In-Vessel bioconversion of garden waste into compost with an emphasis on process efficiency and compost quality
Main Article Content
Abstract
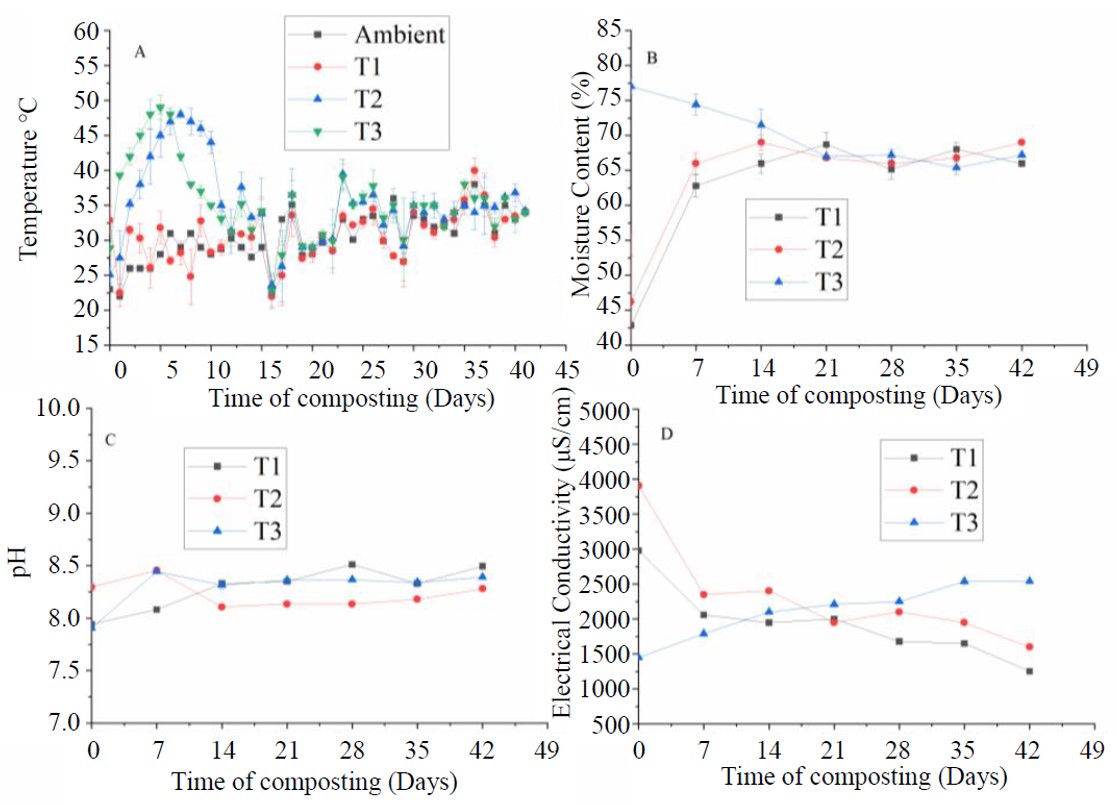
With the fast-growing urbanization efficient management of garden waste, whether at residential or social levels, has now become a challenge and an opportunity to enhance soil quality. Three different trials T1, T2, and T3 were executed constituting different forms of garden waste like un-shredded, shredded and shredded dry leaves with additives with varying processing conditions carried for 42 days using cylindrical In-vessel composters made up of HDPE. The composting process is scrutinized regularly at fixed intervals for all parameters like temperature, moisture, pH, electrical conductivity, germination index, C/N, micro & macronutrients etc. The temperature reached thermophilic in two trials T2 and T3. The pH reached the basic range of 8-8.5 in the final compost of all trials. The moisture was maintained up to 65% throughout the composting period. The trial 3 was the best combination among all the trials in which the variation of pH was (7.7-8.5), total organic carbon (42.2-35.6), total nitrogen (0.7-1.4), C: N ratio (60.3-25.4), cellulose (43.4-4.2), hemicellulose (10.2-0.9) and lignin (13.1-0.15) at the end of 42 days. The degradation rate of Un-shredded leaves was found to be very slow due large size of dry leaves. The findings highlighted that effective garden waste management is possible by following particular guidelines and it reduces the environmental impact of current disposal techniques and in addition, improves soil health using garden waste compost.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
References
Mishra SK, Yadav KD. Application of locally available microbial inoculant to accelerate green waste composting at a community level. Bioresour Technol Rep. 2021;16:100859.
Teshome ZT. Effects of banana peel compost rates on Swiss chard growth performance and yield in Shirka district, Oromia, Ethiopia. Heliyon. 2022;8(8):e10097.
Yang W, Zhang L. Addition of mature compost improves the composting of green waste. Bioresour Technol. 2022;350:126927.
Adhikari BK, Barrington S, Martinez J, King S. Effectiveness of three bulking agents for food waste composting. Waste Manag. 2009;29(1):197-203.
Oazana S, Varma VS, Saadi I, Sharma D, Hanan A, Medina S, et al. High-rate stabilization and associated air emissions prospected during on-site in-vessel sewage sludge composting. Bioresour Technol Rep. 2020;11:100543.
Sharma D, Saadi I, Oazana S, Lati R, Laor Y. Distribution of residence time in rotary-drum composting and implications for hygienization. Waste Manag. 2024;179:22-31.
Guo R, Li G, Jiang T, Schuchardt F, Chen T, Zhao Y, et al. Effect of aeration rate, C/N ratio and moisture content on the stability and maturity of compost. Bioresour Technol. 2012;112:171-8.
FAI Abstract May 2007. Carbon Dioxide Recovery (Cdr) From Flue Gases [Internet]. 2007 [Cited 2024 Aug 21]. Available from: https://www.faidelhi.org/Member/Monthly%20Abstract%20service/abst-may-07.pdf.
US Composting Council. Test Methods for the Examination of Compost and Composting (TMECC) [Internet]. 2024 [Cited 2024 Aug 21]. Available from: https://www.compostingcouncil.org/store/ViewProduct.aspx?id=13656204.
Bernal MP, Alburquerque JA, Moral R. Composting of animal manures and chemical criteria for compost maturity assessment. A review. Bioresour Technol. 2009;100(22):5444-53.
Sharma D, Prasad R, Patel B, Parashar CK. Biotransformation of sludges from dairy and sugarcane industries through vermicomposting using the epigeic earthworm Eisenia fetida. Int J Recycl Org Waste Agricult. 2022;11(2):165-75.
Nema A, Bin Zacharia KM, Kumar A, Singh E, Varma VS, Sharma D. Challenges and opportunities associated with municipal solid waste management. In: Kumar S, Kumar R, Pandey A, editors. Current Developments in Biotechnology and Bioengineering. Amsterdam: Elsevier; 2021. p. 231-58.
Yadav KD, Sharma D, Prasad R. Challenges and opportunities for disposal of floral waste in developing countries by using composting method. In: Hussain C, Hait S, editors. Advanced Organic Waste Management. Amsterdam: Elsevier; 2022. p. 55-77.
Yao X, Wang X, Zheng S, Zhao H, Ju J, Wang C. Research on composting of garden waste and its application in cultivation substrates. Sustainability. 2024;16(18):8216.
Reyes-Torres M, Oviedo-Ocaña ER, Dominguez I, Komilis D, Sánchez A. A systematic review on the composting of green waste: feedstock quality and optimization strategies. Waste Manag. 2018;77:486-99.