Use of Modified Blast Furnace Slag for Cadmium Removal in An Aqueous Medium
Main Article Content
Abstract
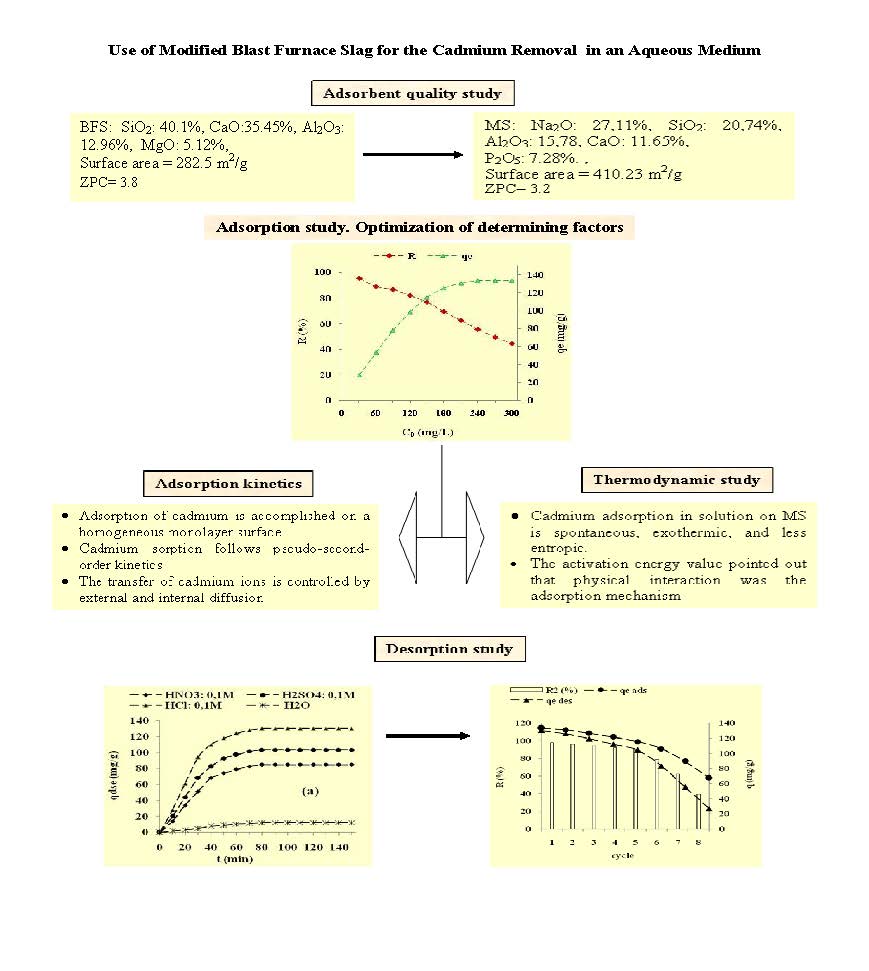
In this work, blast furnace slag was converted to hydroxyapatite-zeolite (MS) through alkaline fusion and hydrothermal treatment, and then it was used to remove cadmium in solution by adsorption in batch mode. The process was accomplished under the influence of determining parameters, namely the contact time, mass of the adsorbent, stirring speed, pH of the medium, temperature of the solution, particle size of the slag, and initial concentration. MS consists mainly of sodium oxide, silica, alumina, lime, and phosphorus pentoxide. The Ca/P, Na/Al, and Si/Al ratios revealed that the converted slag is a hydroxyapatite-zeolite. Following the modification of the treated slag, the specific surface area increased from 282.5 to 410.23 m² g-1. Its zero charge point was detected at pH 3.2. After 50 min, the test results revealed that equilibrium was established. Furthermore, they demonstrated that the adsorption capacity was maximum (133.34 mg) at a pH of 6, at a temperature of 25 °C, at a stirring speed of 200 rpm, at a solid mass of 1g, at a particle size of 300 µm, and at an initial concentration of 240 mg L-1. Exploration of the adsorption isotherms revealed that the Langmuir model better presented the adsorption process, thus revealing that the adsorption occurred on a monolayer surface. The parameters of the examined models, namely RL and n, affirmed that the adsorption is favorable. The kinetic study revealed that this process agreed more with the pseudo-second-order kinetic model, and the transport of pollutant is ensured by external and intraparticle diffusion. Thermodynamic analysis has shown that this process is spontaneous, exothermic, less entropic, and performed under physical interactions. The desorption process revealed that the reuse of MS is possible over five cycles with hydrochloric acid as an eluent. This study opens up advantageous perspectives for the sorption of cadmium from water.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Published articles are under the copyright of the Applied Environmental Research effective when the article is accepted for publication thus granting Applied Environmental Research all rights for the work so that both parties may be protected from the consequences of unauthorized use. Partially or totally publication of an article elsewhere is possible only after the consent from the editors.