Fabrication and electrochemical properties of porous carbon/LiFePO4 composite nanostructure
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.55674/ias.v13i3.251712Keywords:
Porous carbon, LiFePO4, Electrochemical properties, Electrospinning, Energy storage devicesAbstract
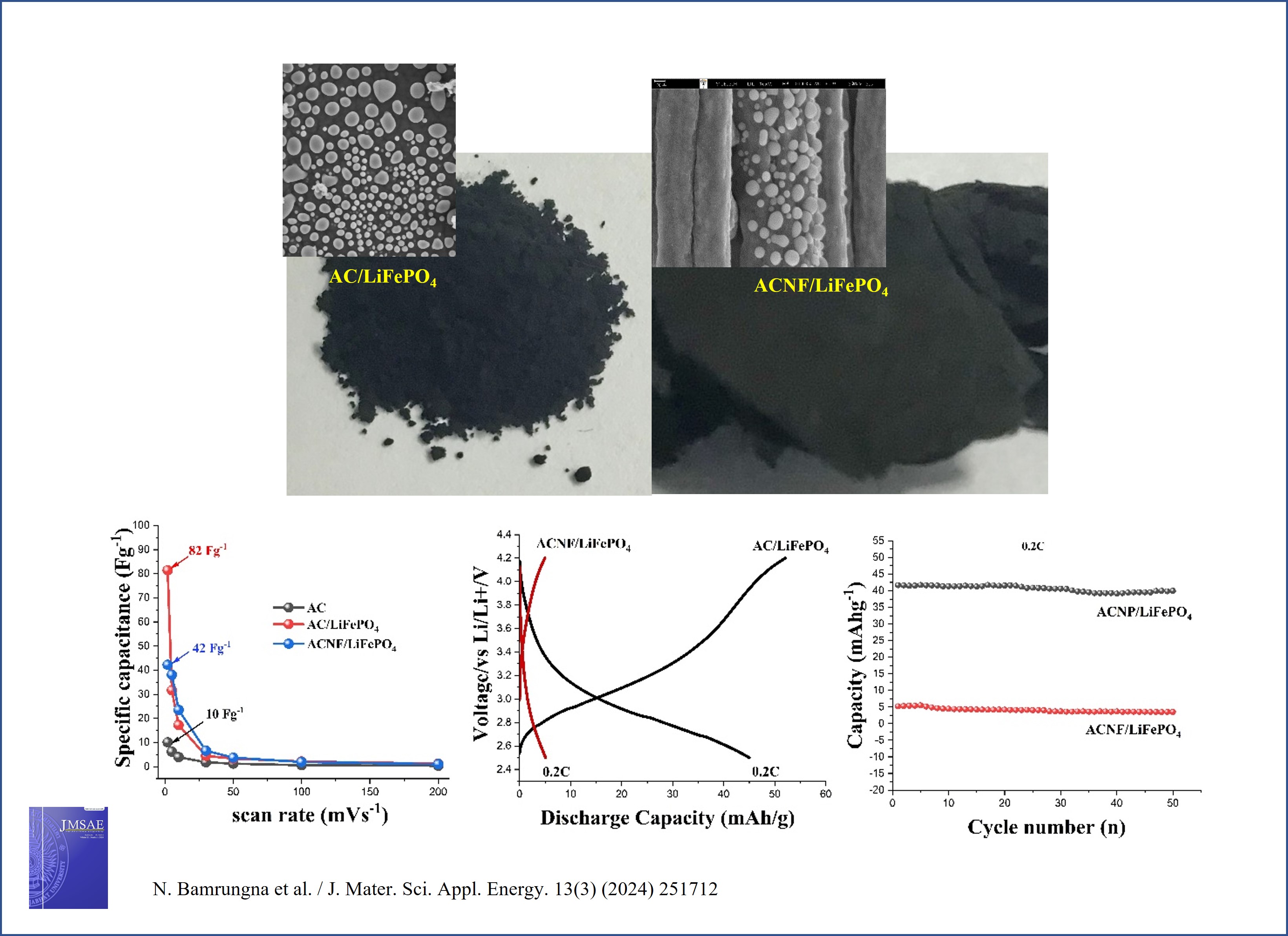
This work reports the synthesis and electrochemical properties of porous carbon composite with lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4) for use as electrode materials in energy storage devices. Two forms of carbon were prepared; including activated carbon (AC) and carbon nanofibers (ACNF). The ACNF/LiFePO4 composite nanostructure was fabricated by electrospinning while the AC/LiFePO4 composite nanostructure was obtained by the sol-gel method followed by the heat treatment process. All samples were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), and Brunauer-Emmett-Teller analyzer (BET). The electrochemical properties were tested using cyclic voltammetry (CV) and galvanostatic charge-discharge at various current densities (0.25 – 10 Ag–1) and various C-rates (0.20 – 5 C). The AC/LiFePO4 electrode showed better electrochemical properties than those of the ACNF/LiFePO4 electrode. A maximum specific capacitance of 82 F g–1 at 2 m Vs–1 and initial discharge capacities of 45 mA hg–1 at 0.20 C were observed. Moreover, the AC/LiFePO4 electrode showed better cycle performance than that of the ACNF/LiFePO4 electrode at all C-rates. The interesting electrochemical properties of AC/LiFePO4 composite nanostructure make it a potential candidate for use as electrode materials in energy storage devices.
