การออกแบบและสร้างรหัสรักษาความปลอดภัยสำหรับกระบวนการตรวจสอบ และยืนยันตัวตนของระบบเก็บค่าผ่านทางพิเศษอัตโนมัติ
Main Article Content
บทคัดย่อ
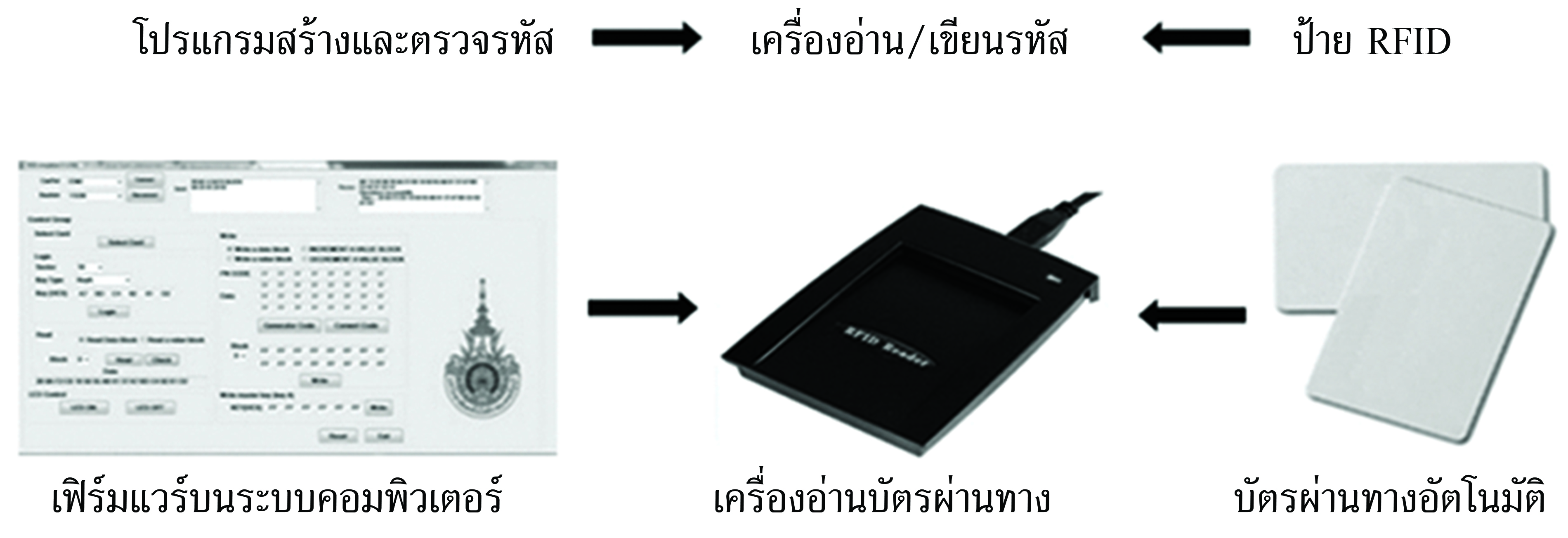
การขับเคลื่อนวิสัยทัศน์ประเทศไทย 4.0 ด้านอุตสาหกรรมการบินและโลจิสติกส์ไปสู่ความสำเร็จจำเป็นต้องใช้เทคโนโลยีที่รวดเร็ว ปลอดภัย และน่าเชื่อถือสูง อาร์เอฟไอดีเป็นเทคโนโลยีสำคัญที่นำมาประยุกต์ใช้ในระบบคมนาคมขนส่งเพื่อตรวจสอบและยืนยันตัวตนของผู้โดยสาร ยานพาหนะ และสินค้า อย่างไรก็ตาม การนำอาร์เอฟไอดีมาประยุกต์ใช้ยังพบปัญหาด้านการรักษาความลับหรือความปลอดภัยของข้อมูลรหัสที่ใช้ตรวจสอบและยืนยันตัวตน บทความวิจัยนี้นำเสนอวิธีการเพิ่มความปลอดภัยในการนำอาร์เอฟไอดี มาประยุกต์ใช้ในระบบเก็บค่าผ่านทางพิเศษอัตโนมัติ โดยการออกแบบและสร้างรหัสรักษาความปลอดภัยที่เรียกว่า Meta_ID และโพรโทคอลยืนยันตัวตนของเครื่องอ่านและป้ายอาร์เอฟไอดี จำลองสถานการณ์ ระบบเก็บค่าผ่านทางพิเศษอัตโนมัติที่ใช้รหัส Meta_ID และโพรโทคอลที่นำเสนอเปรียบเทียบกับระบบดั้งเดิมที่โปรแกรมรหัสลงบนป้ายของผู้ใช้งานแบบตายตัว กรณีมีจำนวนผู้ใช้ป้ายในระบบ 10,000 100,000 และ 1,000,000 ป้าย ผลการจำลองพบว่า ระบบที่นำเสนอมีค่าความน่าจะเป็นของความสำเร็จในการล้วงรหัส ตํ่ากว่าระบบดั้งเดิมทั้ง 3 กรณี จึงสรุปได้ว่าระบบที่นำเสนอมีสมรรถนะด้านการรักษาความลับหรือ ความปลอดภัยดีกว่าระบบดั้งเดิม
Article Details
เอกสารอ้างอิง
[2] Kovinthaweewattana, P., Cheunta, W., Kuankid, S., Baongam, W., and Dinsakul, H. (2009). Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) System. National Science and Technology Development Agency (NSTDA.). (in Thai)
[3] Vaodee, S., Dabbang, P., and Oncheanjit, J. (2010). Anti-Collision Protocol Analysis for Radio Frequency Identification in Logistics Management System. In Proceedings of the Industrial Engineering Network 2010. Ubonratchathani. (in Thai)
[4] Tang Z. (2016). The Design of ETC System Based on RFID and Image Identification. In Proceedings
of the 2016 International Conference on Energy, Power and Electrical Engineering. pp. 236-240. Shenzhen, China. DOI: 10.2991/epee-16.2016.53
