Efficient Oxidation of Methylene Blue via Catalytic Activation of Peroxymonosulfate via an Engineered δ-FeOOH/Pili Nutshell Biochar Composite
Main Article Content
Abstract
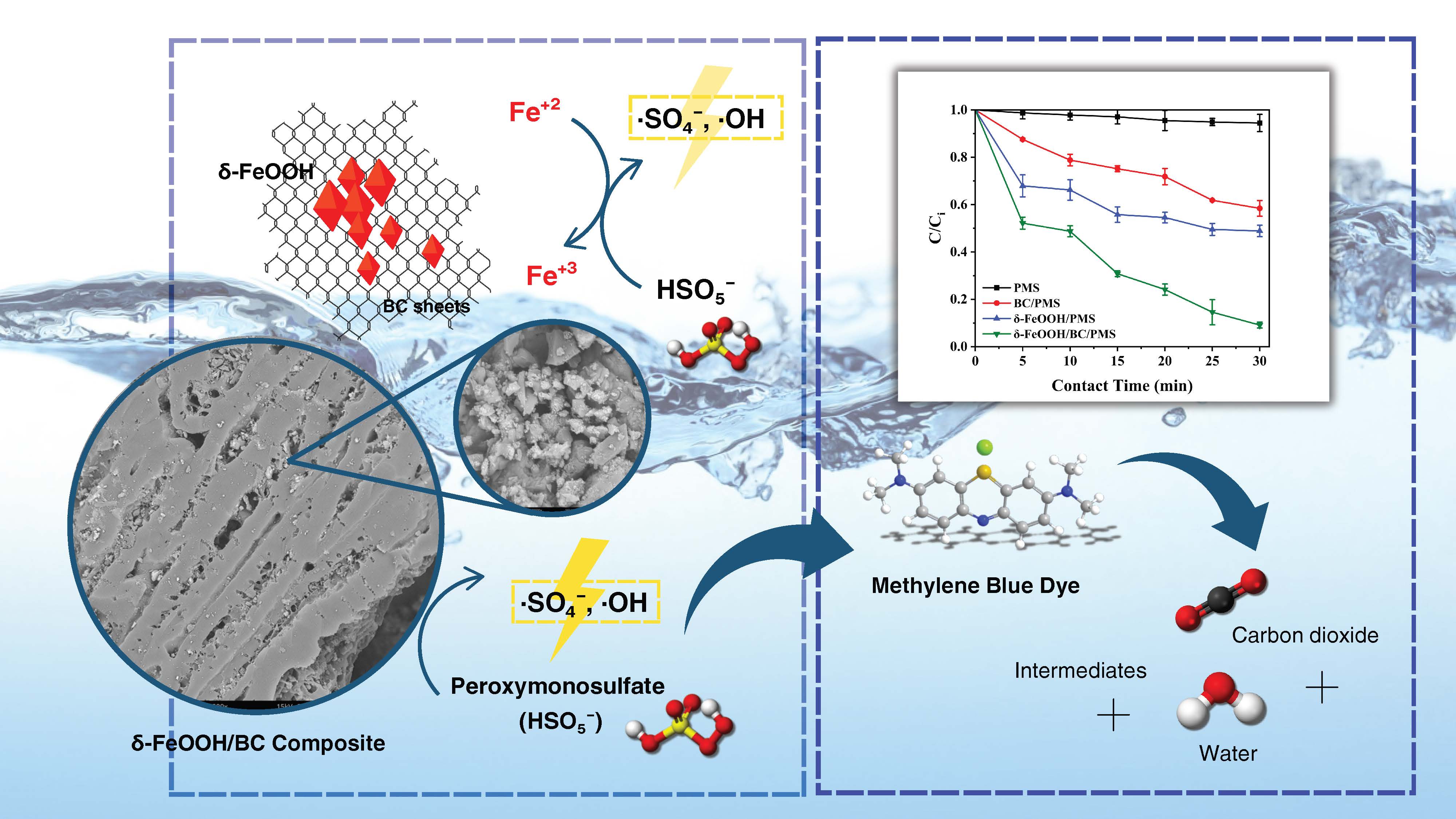
This study introduces a novel composite catalyst formed by anchoring delta iron oxyhydroxide (δ-FeOOH) onto pyrolyzed Pili nutshell biochar via a room-temperature coprecipitation technique, marking the first application of Pili nutshell waste in advanced oxidation processes for wastewater treatment. This innovative methodology enhances catalyst dispersion and stability, facilitating the activation of peroxymonosulfate (PMS) to generate reactive sulfate radicals (SO4•–) for the degradation of methylene blue (MB), a thiazine dye commonly used in the medical field and the dye industry. Different techniques have been used to characterize synthesized composites in terms of their morphology, elemental composition, surface functional groups, and crystalline phase structure. The system achieved a maximum MB degradation efficiency of 90.88% within 30 min at pH 6.0 when low dosages of PMS and the δ-FeOOH/biochar composite were used, following pseudo-first-order degradation kinetics. Radical scavenging experiments confirmed that SO4•– radicals were primarily responsible for the degradation process. Notably, the composite maintained over 70% removal efficiency after four reuse cycles, indicating its potential for sustainable and cost-effective wastewater treatment. This research highlights the effectiveness of the δ-FeOOH/biochar/PMS system as a promising solution for treating MB-laden wastewater, contributing to environmental sustainability and waste valorization.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Published articles are under the copyright of the Applied Environmental Research effective when the article is accepted for publication thus granting Applied Environmental Research all rights for the work so that both parties may be protected from the consequences of unauthorized use. Partially or totally publication of an article elsewhere is possible only after the consent from the editors.
