Effect of warm deformation parameters on hardness and microstructure of AISI 1020 low carbon steel for near-net shape forging
Main Article Content
Abstract
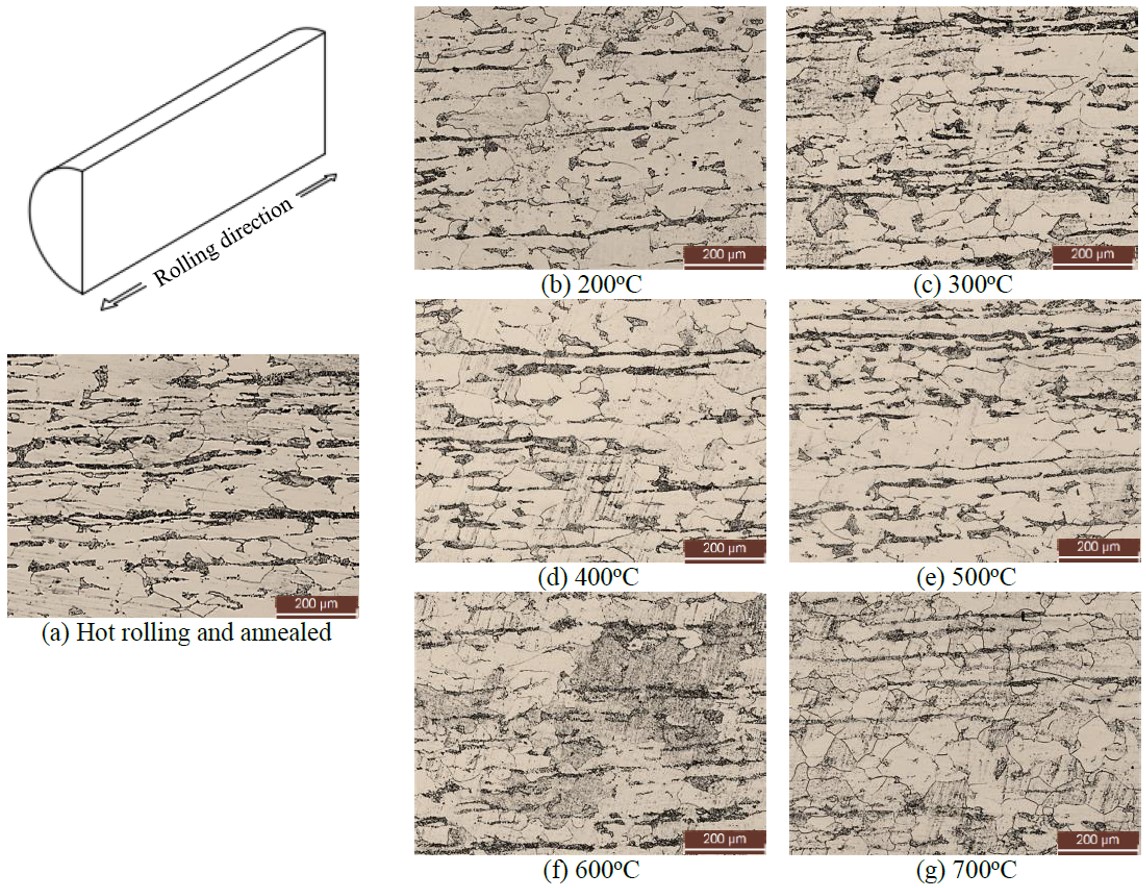
This research aims to present a concept for altering a metal manufacturing process from cold to warm forging thereby reducing unnecessary steps and energy consumption. This will lower costs and increase production profits. The study explores the impact of warm forging process parameters on the hardness and microstructure of low-carbon steel for near-net-shape forging in more than two continuous stages. The material used in this experiment is annealed AISI 1020 carbon steel with chemical additions of 0.01% Ni, 0.03% Cr, and 0.044% Al. The study procedure involves: (i) heating slugs with a height-to-diameter ratio (ho/do) of 2.07 to a temperature range of 200–700 and soaking them for 1 hour. The grain size noticeably increases at temperatures above 500 °C. (ii) The materials were forged at six different temperatures from 200 to 700 with both hardness and microstructure examined at each stage. This was done to determine the recrystallization temperature. The experimental results showed that recrystallization begins at 500 in a warm forging process and becomes more pronounced at 600 to 700 °C. The lowest average hardness value in the transverse direction (TD) occurs at 500 to 700 °C. This suggests that the suitable warm working temperature range should be below 500 °C, as the primary microstructure in the forging process has not yet undergone recrystallization. Our research provides valuable insights for manufacturers aiming to transition from cold to warm forging, emphasizing the importance of precise control over deformation parameters to achieve desired material properties.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
References
Tschaetsch H. Metal forming practise: processes, machines, tools. Berlin: Springer; 2006.
Altan T, Ngaile G, Shen G. Cold and hot forging: fundamentals and applications. Ohio: ASM international; 2004.
AIDA Engineering. AIDA press handbook. 4th ed. Japan: AIDA Engineering Ltd; 2007.
Hirscvogel M, Dommelen HV. Some applications of cold and warm forging. J Mater Process Technol. 1992;35(3-4):343-56.
Islam T, Rashed HMMA. Classification and application of plain carbon steels. Reference module in materials science and materials engineering. Amsterdam: Elsevier. 2019.
