Effect of Hydrothermal Processing on Carotenoids, Tocopherol, Fatty Acids and Oxidative Parameters of Palm (Elaeis guinensis Jacq) Oil
Keywords:
Hydrothermal, carotenoids, tocopherols, fatty acids, peroxide valueAbstract
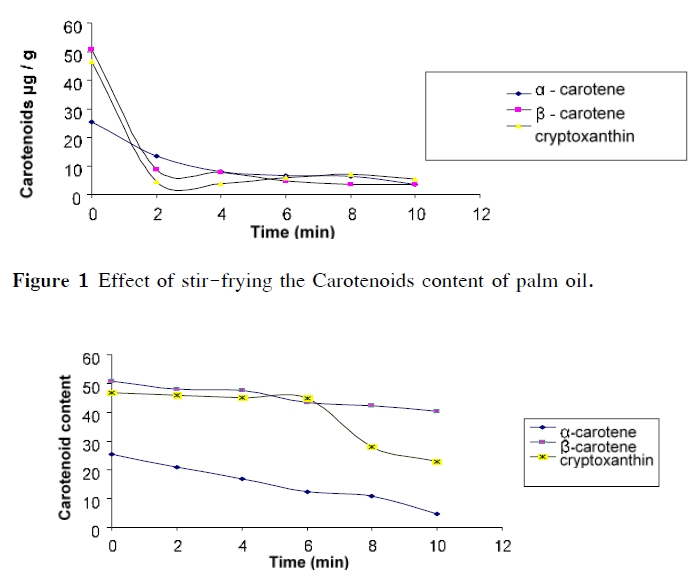
The study investigated the impact of hydrothermal processing on carotenoids, total tocopherol, fatty acids and oxidative changes in palm (Elaes guinensis) oil. The oil samples were subjected three thermal processes namely boiling (oil with water), stir-frying (oil without water) and batch frying (frying plantain in oil). In each of the thermal operations, samples of oil were withdrawn at time interval for analysis. The oil samples obtained from each operation analysed for chemical parameters using standard methods, fatty acid profile analysed using gas chromatography, carotenoids by spectrophotometric methods after separation by open column chromatography and tocopherol by colorimetric method. The results indicated that stir frying and boiling processes caused a drastic decrease in the carotenoid within 2mins, β -carotene and tocopherol decreased by 50 % within 100 min of processing. The peroxide value and thiobarbituric acid values increased from 8.5 to 118 meq/kg and 2.23 to 7.59 (240 %) respectively. From batch frying, peroxide value, free fatty acids and acid value increases from 9.48 to 33.21 meq/kg, 0.93 to 1.42 and 1.85 to 2.82, correspondingly as frying time was increased. The trans fatty acids was discovered to be present due to increase frying time. The study revealed that heat treatment to which palm oil is subjected especially during food preparation could lead to loss of lipophilic vitamins and essential fatty acids with formation of trans fatty acid; and also, oxidative deterioration of the oil. Hence, repeatedly used vegetable oil should be constantly analysed as it may be detrimental to nutrition and health of consumers.
References
AOAC. (2000). Official methods of Analysis. Association of Official Analytical Chemists.Arlington.
Aladedunye, F.,Przybylski, R., &Matthäus, B. (2017) Performance of antioxidative compounds under frying conditions.Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 57(8), 1539–1561.
Amorim‐Carrilho,K. T., Cepeda,A., Fente,C., & Regal,P. (2014). Review of methods for analysis of carotenoids. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry,56, 49–73.
Cervantes-Paz, B., Yahia, E. M., de Jesús Ornelas-Paz, J., Victoria-Campos, C. I., Ibarra-Junquera, V., Pérez-Martínez, J. D., & Escalante-Minakata, P. (2014). Antioxidant activity and content of chlorophylls and carotenoids in raw and heat-processed Jalapeño peppers at intermediate stages of ripening. Food chemistry, 146, 188-196.
Chaves, M. H., Araújo, F. D. S., Moura, C. V. R., Tozetto, J, S. -Pimentel, A., & Caruso,M. S. F (2012). Chemical Characterization and Stability of the Bombacopsis glabra Nut Oil. Food and Public Health, 2(4),104-109.
Cilla, A., Alegria,A., de Ancos,B., Sanchez‐Moreno,C., Cano,M. P., Plaza,L., Clemente,G., Lagarda, M.J., & Barbera, R. (2012). Bioaccessibility of tocopherols, carotenoids, and ascorbic acid from milk‐and soy‐based fruit beverages: influence of food matrix and processing. JournalAgric Food Chem,60,7282–90.
Dauqan, M. A., Abdullah, A.,&Sani, H. A. (2011). Natural Antioxidants, Lipid Profile, Lipid Peroxidation, Antioxidant Enzymes of Different Vegetable Oils Advance.Journal of Food Science and Technology,3, (4), 308-316.
