An Optimal Culture Medium for Laccase Production and Sugar Cane Vinasse Biotreatment with Trametes villosa Using Plackett-Burman and Central Composite Designs
Main Article Content
Abstract
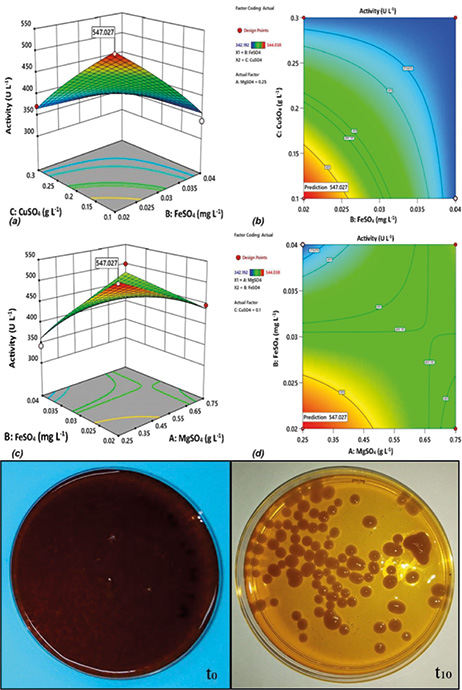
The optimal conditions for laccase production and vinasse biotreatment with a native strain of Trametes villosa were determined by a screening-optimization approach. Eleven factors including nutrient concentration, vinasse dilution (%v/v), inoculum volume, carbon to nitrogen ratio and initial pH, were investigated for their effects on laccase activity applying the Plackett-Burman screening design. The selected factors were optimized using a central composite design, and then evaluated on a vinasse biotreatment experiment. The factors that contributed the most to the enzymatic activity were the concentrations of MgSO4∙7H2O (A), FeSO4∙7H2O (B) and CuSO4∙5H2O (C), alongside initial pH. After 10 days, laccase activity was 544.038 U L-1 for the following concentrations of A, B and C: 0.250 g L-1, 0.020 mg L-1, and 0.100 g L-1, respectively. Vinasse biotreatment under optimized conditions resulted in 82.74%, 78% and 75.97% of phenol, color, and COD removal respectively, while final pH value was 6.90. These results showed that the native strain of T. villosa has a good potential for further research on laccase production and vinasse sustainable management.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Published articles are under the copyright of the Applied Environmental Research effective when the article is accepted for publication thus granting Applied Environmental Research all rights for the work so that both parties may be protected from the consequences of unauthorized use. Partially or totally publication of an article elsewhere is possible only after the consent from the editors.