. Car radio is considered a type of electronic device that may be overlooked because this device is not branded by the manufacturer and is not sold directly to consumers, but rather to car manufacturers that selling cars to consumers. This research was conducted to survey the groups of stakeholders involved in the process of used car radios in Bang Bo District and Bang Sao Thong District, Samut Prakan Province. A survey of 100 car users found that about 25 % of their used cars were resold to used car dealers and 75% of them would keep their old cars for themselves and pass them on to their family members. A survey of 10 used car dealerships found that 11,400 cars were repair for refurbishment per year. Of the cars that were refurbished, 264 car radios were found to be damaged, 252 pieces were sold to antique shop and 12 pieces were disposed as general waste. A survey of 10 repair shops found that there were 4,380 pieces of car audio had been refurbished per year, with 2,520 of them being returned to owners, 660 pieces were sold to the second buyer, 900 pieces were disposed as general waste, and 300 were sold to antique shops. A survey found that 10 antique shops buys more than 330 used car radios per year, with 550 pieces from used car buyers and audio tuning shops, the number of broken car radios that will be included in the antique shop would be more than 880 pieces. From the survey, the material flow analysis for the unused car audio was constructed. The roles and duties of stakeholders in the current legislation were compared to those of the draft of Electrical and Electronic Equipment Waste Management Legislation as a guideline for preparation and adaptation when the draft legislation is enforced.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
เนื้อหาและข่อมูลในบทความที่ลงตีพิมพ์ในวารสารวิชาการ เทคโนโลยี พลังงาน และสิ่งแวดล้อม บัณฑิตวิทยาลัย วิทยาลัยเทคโนโลยีสยาม ถือเป็นข้อคิดเห็นและความรับผิดชอบของผู้เขียนบทความโดยตรง ซึ่งกองบรรณาธิการวารสารไม่จำเป็นต้องเห็นด้วย หรือว่าร่วมรับผิดชอบใด ๆ
บทความ ข้อมูล เนื้อหา รูปภาพ ฯลฯ ที่ได้รับการตีพิมพ์ในวารสารวิชาการ เทคโนโลยี พลังงาน และสิ่งแวดล้อม บัณฑิตวิทยาลัย วิทยาลัยเทคโนโลยีสยาม ถือเป็นลิขสิทธิ์ของวารสารวิชาการ เทคโนโลยี พลังงาน และสิ่งแวดล้อม บัณฑิตวิทยาลัย วิทยาลัยเทคโนโลยีสยาม หากบุคคล หรือหน่วยงานใดต้องการนำทั้งหมด หรือส่วนหนึ่งส่วนใดไปเผยแพร่ต่อ หรือเพื่อกระทำการใด ๆ จะต้องได้รับอนุญาต เป็นลายลักษณ์อักษรจากวารสารวิชาการ เทคโนโลยี พลังงาน และสิ่งแวดล้อม บัณฑิตวิทยาลัย วิทยาลัยเทคโนโลยีสยาม เท่านั้น
References
คัดคณัฐ ชื่นวงศ์อรุณ, ณภัทร ดนัย.(20 เมษายน 2565). ขยะอิเล็กทรอนิกส์ เศษซากจากความเจริญรุ่งเรือง.สืบค้น
[ระบบออนไลน์] แหล่งที่มา: https://ngthai.com/science/33111/e-waste/
OFFICE OF KNOWLEDGE MANAGEMENT AND DEVELOPMENT.(20 เมษายน 2565). E-Waste ปัญหาขยะ
ที่เป็นภาระสิ่งแวดล้อม.สืบค้น[ระบบออนไลน์] แหล่งที่มา: https://www.okmd.or.th/okmd-kratooktomkit/4287
สายใจ วิทยาอนุมาส. “การจัดการขยะอิเล็กทรอนิกส์ในประเทศไทย” .สถาบันวิจัยเพื่อการพัฒนาประเทศไทย ฉบับ
ที่ 133.2560.
สิริลัคน์ สุบงกฎ. “มาตรการทางกฎหมายเกี่ยวกับการจัดการซากผลิตภัณฑ์เครื่องใช้ไฟฟ้าและอิเล็กทรอนิกส์ :
ศึกษากรณีการจัดการซากโทรทัศน์” .นิติศาสตรมหาบัณฑิตสาขากฎหมายทรัพยากรธรรมชาติและสิ่งแวดล้อมคณะ
นิติศาสตร์ มหาวิทยาลัยธรรมศาสตร์.2560.
