A Machine Learning Approach for Dengue Fever Prediction: Case Study of Phayao Province
Keywords:
Dengue fever, Machine learning, Prediction model, Linear Regression, Deep LearningAbstract
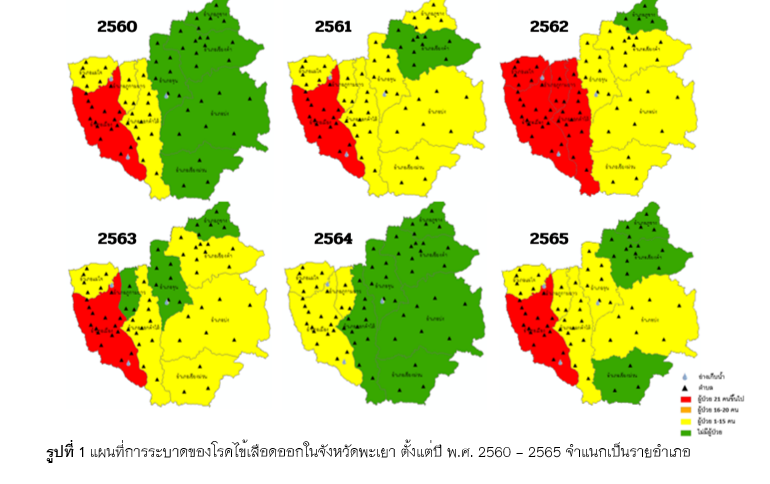
Dengue fever is a serious disease caused by a virus carried by Aedes mosquitoes. It is an important problem of ministries of health in many countries around the world. This research therefore aims to study factors affecting the outbreak of dengue fever and create an effective dengue fever prediction model using machine learning techniques. Data from the Phayao Meteorological Station, including climate, temperature, relative humidity, rainfall, number of rainy days and population data in Phayao Province was collected from the provincial public health database. In addition, the number of dengue fever patients, gender and age group collected from Phayao Hospital between 2017 and 2022 was analyzed and build a model with 10 machine learning techniques. Regression types include Support Vector Machines and Linear Regression. Classification types include Artificial Neural Network, Decision Tree, Naïve Bayes, K-Nearest Neighbors, Deep learning, Random Trees, Gradient Boosting, and Logistic Regression and measure model performance using the 5-Fold Cross Validation method.
All data is created in monthly and weekly datasets. Considering the highest overall accuracy and efficiency. From the performance measurement results of Regression, it was found that Linear Regression provides the best performance with an RMSE of 1.190. From the Classification results, Deep Learning was found to be the most effective model with the highest overall performance, reaching an Accuracy of 99.84%. The results from this research can be used as guidelines for application, especially by various agencies involved in surveillance planning to find areas at risk of spreading and to effectively prevent and control dengue fever.
References
กรมควบคุมโรค. (2560). ความรู้ทั่วไปโรคไข้เลือดออก. นนทบุรี: กระทรวงสาธารณสุข.
กลุ่มโรคติดต่อระหว่างประเทศ กองโรคติดต่อทั่วไป กรมควบคุมโรค. (2563). ไข้เลือดออก (Dengue Fever และ Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever) (ICD 10 A90, A91). พะเยา: กรมควบคุมโรค.
กาญจนา ยังขาว และ กัญญรัตน์ สระแก้ว. (2558). การพยากรณ์โรคไข้เลือดออกโดยใช้ข้อมูล 5 มิติเขตสุขภาพที่ 9. วารสารควบคุมโรค, 41(3), 208 - 218.
กอบเกียรติ สระอุบล. (2563). เรียนรู้ Data Science และ AI: Machine Learning ด้วย Python. กรุงเทพฯ: หสม มีเดีย เนทเวิร์ค.
จิรโรจน์ ตอสะสุกุล. (2564). แบบจำลองการพยากรณ์ของการระบาดโรคไข้เลือดออกโดยใช้เทคนิคการทำเหมือง ข้อมูล. วารสารวิชาการซายน์เทค มรภ.ภูเก็ต, 5(2), 51 - 60.