References
N. Bugday, M.N. Ates, O. Duygulu, W. Deng, X. Ji, S. Altin, S. Yasar, ZIF-12-derived N-doped Fe/Co/S/@C nanoparticles as high-performance composite anode electrode materails for lithium-ion batteriers, J. Alloys Compd. 928 (2022) 167037.
Ya. V. Shatilo, E.V. Makhonina, V.S. Pervov, V.S. Dubasova, A.F. Nikolenko, Zh. V. Dobrokhotova, and I.A. Kedrinskii, LiCoO2- and LiMn2O4-Based Composite Cathode Materials, Inorg. Mater. 42(7) (2006) 782 − 787.
P. Kurzhals, F. Riewald, M. Bianchini, H. Sommer, H.A. Gasteiger, and J. Janek, The LiNiO2 Cathode Active Material: A Comprehensive Study of Calcination Conditions and their Correlation with Physicochemical roperties. Part I. Structural Chemistry, J. Electrochem Soc. 168 (2021) 110518.
[A.K. Padhi, K.S. Nanjundaswamy, J.B. Goodenough, Phospho-olivines as positiveelectrode materials for rechargeable lithium batteries, J. Electrochem. Soc. 144 (1997) 1188 − 1194.
E.C. Evarts, Lithium batteries: To the limits of lithium. Nature 526 (2015) S93 − S95.
R. Susantyoko, T.S. Alkindi, A.B. Kanagaraj, B. An, H. Alshibli, D. Choi, S. Aldahmani, H. Fadaq, S. Almheiri, Performance optimization of freestanding MWCNF-LiFePO4 sheets as cathodes for improved specific capacity of lithium-ion batteries. RSC Adv 8 (2018) 16566 − 16573.
Y. Liu, J. Liu, J. Wang, M.N. Banis, B. Xiao, A. Lushington, W. Xiao, R. Li, T.K. Sham, G. Liang, X. Sun, Formation of size-dependent and conductive phase on lithium iron phosphate during carbon coatin, Nat. Commun. 9 (2018) 1 − 8.
H.C. Shin, K.Y. Chung, W.S. Min, D.J. Byun, H. Jang, B.W. Cho, Asymmetry between charge and discharge during high rate cycling in LiFePO4– In Situ X-ray diffraction study, Electrochem. Commun. 10 (2008) 536 − 540.
A. Eftekhari, LiFePO4/C nanocomposites for lithium-ion batteries J. Power Sources. 343 (2017) 395 − 411.
Kang B, Ceder G. Battery materials for ultrafast charging and discharging, Nature. 458 (2009) 190 − 193.
C.S. Sun, Y. Zhang, X.J. Zhang, Z. Zhou, Structural and electrochemical properties of Cl-doped LiFePO4/C, J. Power Sources 195 (2010) 3680 − 3863.
N. Ye, T. Yan, Z. Jiang, W. Wu, T. Fang, A review: conventional and supercritical hydro solvothermal synthesis of ultrafine particles as cathode in lithium battery, Ceram. Int. 44 (2018) 4521 − 4537.
