Comparison of the structural properties of a-C:H films prepared by pulsed and continuous RF
Keywords:
hydrogenated amorphous carbon film, continuous-wave (CW) mode, pulsed-wave (PW) mode, RF-PECVD, structural propertiesAbstract
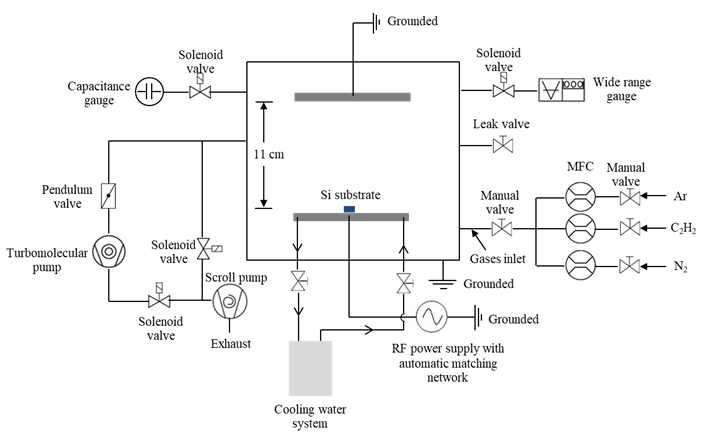
Hydrogenated amorphous carbon (a-C:H) films were grown on silicon substrates by radio frequency plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition (RF-PECVD) with the RF power of 100 W. The structural properties of a-C:H films prepared using the RF on in continuous-wave (CW) and pulsed-wave (PW) modes were compared. The pulse frequency of 1 Hz and a duty cycle of 10% were used for PW mode. The deposition time for CW and PW modes were set as 3 and 30 minutes, respectively. A mixture of argon and acetylene (1:10) was used as a precursor gas and carbon source, respectively. Raman spectroscopy was used to characterize ID/IG. Near edge X-ray absorption fine structure (NEXAFS) spectroscopy was used to identify sp2 content, while the X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) was used to analyze sp3 content. The X-ray reflectivity (XRR) was used to evaluate the density, roughness, and thickness of the films. The experimental results show that the a-C:H film prepared using the RF on in PW mode gives the ratio of ID/IG, sp2, and sp2 contents of 0.76, 59.3%, and 33.2 %, respectively, with the thickness and density of 53.0 nm and 2.1 g/cm3, respectively. While the RF on in CW mode gives the ratio of ID/IG, sp2, and sp2 contents of 0.57, 62.5%, and 29.5 %, respectively, with the thickness and density of 54.5 nm and 2.0 g/cm3, respectively. Therefore, with the same RF power and RF on time, the a-C:H film prepared using PW mode gives the structural properties better than using CW mode.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2021 The Journal of Applied Science

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.