Dobarganes, M. C., Velasco, J.,&Dieffenbacher, A. (2000). Determination of Polar Compounds, Polymerized and Oxidized Triacylglycerols and Diacylglycerols in Oils and Fats. Pure and Applied Chemistry, 72(8), 1563-1575. https://doi.org/10.135/pac200072981563.
Dorbarganes, M.C., &Maquis-ruitz, G. (2015). Possible adverse effects of frying with vegetable oils. British Journal of Nutrition, 113(52), 549-557.
FAO/WHO.(1988). Dietary Fats and Oils in Human Nutrition. FAO Food and NutritionSeries 20.(pp.1-44). Rome: Food and Agricultural Organization of the United Nations.
Harrison E.H. (2012). Mechanisms involved in the intestinal absorption of dietary vitamin A and provitamin A carotenoids. Biochim Biophys Acta,1821, 70–77.
Holownia,M. C., Erickson, M. S., &Eitenmiller, R. R. (2001). Tocopherol losses in peanut oil during pressure frying of marinated chicken with strips coated with edible fibre. Food Research International, 34, 77 –80. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0963-9969(00)00134.4
Falade, A. O, Oboh, G, &Okoh, A. I, (2017). Potential Health Implications of the Consumption of Thermally-Oxidized Cooking Oils –a Review Pol. Polish journal of food and nutrition sciences, 67(2), 95–105. https://doi.org/10.1515/pjfns-2016-0028
Klein, B. P.,&Perry, A. (1982). Ascorbic Acid and Vitamin A Activity in Selected Vegetables from Different Geographical Areas of the United States.Journal of Food Science, 47, 741-945.
Norizzah, A. R., Norsyamimi, M., Zaliha, O., Nur-Azimah, K., & Hazirah, M. F. (2014). Physicochemical properties of palm oil and palm kernel oil blend fractions after interesterification. International Food Research Journal,22(4),1390-1395.
Flores, M., Avendano, V., Bravo, J., Valdes, C., Forero-Doria, O., Quintral, V., Vilcanqui Y.,&Ortiz-viedma, J. (2021). Edible oil parameters during deterioration processes. Int. J. of Food Sciences, 2021,1-16
Odia, O.J., Ofori, O.,&Maduka,O. (2015). Palm oil and the heart: A review. World Journal of Cardiology,7(3),144-149.
Puah, C. W., Choo, Y. M., Ma, A. N.,&Chuah,C. H. (2007). The Effect of Physical Refining on Palm Vitamin E (Tocopherol, Tocotrienol and Tocomonoenol).American Journal of Applied Sciences,4(6),374-377.
Siddique, B. M., Ahmad, A., Ibrahim, M. H., Hena, S., Rafatullah M., &Omar,M. (2010). Physico-chemical properties of blends of palm olein with other vegetable oils. Grasas y aceites, 61(4), 423-429.https://doi.org/10.3989/gya.010710
Suleiman, A. M., Attyr,E., & Mohammed, F. R. (2006). Anti-radical performance and physiochemical characteristics of vegetable oils. Electronic.Journal of. Environmental, Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 5, 1429 –144.
Sun, Q., Sonegal, A., Chinachoti, P., & Faustman, C. (2002). Effect of water activity on lipid oxidation and protein solubility in freeze-dried beef during storage. Journal of Food Science, 67, 2512 –2516.
Tannenbaum, S. R., Young, V. R., & Archer, M. C. (1985). Vitamins and Minerals. In Food Chemistry. InO.R. Fennema (Ed.),Food chemistry(pp. 513 –517).New York: Mercel and Dekkar Inc.
Van-Rooyen, J. V., Adrian, J. E., Engelbrecht, A. M.,&Eugene, F. T. (2008). Health benefit of a natural carotenoid rich oil: a proposed mechanism of protection against Ischemia / reperfusion Injury Asia Pacific.Journal of Clinical Nutrition,17, 316-319.
Vitrac, O., Trysram, A. L.,&Raoult-Wack, P. (2000). Deep-fat frying of food: heat and mass transfer, transformations and reactions inside frying medium. European Journal of Lipid Science and Technology, 102, 529-538
Vollhardt, K. P., &Schore, N. E. (2004). Organic Chemistry: structure and function(4thed.). New York: W.H. Freeman and Company.
Wattanapenpaiboon, N., &Wahlqvist, M. L (2003). Phytonutrient deficiency: the place of palm fruit.Asia Pacific journal ofClinicalNutrition,12, (3), 363-368.
Wiege, B., Fehling, E., Matthäus, B., & Schmidt M. (2020). Changes in Physical and Chemical Properties of Thermally and Oxidatively Degraded Sunflower Oil and Palm Fat. Foods, 9, 1273. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9091273
Xin-Fang, L., Jumat, S., Mohd, R. M., & Kamsiah, J. (2012). Effects of repeatedly heated palm olein on blood pressure –regulating enzyme activities and lipid peroxidation in rats. Malaysia Journal of Medical Sciences, 19(1), 20 –29
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Journal of Applied Science and Emerging Technology

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.

