Assessment of Wildfire Risk Zonation using Analytical Hierarchical Process in Phayao Province
Keywords:
Wildfire, Geographic Information System, Analytical Hierarchical Process, Phayao provinceAbstract
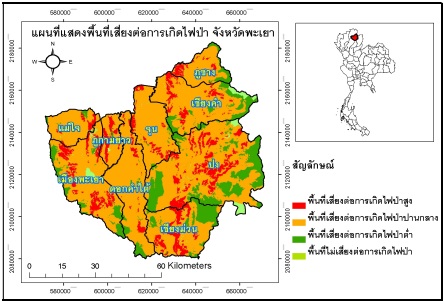
The northern region has more forest fires than every region. The average forest fire rate is about 1,167 times per year. Phayao has a hot climate. This makes the forest conditions drought and easy to cause wildfires. February to April, in particular, are the months most vulnerable to forest fires. The main objectives of this research study were to assess the areas prone to forest fires in Phayao Province. The methodology used an expert interview form to give weight scores for 8 relevant factors, namely land use, forest type, distance from transportation routes. Distance from the waterway distance from village location distance from agricultural land, slope and elevation and analyzed with an analytical hierarchical process model. The risk levels are divided into 4 levels, which are high, medium, low and not at risk of forest fires. The study found that 4,553.11 sq.km. or 71.87% of the area at moderate forest fire risk, 939.64 sq.km. or 14.83% of the low-level forest fire risk area. High-level forest fires amounted to 796.25 sq.km., representing 12.57%, and the area not prone to forest fires was 46.21 sq.km., representing 0.73%. The district with the highest forest fire risk was Phu Kam Yao, followed by Chiang Muan. Therefore, relevant agencies or disaster prevention and mitigation officials can use the results of the study as a guideline for future forest fires.
References
Rotjanakusol, T. & Laosuwan, T. (2018). Inundation area investigation approach using remote sensing technology on 2017 flooding in Sakon Nakhon province Thailand”. Studia Universitatis Vasile Goldis Arad, Seria Stiintele Vietii, 28(4), 159-166.
Milly, P.C., Wetherald, R.T., Dunne, K.A., & Delworth, T.L. (2002). Increasing Risk of Great Floods in a Changing Climate. Nature. 15(6871), 514-517.
ไพศาล จี้ฟู (2561). การพัฒนาโปรแกรมประยุกต์สำหรับระบบสารสนเทศภูมิศาสตร์บนเว็บ (Application Development for Web-based GIS), พิมพ์ครั้งที่ 1 จำนวน 500 เล่ม, สำนักพิมพ์จุฬาลงกรณ์มหาวิทยาลัย, ISBN : 9789740337508.
สัญญา สราภิรมย์. (2549). เอกสารประกอบการสอนวิชาระบบสารสนเทศภูมิศาสตร์ (106611). นครราชสีมา: สาขาการรับรู้ระยะไกล สำนักวิชาวิทยาศาสตร์ มหาวิทยาลัยเทคโนโลยีสุรนารี
จรรยา บุญสอน. (2560). การวิเคราะห์พื้นที่เสี่ยงน้ำท่วมฉับพลัน : กรณีศึกษาห้วยแม่ท่าแพ อ.ศรีสัชนาลัย จ.สุโขทัย. วิทยานิพนธ์ระดับปริญญาตรี ภาควิชาทรัพยากรธรรมชาติและสิ่งแวดล้อม คณะเกษตรศาสตร์ ทรัพยากรธรรมชาติและสิ่งแวดล้อม มหาวิทยาลัยนเรศวร.
Fundamental Geographic Data Set (FGDS). (2556). Retrieved from www.ngis.go.th/home/wp-content/uploads/2019/03/FundamentalGeographicDataSet_FGDS.pdf (in Thai)
Saaty, T.L. (1980). The analytical hierarchy process”, New York: McGraw-Hill.
Pawattana, C., and Tripathi, N.K. (2008). Analytical Hierarchy Process (AHP) – Based Flood Water Retention Planning in Thailand. GIScience and Remote Sensing, 45, 343-355.
Tseng, C.C., Hong, C.F., and Chamg, H.L. (2008). Multiple Attribute Decision-Making Model for Medical Service Selection: an AHP approach. Journal of Quality, 15, 155-165.
Jeefoo, P., and Tripathi, N.K. (2011). Dengue Risk Zone Index (DRZI) for Mapping Dengue Risk Areas. International Journal of Geoinformatics, 7(1), 53-62.
Thirumalaivasan, D., Karmegam, M., and Venugopal, K. (2003). AHP-DRASTIC: Software for Specific Aquifer Vulnerability Assessment using DRASTIC model and GIS. Environmental Modelling and Software. 18, 645-656.