ชาญชัยณรงค์ ทรงคาศรี. (2555). รูปแบบการพยากรณ์โรคไข้เลือดออกในพื้นที่สำนักงานป้องกันควบคุมโรคที่ 6จังหวัดขอนแก่น พ.ศ. 2555. วารสารวิชาการสำนักป้องกันควบคุมโรคที่ 7 ขอนแก่น, 20(1), 65 - 81.
สำนักงานสาธารณสุขจังหวัดพะเยา. (2566). บทสรุปผู้บริหาร สถานการณ์โรคไข้เลือดออก จังหวัดพะเยา (ฉบับที่ 1 ปี 2566). พะเยา.
สำนักโรคติดต่อนำโดยแมลง สำนักระบาดวิทยา. (2560). รายงานพยากรณ์โรค “ไข้เลือดออก” ปี 2560 (ฉบับที่ 1 ปี 2560). พะเยา.
สายชล สินสมบูรณ์ทอง. (2560). การทำเหมืองข้อมูล เล่ม 1: การค้นหาความรู้จากข้อมูล. กรุงเทพฯ: บริษัทจามจุรีโปรดักส์ จำกัด.
สุรศักดิ์ สุขสาย. (2550). การพยากรณ์พื้นที่เสี่ยงต่อการเกิดโรคไข้เลือดออกเพื่อการวางแผนเฝ้าระวังและป้องกันในจังหวัดอุบลราชธานี. วารสารวิจัย มข. (บศ.), 7(2), 83-96. สืบค้นจาก https://aigencorp.com/what-is-machine-learning-technology.
Chaw, J. K., Chaw, S. H., Quah, C. H., Sahrani, S., Ang, M. C., Zhao, Y., & Ting, T. T. (2023). A predictive analytics model using machine learning algorithms to estimate the risk of shock development among dengue patients, Healthcare Analytics, 5, 2-7.
Majeed, M. A., Shafri, H. Z. M., Zulkafli, Z., & Wayayok, A. (2023). A Deep Learning Approach for Dengue Fever Prediction in Malaysia Using LSTM with Spatial Attention. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 20(5), 2-4. Form: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10002017/.
Mehta, A. M., & Patel, K. S. (2023), LSTM-based Forecasting of Dengue Cases in Gujarat: A Machine Learning Approach, Indian Journal of Science and Technology, 17(7), 635 - 642. Form: https://indjst.org/articles/lstm-based-forecasting-of-dengue-cases-in-gujarat-a-machine-learning-approach.
Mierswa, I., & Klinkenberg, R. (2018). RapidMiner Studio (9.1) [Data science, machine learning, predictive analytics]. Form: https://rapidminer.com/.
Ninenox Developer. (2020). Understand accuracy, precision, recall, f1-score. Form: https://www.ninenox.com/2020/09/24/-accuracyprecisionrecallf1-score/.
Satangmongkol, K.. (2019). Explaining K-Fold Cross Validation with sample code in R. Form: https://datarockie-com.translate.goog/blog/k-fold-cross-validation/comment-page-.
Sebastianelli, A., Spiller, D., Carmo, R., Wheeler, J., Nowakowski, A., Jacobson, V. A., Kim, D., Barlevi, H., Cordero, Z. E. R., Colón-González, F. J., Lowe, R., Ullo, S. L., & Schneider, R. (2024). A reproducible ensemble machine learning approach to forecast dengue outbreaks. Scientific Reports, 14(3807). Form: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-024-52796-9.
Tian, N., Zheng, J. X., Li, L. H., Xue, J. B., Xia, S., Lv, S., & Zhou, X. N. (2024). Precision Prediction for Dengue Fever in Singapore: A Machine Learning Approach Incorporating Meteorological Data. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease, 4(9), 5-7. Form: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38668533/.