[5] Dimitriou, T. (2005). A lightweight RFID Protocol to Protect Against Traceability and Cloning Attacks. In First International Conference on Security and Privacy for Emerging Areas in Communications Networks (SECURECOMM’05). Athens, Greece. pp.59-66. DOI: 10.1109/SECURECOMM.2005.4
[6] Kungpisdan, S. and Metheekul, S. (2009). A Secure Offline Key Generation with Protection Against Key Compromise. In WMSCI 2009: 13th World Multi-Conference on Systemics, Cybernetics and Informatics. 10-13 July 2009, Orlando, Florida. pp. 63-67
[7] Mungmee, S. and Sittichivapak, S. (2009). Development Efficiency of RFID System in Frame ALOHA Communication. Ladkrabang Engineering Journal. Vol. 26, No. 2, pp. 7-12 (in Thai)
[8] Pechto, S. and Kungpisadan, S. (2010). Design and Development of a Lightweight RFID Security Protocol Offering Mutual Authentication. In Proceedings of the 3rd National Conference on Information Technology (NCIT2010). Bangkok. (in Thai)
[9] Lee, Y. K. and Verbauwhede, I. (2005). Secure and Low-Cost RFID Authentication Protocols. Access (4 June 2019). Available (https://www.researchgate.net/publication/250139714_Secure_and_ Low-ost_RFID_Authentication_Protocols)
[10] Khan, G. N. and Moessner, M. B. (2011). Secure Authentication Protocol for RFID Systems. In Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Computer Communications and Networks (ICCCN). Mauri, Hawaii. pp. 379-384
[11] Peng, P. and Zhao, Y. (2012). Anti-Cloning and Secure RFID Mutual Authentication Protocols. In Proceedings of the 4th IEEE Conference on Broadband Network and Multimedia Technology. Shenzhen, China. pp. 379-384
[12] Dabbang, P. (2003). Performance Analysis of Hybrid DS/SFH SSMA in Multi-user and Multi-rate Environment. M. Eng. Dissertation King Mongkut’s University of Technology Ladkrabang.
[13] GS1 EPC global. (2011). Specification for EPC HF RFID Air Interface. Access (4 June 2019). Available (https://www.gs1.org/sites/default/fi les/docs/epc/epcglobal_hf_2_0_3-standard-20110905r3.pdf)