สุจิตรา วาสนาดำรงดี. “เรียนรู้ความพยายามของสิงคโปร์ในการจัดการขยะอย่างยั่งยืน – จากเตาเผาสู่การลดขยะที่
ต้นทาง” .วารสารสิ่งแวดล้อมปีที่ 26 ฉบับที่ 2.2565.
นิกร ภิญโญ. “การจัดการขยะอิเล็กทรอนิกส์ในชุมชน: หลักการและแนวคิดภายใต้มาตรการทางกฎหมายของ
ประเทศไทยและต่างประเทศ” .คณะบริหารการพัฒนาสิ่งแวดล้อม สถาบันบัณฑิตพัฒนบริหารศาสตร์.2563.
กัญญ์กณิษฐ์ กมลกิตติวงศ์. บุษบา พฤกษาพันธุ์รัตน์. “ปัจจัยสำคัญที่มีผลต่อการจัดการกรีนซัพพลายเชนในกลุ่ม
อุตสาหกรรมผลิตเครื่องใช้ไฟฟ้าและอิเล็กทรอนิกส์ไทย ; The Critical Factors Affecting Green Supply Chain
Management Implementation in Electrical and Electronic Industry in Thailand”.ภาควิชาการจัดการโลจิสติกส์
คณะบริหารธุรกิจ มหาวิทยาลัยรังสิต ภาควิชาวิศวกรรมอุตสาหการ คณะวิศวกรรมศาสตร์
มหาวิทยาลัยธรรมศาสตร์.2558
บริษัท ฐานเศรษฐกิจ มัลติมีเดีย จํากัด.16 พฤศจิกายน 2563.กรมศุลฯแจงนำเข้า-ส่งออกขยะอิเล็กทรอนิกส์และ
พลาสติกยังสูง.สืบค้น[ระบบออนไลน์] แหล่งที่มา: https://www.thansettakij.com/business/289650
สำนักงานบริหารนโยบายของนายกรัฐมนตรี.9 กุมภาพันธ์ 2565.แก้ปัญหาขยะอิเล็กทรอนิกส์ปกป้องสิ่งแวดล้อม-
สุขภาพประชาชน.สืบค้น[ระบบออนไลน์] แหล่งที่มา: https://www.pmdu.go.th/electronic-waste/
สำนักอนามัยสิ่งแวดล้อม กรมอนามัย กระทรวงสาธารณสุข.วราภรณ์ บุญภักดี.3 สิงหาคม 2563.คู่มือประชาชน
ขยะอิเล็กทรอนิกส์ของเสียที่มาพร้อมเทคโนโลยี.สืบค้นจากhttps://dl.parliament.go.th/handle/lirt/588461
ดร.สุจิตรา วาสนาดำรงดี.3 สิงหาคม 2563.ร่างพ.ร.บ. การจัดการซากผลิตภัณฑ์เครื่องใช้ไฟฟ้าและอุปกรณ์
อิเล็กทรอนิกส์ (ฉบับปรับปรุงแก้ไข): ความหวังหรือความสิ้นหวัง สถาบันวิจัยสภาวะแวดล้อม จุฬาลงกรณ์
มหาวิทยาลัย.สืบค้น[ระบบออนไลน์] แหล่งที่มา: https://thaipublica.org/2015/11/sujittra-e-waste/
สุธิดา ภูกองชนะ. “การศึกษาความตระหนักและแนวปฏิบัติในการเก็บรวบรวมและการคืนซากแบตเตอรี่
โทรศัพท์มือถือในประเทศไทย” .วิศวกรรมศาสตรมหาบัณฑิต มหาวิทยาลัยธรรมศาสตร์.2560.
อภิญญา กิจเกิดแสง,สวรรยา ธรรมอภิพล. “พฤติกรรมและความรู้ของประชาชนในการจัดขยะอิเล็กทรอนิกส์
กรณีศึกษา ตำบลหัวโพ จังหวัดราชบุรี.ศิลปศาสตรมหาบัณฑิต มหาวิทยาลัยศิลปากร.2561.