Groundwater Potential Mapping at Highly Populated Sub-districts of Thimphu District Using Fuzzy Analytic Hierarchy Process
Main Article Content
Abstract
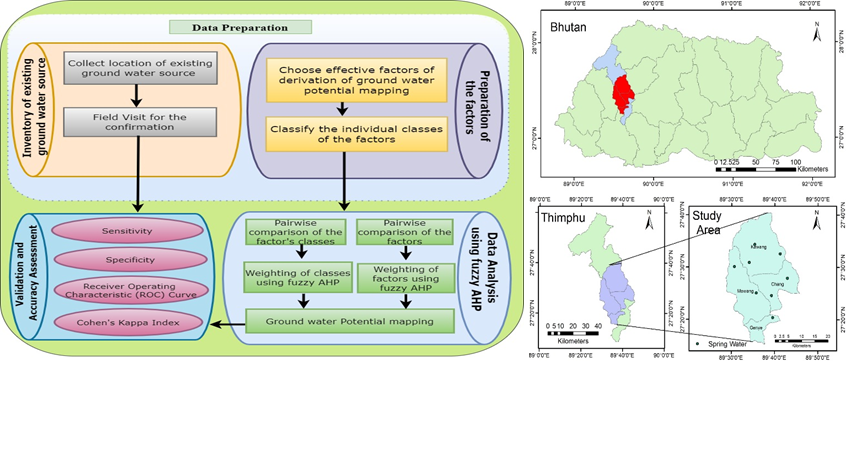
Groundwater is important when there is an insufficient spring water supply for daily needs. The population growth and expansion of the cities demand more water. Thimphu is the capital city of Bhutan and facing water shortage in recent times due to urban expansion and population growth. This study aims to find the potential area for groundwater using the Fuzzy Analytic Hierarchy Process. The factors used for this study are elevation, slope, curvature, topographic wetness index, drainage density, normalized difference vegetation index, distance from fault density, rainfall distribution map, soil texture map, and drainage density. The rating for the factors and classes of the factors were carried out with the help of field experts. As per the fuzzy weight, the highest contributing factor for the groundwater is rainfall with a fuzzy weight of 0.215. Only 1.19% of the study area falls under very high potential zone for groundwater and the area under the curve of the groundwater potential map is 70.37%. The groundwater potential map will help concerned officials to explore the subsurface groundwater using geophysical investigation using test drilling and borehole geophysical logging techniques.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Published articles are under the copyright of the Applied Environmental Research effective when the article is accepted for publication thus granting Applied Environmental Research all rights for the work so that both parties may be protected from the consequences of unauthorized use. Partially or totally publication of an article elsewhere is possible only after the consent from the editors.
References
Park, S., Hamm, S.-Y., Jeon, H.-T., Kim, J. Evaluation of logistic regression and multivariate adaptive regression spline models for groundwater potential mapping using R and GIS. Sustainability, 2017, 9(7), 1157.
Razavi-Termeh, S. V., Sadeghi-Niaraki, A., Choi, S.-M. Groundwater potential mapping using an integrated ensemble of three bivariate statistical models with random forest and logistic model tree models. Water, 2019, 11(8), 1596.
Arulbalaji, P., Padmalal, D., Sreelash, K. GIS and AHP techniques based delineation of groundwater potential zones: a case study from southern Western Ghats, India. Scientific reports, 2019, 9(1), 1-17.
Shano, L., Raghuvanshi, T. K., Meten, M. Landslide susceptibility evaluation and hazard zonation techniques–a review. Geoenvironmental Disasters, 2020, 7, 1-19.
NEC. (2007). Bhutan Water Policy. Thimphu, Bhutan National Environment Commission.
Suganthi, S., Elango, L., Subramanian, S. Groundwater potential zonation by Remote Sensing and GIS techniques and its relation to the Groundwater level in the Coastal part of the Arani and Koratalai River Basin, Southern India. Earth Sciences Research Journal, 2013, 17(2), 87-95.
WHO. (2015). UN-Water global analysis and assessment of sanitation and drinking-water (GLAAS) 2015 report: Sanitation, drinking-water and hygiene status overview.
NSB. (2018). Rural-urban migration and urbanization in Bhutan. Thimphu, Bhutan: National Statistics Bureau of Bhutan.
NSB. (2020). Statistical Yearbook of Bhutan 2020. Thimphu, Bhutan National Statistical Bureau.
Chaudhry, A. K., Kumar, K., Alam, M. A. Mapping of groundwater potential zones using the fuzzy analytic hierarchy process and geospatial technique. Geocarto International, 2019, 1-22.
Chang, D.-Y. Extent analysis and synthetic decision. Optimization techniques and applications, 1992, 1(1), 352-355.
Ghezelsofloo, A. A., Hajibigloo, M. Application of Flood Hazard Potential Zoning by using AHP Algorithm. Civil Eng Res J 2020, 9(5). doi:10.19080/CERJ.2020.09.555775
Adeyeye, O. A., Ikpokonte, E. A., Arabi, S. A. GIS-based groundwater potential mapping within Dengi area, North Central Nigeria. The Egyptian Journal of Remote Sensing and Space Science, 2019, 22(2), 175-181.
Cao, C., Xu, P., Wang, Y., Chen, J., Zheng, L., Niu, C. Flash flood hazard susceptibility mapping using frequency ratio and statistical index methods in coalmine subsidence areas. Sustainability, 2016, 8(9), 948.
Devkota, K. C., Regmi, A. D., Pourghasemi, H. R., Yoshida, K., Pradhan, B., Ryu, I. C., . . . Althuwaynee, O. F. Landslide susceptibility mapping using certainty factor, index of entropy and logistic regression models in GIS and their comparison at Mugling–Narayanghat road section in Nepal Himalaya. Natural hazards, 2013, 65(1), 135-165.
Jebraeili, M. R., Zarei, P. Prioritizing suitable lands for flood spreading for artificial discharge using integrated model AHP/fuzzy (case study: Shourdasht Basin). Water Harvesting Research, 2018, 3(1&2), 1-14.
Şener, E., Şener, Ş., Davraz, A. Groundwater potential mapping by combining fuzzy-analytic hierarchy process and GIS in Beyşehir Lake Basin, Turkey. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 2018, 11(8), 1-21.
Silwal, C. B., Pathak, D. Review on practices and state of the art methods on delineation of ground water potential using GIS and remote sensing. Bulletin of the Department of Geology, 2018, 7-20.
Kuensel. (22nd March 2022). Groundwater study to begin soon. Kuensel. Retrieved from https://kuenselonline.com/groundwater-study-to-begin-soon/