The Study of Workpiece Temperature During Machining in Dry Milling Stainless Steel
Main Article Content
Abstract
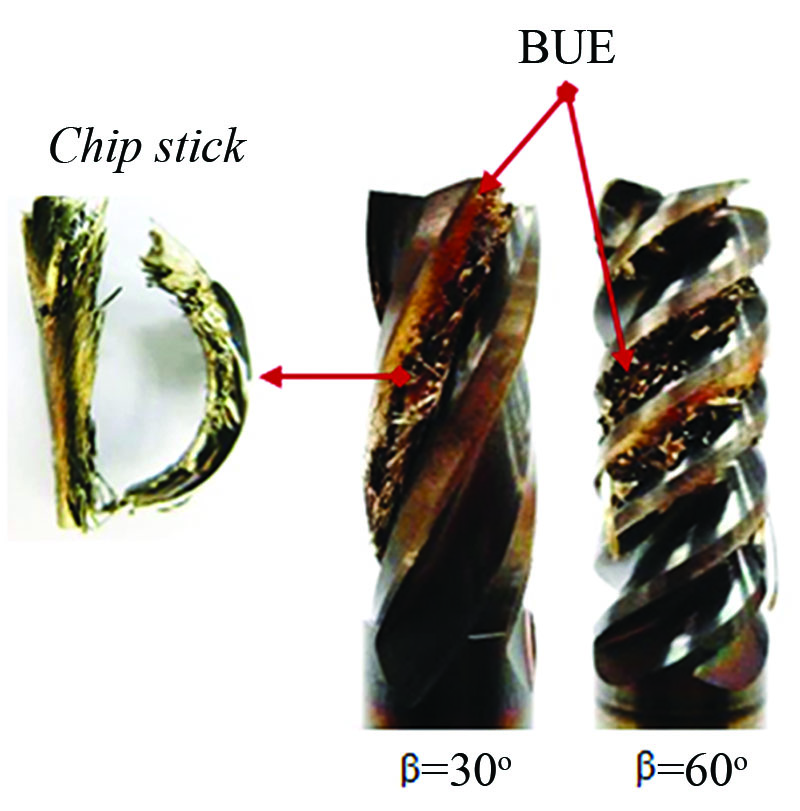
Milling is one of the most important machining processes that can be developed for more effective cutting performance to avoid use of coolants and maintain environmental friendliness. Stainless steel is widely known as a hard-to-cut material due to its high ductility, strength and low thermal conductivity. The cutting temperature is high which causes a built-up edge on the cutting tool. A commonly used solution to this problem is to apply the coolant which has a harmful effect on workers’ health. Therefore, this research aimed to study the relationship between cutting temperature of workpiece and shapes of end mill as well as coating material for higher efficiency and environmental friendliness. The results showed that the end mill with a 60-degree helix angle coated with TiAlN was the best one that could prevent the wear of the end mill’s cutting edge and the increase in cutting temperature since the higher cutting temperature did not only stem from the wider cutting edge, but also the chipping wear.