References
Cwalinski, T., et al., Methylene blue—current knowledge, fluorescent properties, and its future use. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 2020. 9(11): p. 3538.
Li, X., et al., Application of sulfate radicals-based advanced oxidation technology in degradation of trace organic contaminants (TrOCs): Recent advances and prospects. Journal of Environmental Management, 2022. 308: p. 114664.
Fan, J., et al., Synthesis of different crystallographic FeOOH catalysts for peroxymonosulfate activation towards organic matter degradation. RSC advances, 2018. 8(13): p. 7269-7279.
Gęca, M., M. Wiśniewska, and P. Nowicki, Biochars and activated carbons as adsorbents of inorganic and organic compounds from multicomponent systems–A review. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 2022: p. 102687.
Lirag, B., et al., Demographic Evaluation of Pili Farmers and Their Production Capacity in Bicol Region, Philippines. Asian Journal of Agricultural Extension, Economics & Sociology, 2023. 41(1): p. 15-25.
Threepanich, A. and P. Praipipat, Powdered and beaded lemon peels-doped iron (III) oxide-hydroxide materials for lead removal applications: Synthesis, characterizations, and lead adsorption studies. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2021. 9(5): p. 106007.
Mei, L., et al., Interactions between phosphoric/tannic acid and different forms of FeOOH. Advances in Materials Science and Engineering, 2015. 2015.
Nasrazadani, S. and S. Hassani, Modern analytical techniques in failure analysis of aerospace, chemical, and oil and gas industries. Handbook of materials failure analysis with case studies from the oil and gas industry, 2016: p. 39-54.
Zeng, B., et al., Preparation of sludge biochar rich in carboxyl/hydroxyl groups by quenching process and its excellent adsorption performance for Cr (VI). Chemosphere, 2021. 285: p. 131439.
Yang, F., et al., Corn straw-derived biochar impregnated with α-FeOOH nanorods for highly effective copper removal. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2018. 348: p. 191-201.
Saleh, M.E., A.H. Mahmoud, and M. Rashad. Biochar usage as a cost-effective bio-sorbent for removing NH4-N from wastewater. in The international conference the Global Climate Change, Biodiversity and Sustainability: Challenges and Opportunities in Arab MENA region and EuroMed. 2013.
Zhang, L., et al., Promote the electrocatalysis activity of amorphous FeOOH to oxygen evolution reaction by coupling with ZnO nanorod array. Journal of Solid State Electrochemistry, 2020. 24(4): p. 905-914.
Xiao, R., et al., Activation of peroxymonosulfate/persulfate by nanomaterials for sulfate radical-based advanced oxidation technologies. Current opinion in chemical engineering, 2018. 19: p. 51-58.
Xu, L., et al., Peroxymonosulfate activation by nitrogen-doped biochar from sawdust for the efficient degradation of organic pollutants. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020. 387: p. 124065.
Zhang, C., et al., Degradation of tetracycline by activated peroxodisulfate using CuFe2O4-loaded biochar. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2022. 368: p. 120622.
Jiang, S.-F., et al., High efficient removal of bisphenol A in a peroxymonosulfate/iron functionalized biochar system: mechanistic elucidation and quantification of the contributors. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019. 359: p. 572-583.
Devi, L.G., M. Srinivas, and M. ArunaKumari, Heterogeneous advanced photo-Fenton process using peroxymonosulfate and peroxydisulfate in presence of zero valent metallic iron: A comparative study with hydrogen peroxide photo-Fenton process. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 2016. 13: p. 117-126.
Crincoli, K.R., C. Green, and S.G. Huling, Sulfate radical scavenging by mineral surfaces in persulfate-driven oxidation systems: reaction rate constants and implications. Environmental science & technology, 2020. 54(3): p. 1955-1962.
Huang, W., et al., nZVI-biochar derived from Fe3O4-loaded rabbit manure for activation of peroxymonosulfate to degrade sulfamethoxazole. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 2022. 45: p. 102470.
Lei, Y., et al., Assessing the use of probes and quenchers for understanding the reactive species in advanced oxidation processes. Environmental Science & Technology, 2023. 57(13): p. 5433-5444.