Statistical Models for Studying the Incidence Rate of Deaths Among People Infected with COVID-19 in Southeast Asian (ASEAN) Countries
Keywords:
Poisson regression model, negative-binomial regression model, incidence rate, reproduction rate, stringency indexAbstract
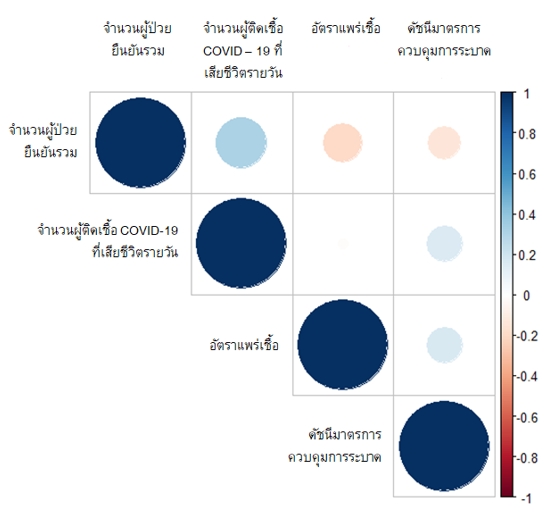
The objective of this research is to study the relationship between countries in Southeast Asia (ASEAN), the total confirmed cases of COVID-19, the reproduction rate, the stringency index, and the new deaths attributed to COVID-19. Another purpose of this research is to find a suitable statistical model to study the incidence rate of deaths among people infected with COVID-19 in Southeast Asian countries (ASEAN). The online secondary data is used in this study, and the models considered are the Poisson regression model and the negative-binomial regression model. The results show that the Poisson regression model is unsuitable for the data used in this study because the variance of this data is significantly higher than its mean; this is called the overdispersion problem. On the other hand, the negative-binomial regression model is the most suitable model for studying the incidence rate of deaths among people infected with COVID-19 in Southeast Asian countries. Moreover, Thailand has been found to have a higher incidence rate of death from COVID-19 than other Southeast Asian countries; the incidence rate of death from COVID-19 in Cambodia, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Philippines, Singapore, and Vietnam is lower than in Thailand by 99.5%, 99.4%, 28.1%, 99.4%, 72.0%, 99.7%, 56.0%, 97.9%, and 45.4%, respectively.
References
Batra, M., Shah, A.F., Rajput, P., & Shah, I.A. (2016). Comparison of linear and zero-inflated negative binomial regression models for appraisal of risk factors associated with dental caries. Journal of Indian Society of Pedodontics and Preventive Dentistry, 34(1), 71-75.
Byers, A.L., Allore, H., Gill, T.M.,& Peduzzi, P.N. (2003). Application of Negative Binomial Modeling for Discrete Outcomes: A Case Study in Aging Research. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology, 56, 559-564.
Chaiwan, A., Boonho, W.,& Tongkhow, P. (2013). Risk Factors for Defective Products in Autoparts FactoryUsing Generalized Linear Model (GLM). In The 10th National Kasetsart University Kamphaeng Saen Conference, (pp. 238-246).Nakhon Pathom.
Chaiyawan,A.,Boonho, W., & Tongkhan, P.(2013). Analysis of risk factors for defective products in automobile parts factories using general linear models (GLM). National Academic Conference. Kasetsart University Kamphaeng Saen Campus 9th, Kasetsat university. (in Thai)
Charatiam, N. (2010). Comparative Test Statistics for Zero-Inflated Generalized Poisson Regression Model.against Generalized Poisson Regression Model in the Presence of Covariate Outliers[Unpublished master’s thesis].Thammasat University. (in Thai)
Guo, Y.R., Cao, Q.D., Hong, Z.S., Tan, Y.Y., Chen, S.D., Jin, H.J., Tan, K. S., Wang, D. Y., & Yan, Y.(2020). The origin, transmission and clinical therapies on coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak -an update on the status. Military Medical Research, 7, 1-10.
Hu, M.C., Pavlicova, M., & Nunes, E.V. (2011).Zero-inflated and Hurdle Models of Count Data with Extra Zeros: Examples form an HIV –Risk Reduction Intervention Trial. Journal of Drug Alcohol Abuse, 37(5), 367 –375.
McCullagh, P.,& Nelder, J. (1989). Generalized Linear Models(2nded.). Boca Raton: Chapman and Hall/CRC.
Moghimbeigi, A., Eshraghian, M.R., Mohammad, K., & Mcardle, B. (2008). Multilevel zeroinflated negative binomial regression modeling for over-dispersed count data with extra zeros'. Journal of Applied Statistics, 35(10), 1193-1202.
Molla, D.T.,& Muniswamy, B. (2012). Power of Tests for Overdispersion Parameter in Negative Binomial Regression Model. Journal of Mathematics, 1(4), 29-36.
Neter, J., Kutner, M.H., Nachtsheim, C.J.,& Wasserman, W. (1996). Applied linear statistical models (Book 1)(4thed.). Chicago, USA : Irwin.
Nettha,L.(2563). Lessons learned from the COVID-19 response of ASEAN member countries. https://lawforasean.krisdika.go.th/File/files/article_2_May_AMS_covid19.pdf(in Thai)
Office of the Royal Society.(2561). Dictionary of statistical terms Royal Institute edition. Bangkok: Office of the Royal Society.(in Thai)
Pramanick, M. B. B. S., Choolani, M., & Seng, L. B. (2021). The epidemiology of COVID-19 in ten Southeast Asian countries. Med J Malaysia, 76(6), 783.
Puno, G.R. (2021). COVID-19 case fatality rates across Southeast Asian countries (SEA): a preliminary estimate using a simple linear regression model. Journal of Health Research, 35(3), 286-294.
Tran, T.T.P., Khuong, L.Q., Dao, A.T.M., Nguyen, H.V., Djalante, R.,& Tran, H.T.T. (2020). The COVID-19 pandemic in the ASEAN: A preliminary report on the spread, burden and medical capacities. Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Medicine, 13(6), 247-251.
Üçer, B. H., & Çelikoğlu, C. (2004). Latent process in a Poisson regression model.Journal of Science and Technology, 5(2), 259-267.
Violato, C., Violato, E.M.,& Violato, E.M. (2021). Impact of the stringency of lockdown measures on covid-19: A theoretical model of a pandemic. PLOS ONE, 16(10),e0258205.
Vittinghoff, E., Glidden, D.V., Shiboski, S.C.,& McCulloch, C.E. (2011). Regression Methods in Biostatistics: Linear, Logistic, Survival, and Repeated Measures Models. New York, NY: Springer.
Yesilova, A.,&Yilmaz, A. (2007). The Application of Overdispersion and Generalized Estimating Equations in Repeated Catagorical Data Related to the Sexual Behaviour Traits of Farm Animals. Journal of Applied Sciences, 7(12), 1762-1767.
Yusuf, O.B., Bello, T., & Gureje, O. (2017). Zero Inflated Poisson and Zero Inflated Negative Binomial Models with Application to Number of Falls in the Elderly. Biostatistics and Biometrics Open Access Journal, 1(4), 1-7.
Zhu, N., Zhang, D., Wang, W., Li, X., Yang, B.,&Song, J.(2020) A novel coronavirus from patients with pneumonia in China, 2019. The New England Journal of Medicine, 382, 727-33.
Downloads
Published
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Journal of Applied Science and Emerging Technology

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.