Article Details
References
[2] Cordes, S. E. (2012). Thermal Stability of γ-alumina PVD Coatings and Analysis of Their Performance in Machining of Austenitic Stainless Steels. CIRP Journal of Manufacturing Science and Technology. Vol. 5, pp. 20-25. DOI: 10.1016/j.cirpj.2011.11.003
[3] Munoz-Escalona, P., Shokrani, A., and Newman, S. T. (2015). Influence of Cutting Environments on Surface Integrity and Power Consumption of Austenitic Stainless Steel. Robotics and Computer-Integrated Manufacturing. Vol. 36, pp. 60-69. DOI: 10.1016/j.rcim.2014.12.013
[4] Emel Kuram, Babur Ozcelik, Mahmut Bayramoglu, Erhan Demirbas, and Bilgin Tolga Simsek. (2013). Optimization of Cutting Fluids and Cutting Parameters During end Milling by using D-optimal Design of Experiments. Journal of Cleaner Production. Vol. 42, pp. 159-166
[5] Deng Jianxin, Zhou Jiantou, Zhang Hui, and Yan Pei. (2011). Wear Mechanisms of Cemented Carbide Tools in Dry Cutting of Precipitation Hardening Semi-Austenitic Stainless Steels. Wear. Vol. 270, Issue 7-8, pp. 520-527. DOI: 10.1016/j.wear.2011.01.006
[6] Endrino, J. L., Fox-Rabinovich, G. S., and Gey, C. (2005). Hard AlTiN, AlCrN PVD Coatings for Machining of Austenitic Stainless Steel. Surface and Coatings Technology. Vol. 200, Issue 24, pp. 6840-6845. DOI: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2005.10.030
[7] Li Chen, Yong Du, Xiang Xiong, Ke K. Chang, and Ming J. Wu. (2011). Improved Properties of Ti-Al-N Coating by Multilayer Structure. International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials. Vol. 29, Issue 6, pp. 681-685. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2011.05.001
[8] Dirk Biermann, Markus Steiner, and Eugen Krebs. (2013). Investigation of Different Hard Coatings for Micromilling of Austenitic Stainless Steel. Procedia CIRP. Vol. 7, pp. 246-251. DOI: 10.1016/j.procir.2013.05.042
[9] Sen Lin, Fangyu Peng, Jie Wen, Yizhi Liu, and Rong Yan. (2013). An Investigation of Workpiece Temperature Variation in end Milling Considering Flank Rubbing Effect. International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture. Vol. 73, pp. 71-86. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2013.05.010
[10] Baowan, P., Saikaew, C., and Wisitsoraat, A. (2017). Influence of Helix Angle on Tool Performances of TiAlN and DLC-Coated Carbide end Mills for Dry Side Milling of Stainless Steel. International Journal Advanced Manufacturing Technology. Vol. 90, Issue 9-12, pp. 3085-3097. DOI: 10.1007/s00170-016-9601-5
[11] Peckner, D. and Bernstein, I. M. (1977). Handbook of Stainless Steels. McGraw-Hill Book Company. New York
[12] Prengel, H. G., Santhanam, A. T., Penich, R. M., Jindal, P. C., and Wendt, K. H. (1997). Advanced PVD-TiAlN Coatings on Carbide and Cermet Cutting Tools. Surface and Coatings Technology. Vol. 94-95, pp. 597-602. DOI: 10.1016/S0257-8972(97)00503-3
[13] Jindal, P. C., Santhanam, A. T., Schleinkofer, U., and Shuster A. F. (1999). Performance of PVD TiN, TiCN, and TiAlN Coated Cementedcarbide Tools in Turning. International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials. Vol. 17, pp. 163-170. DOI: 10.1016/s0263-4368(99)000086
[14] James, C., Sung, Ming-Chi Kan, and Michael Sung. (2009). Fluorinated DLC for Tribological Applications. International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials. Vol. 27, pp. 421-426
[15] Haruyo Fukui, Junya Okida, Naoya Omori, Hideki Moriguchi, and Keiichi Tsuda. (2004). Cutting Performance of DLC Coated Tools in Dry Machining Aluminum Alloys. Surface and Coatings Technology. Vol. 187, pp. 70-76. DOI: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2004.01.014
[16] Robertson, J. (1999). Deposition and Properties of Diamond Like Carbon. Materials Research Society Symposium Proceedings. Vol. 555, pp. 12. DOI: 10.1557/PROC-555-291
[17] Yunn-Shiuan Liao, Ting-Chang Lin, Cheng-Yu Lai, Yen-Liang Chen, Hao-Hueng Chang, Chun-Pin Lin. (2014). Cutting Performance of Diamond-Like Carbon Coated Tips in Ultrasonic Osteotomy. Journal of Dental Sciences. Vol. 9, Issue 1, pp. 63-68. DOI: 10.1016/j.jds.2013.02.014
[18] Ema, S. and Davies, R. (1989). Cutting Performance of End Mills with Different Helix Angles. International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture. Vol. 29, Issue 2, pp. 217-227. DOI: 10.1016/0890-6955(89)90033-3
[19] Omar, O. E. E. K., El-Wardany, T., and Elbestawi, M. A. (2007). An Improved Cutting Force and Surface Topography Prediction Model in End Milling. International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture. Vol. 47, Issue 7-8, pp. 1263-1275. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2006.08.021