The Development of Rule-based Decision Making Models for Blood Allocation to Enhance Utilization
Main Article Content
Abstract
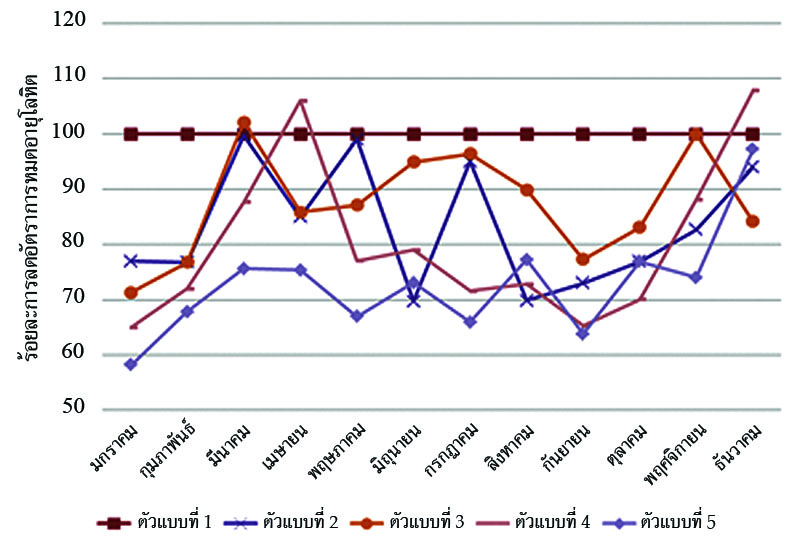
Blood allocation is a complex task. It has to deal with managing blood products, groups, units, and their shelf lives in order to allocate the requested units from Blood Center to hospitals in the network to reduce blood shortage and blood outdated levels. Hence, it is the aim of this study to explore blood allocation policy that helps reducing shortage and outdated rates, using Rule-based decision method. Four blood allocation models are proposed in this study, which are (1) Demand-based, (2) Stock level-based, (3) Crossmatched release period-based, and (4) Hospital performance level-based. Moreover, the evaluation of was done by using simulation method to measure the blood shortage and blood outdated rates in the system. The results of all models are compared based on 12-month data. The shortage rate results indicated that the Demand-based allocation model yielded the highest rate with 14.39 %, followed by model (4), (2), and (3), with 9.41 %, 8.76 %, and 8.05 %, respectively. The outdated rate results showed that Hospital performance level-based model was ranked in the highest rate with 27.89 %, followed by model (3), (1), and (2), with 20.95 %, 17.33 %, and 13.26 %, respectively. The contribution of this study is to illustrate the factors in managing the blood inventory which affect the occurrence of the blood shortage and blood outdated units. Blood service organizations can apply the blood allocation models in their work in order to enhance the allocation procedure more
effectively.
Article Details
References
[2] Katsaliaki, K. and Brailsford, S. C. (2007). Using Simulation to Improve the Blood Supply Chain. Journal of the Operational Research Society. Vol. 58, No. 2, pp. 219-227
[3] Pierskalla, W. P. (2005). Supply Chain Management of Blood Banks. In: Brandeau M.L., Sainfort F., Pierskalla W.P. (eds) Operations Research and Health Care. International Series in Operations Research & Management Science, Vol. 70, Springer, Boston, MA
[4] Prastacos, G. P. and Brodheim, E. (1980). PBDS: A Decision Support System for Regional Blood Management. Management Science. Vol. 26, Issue 5, pp. 451-463. DOI: 10.1287/mnsc.26.5.451
[5] Sapountzis, C. (1984). Allocating Blood to Hospitals from a Central Blood Bank. European Journal of Operational Research. Vol. 16, Issue 2, pp. 157-162. DOI: 10.1016/0377-2217(84)90070-5
[6] Sapountzis, C. (1989). Allocating Blood to Hospitals. The Journal of the Operational Research Society. Vol. 40, No. 5, pp. 443-449. DOI: 10.2307/2583616
[7] Qin, Y. (2011). Optimal Allocation of Blood Inventories. Doctoral dissertation. Business Administration. Information Systems and Operations Management. University of Florida
[8] Nagurney, A. and Masoumi, A. H. (2012). Supply Chain Network Design of a Sustainable Blood Banking System. In: Sustainable Supply Chains: Models, Methods and Public Policy Implications T. Boone, V. Jayaraman, and R. Ganeshan, Editors, Springer, London, England, pp. 49-72
[9] Li, B. N., Dong, M. C., and Chao, S. (2008). On Decision Making Support in Blood Bank Information Systems. Expert Systems with Applications. Vol. 34, Issue 2, pp. 1522-1532. DOI: 10.1016/j.eswa.2007.01.016
[10] Jagannathan, R. and Sen, T. (1991). Storing Crossmatched Blood: A Perishable Inventory Model With Prior Allocation. Management Science. Vol. 37, No. 3, pp. 251-266. DOI: 10.1287/mnsc.37.3.251
[11] Levesque, H. J. and Lakemeyer, G. (2001). The Logic of Knowledge Bases. MIT Press.
[12] Cohen, M. A., Pierskalla, W. P., and Yen, H. C. (1981). An Analysis of Ordering and Allocation Policies for Multi-echelon, Age-Differentiated Inventory Systems. TIMS Studies in the Management Sciences. Vol. 16, No. 1, pp. 353-378
[13] Gonzalez, A. J. and Dankel, D. D. (1993). The Engineering of Knowledge-based Systems. Englewood Cliffs, NJ : Prentice-Hall. pp. 207-230.