Reddy PPK, Dewangan S, Singh RS, Singhal U, Biswas A. Heat treatment effects on microstructure and hardness of low-carbon AISI 1020 steel. J Inst Eng India: Ser D. 2024:1-12.
Sun J, Li J, Wang P, Huang Z. Hot deformation behavior, dynamic recrystallization and processing map of Fe–30Mn–10Al–1C low-density steel. Trans Indian Inst Met. 2022;75:699-716.
Qiu P, Han Y, Huang G, Le J, Lei L, Xiao L, et al. Texture evolution and dynamic recrystallization behavior of hybrid-reinforced titanium matrix composites: enhanced strength and ductility. Metall Mater Trans A. 2020;51(5):2276-90.
Dehghan-Manshadi A, Barnett MR, Hodgson PD. Microstructural evolution during hot deformation of duplex stainless steel. Mater Sci Technol. 2007;23(12):1478-84.
Zhao Q, Li F, Zhu E, Gopi KR, Farah S, An X, et al. Investigation on the grain structure evolution and abnormal stress increase of Al–Mg–Si alloy during hot deformation. Met Mater Int. 2024;30(4):967-89.
Su G, Liu Y, Xiao X, Du J, Zhang P, Shen X. Influences of stress state, temperature, and strain rate on ductility of pure iron. J Mater Eng Perform. 2021;30:2036-46.
Chamanfar A, Chentouf SM, Jahazi M, Lapierre-Boire LP. Austenite grain growth and hot deformation behavior in a medium carbon low alloy steel. J Mater Res Technol. 2020;9(6):12102-14.
Hamada AS, Somani MC, Karjalainen LP. High temperature flow stress and recrystallization behavior of high-Mn TWIP steels. ISIJ Int. 2007;47(6):907-12.
Edalati K, Wang Q, Enikeev NA, Peters LJ, Zehetbauer MJ, Schafler E. Significance of strain rate in severe plastic deformation on steady-state microstructure and strength. Mater Sci Eng A. 2022;859:144231.
Ferro P, Bonollo F, Bassan, F, Berto F. Strain evolution in cold-warm forged steel components studied by means of EBSD technique. Materials. 2017;10(12):1441.
Zhao F, Hu H, Liu X, Zhang Z, Xie J. Effect of billet microstructure and deformation on austenite grain growth in forging heating of a medium-carbon microalloyed steel. J Alloys Compd. 2021;869:159326.
Nasiri Z, Ghaemifar S, Naghizadeh M, Mirzadeh H. Thermal mechanisms of grain refinement in steels: a review. Met Mater Int. 2021;27:2078-94.
Dolzhenko A, Tikhonova M, Kaibyshev R, Belyakov A. Microstructures and mechanical properties of steels and alloys subjected to large-strain cold-to-warm deformation. Metals. 2022;12(3):454.
Kim KM, Kang CG. Forgebility evaluation of SNCM 220 steel by warm compression test and microstructure behaviors characteristics. Int J Precis Eng Manuf-Green Technol. 2016;3:105-10.
Huang W, Lei L, Fang G. Microstructure evolution of hot work tool steel 5CrNiMoV throughout heating, deformation and quenching. Mater Charact. 2020;163:110307.
Yan X, Zhang S, Huang K, Yang Y, Wang W, Wu M. Effect of holding time on the extrusion force and microstructure evolution during the plastic forming of Ti-6Al-4V micro-gears. Materials. 2020;15(4):1507.
Wang H, Cao L, Li Y, Schneider M, Detemple E, Eggeler G. Effect of cooling rate on the microstructure and mechanical properties of a low-carbon low-alloyed steel. J Mater Sci. 2021;56:11098-113.
Sugimoto KI, Hojo T, Srivastava AK. Low and medium carbon advanced high-strength forging steels for automotive applications. Metals. 2019;9(12):1263.
Çalik A. Effect of cooling rate on hardness and microstructure of AISI 1020, AISI 1040 and AISI 1060 Steels. Int J Phys Sci. 2009;4(9):514-8.
Abbaschian R, Abbaschian L, Reed-Hill RE. Physical metallurgy principles. 4th ed. Stamford: Cengage Learning; 2009.
Jhonthong N, Talangkun S. Design of the semi-closed die for shaping the thick coin-like carbon steel parts in a single operation. SN Appl Sci. 2023;5(7):176.
Callister WD, Rethwisch DG. Materials science and engineering: an introduction. 10th ed. Hoboken: Wiley; 2018.
Wang S, Chen M, Yang M, Huang Y, Wang S, Mao X. Effect of cold rolling reduction rate on the microstructure and properties of Q&P steel with a ferrite-pearlite initial structure. Materials. 2023;16(18): 6102.
Lei J, Ma L, Jia W, Le Q, Pan H, Yuan Y. Zonal differences in deformation characteristics of AZ31 Mg alloy constrained by heterogeneous metals. J Mater Res Technol. 2021;13:2161-79.
Dalbosco M, da Silva Lopes G, Schmitt PD, Pinotti L, Boing D. Improving fatigue life of cold forging dies by finite element analysis: a case study. J Manuf Process. 2021;64:349-55.
Narayanan RG, Gopal M, Rajadurai A. Infuence of friction in simple upsetting and prediction of hardness distribution in a cold forged product. J Test Eval. 2008;36(4):371-83.
Lee Y, Yoon E, Nho T, Moon Y. Microstructure control of ferrous driven part fabricated by warm precision forging. Procedia Manuf. 2018;15:404-10.