Y. Tang, F. Huang, H. Bi, Z. Liu, D. Wan, Highly conductive three-dimensional graphene for enhancing the rate performance of LiFePO4 cathode. J. Power Sources. 203 (2012) 130 − 134.
M. Khalid, Ana M.B. Honorato, A.A. Pasa, H. Varela, A sugar derived carbon-red phosphorus composite for oxygen evolution reaction and supercapacitor activities, Materials Science for Energy Technologies, 3 (2020) 508 − 514.
J. Lee, W. Kim, W. Kim, Stretchable carbon nanotube/ion–gel supercapacitors with high durability realized through interfacial microroughness, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 6 (16) (2014) 13578-13586.
S. Nilmoung, W. Limphirat, S. Maensiri, Electrochemical properties of ACNF/Li2FeSiO4 composite nanostructures for supercapacitors. J. Alloys Compd. 907 (2022) 164466.
H. Yang, S. Kannappan, A.S. Pandian, J.H. Jang, Y.S. Lee, W. Lu, Graphene supercapacitor with both high power and energy density, Nanotechnology, 28(44) (2017) 445401.
Y.Huang, H. Lai, Effects of discharge rate on electrochemical and thermal characteristics of LiFePO4/graphite battery, Appl. Therm. Eng. 157 (2019) 113744.
V.A. Streltsov, E.L. Elokoneva, V.G. Tsirelson, N.K. Hansen, Multipole analysis of the electron density in triphylite LiFePO4, using X-ray diffraction data, Acta Crystallogr, B 49 (1993) 147-153.
S. Shen, Y. Zhang, G. Wei, W. Zhang, X. Yan, G. Xia, A. Wu, C. Ke, and J. Zhang, Li2FeSiO4/C hollow nanospheres as cathode materials for lithium-ion Batteries, Nano Res. 12(2) (2019) 357 − 363.
W. Wang, P. Liu, M. Zhang, J. Hu, F. Xing, The pore structure of phosphoaluminate cement, Open J. Compos. Mater. 2 (2012) 104 – 112.
L. Hea, W. Zha, D. Chena, Fabrication and electrochemical properties of 3D nano-network LiFePO4@multiwalled carbon nanotube composite using risedronic acid as the phosphorus source, Prog. Nat. Sci. 29 (2019) 156 − 162.
P. Rosaiah, O.M. Hussain, Microscopic and spectroscopic properties of hydrothermally synthesized nano-crystalline LiFePO4 cathode material, J. Alloys Compd. 614 (2014) 13 − 19.
B. Yao, Z. Ding, J. Zhang, X. Feng, L. Yin, Encapsulation of LiFePO4 by in-situ graphitized carbon cage towards enhanced low temperature performance as cathode materials for lithium ion batteries, J. Solid-State Chem. 216 (2014) 9 − 12.
S. Dhaybi, B. Marsan, A. Hammami, A novel low-cost and simple colloidal route for preparing high-performance carbon-coated LiFePO4 for lithium batteries, J. Energy storage 18 (2018) 259 − 265.
C.K. Lee, A.S.T. Chiang, C.S. Tsay, The characterization of porous solids from gas adsorption measurements, Key Eng. Mater. 115 (1995) 21 − 44.
M. Salanne, B. Rotenberg, K. Naoi, K. Kaneko, P.-L. Taberna, C.P. Grey, B. Dunn, P. Simon, Efficient storage mechanisms for building better supercapacitors, Nat. Energy 1 (2016) 1 − 10.
J. Li, D.B. Le, P.P. Ferguson, J.R. Dahn, Lithium polyacrylate as a binder for tin-cobalt-carbon negative electrodes in lithium-ion batteries, Electrochim. Acta. 55(8) (2010) 2991-2995.
M.K. Sahoo, G.R. Rao, Fabrication of NiCo2S4 nanoball embedded nitrogen doped mesoporous carbon on nickel foam as an advanced charge storage material, Electrochim. Acta 268 (2018) 139 − 149.
S. Sarkar, and S. Mitra, Carbon coated submicron sized-LiFePO4: Improved high rate performance lithium battery cathode, Energy Procedia 54 (2014) 718 − 724.
H. Zhang, G.R. Li, L.P. An, T.Y. Yan, X.P. Gao, H.Y. Zhu. Electrochemical lithium storage of titanate and titania nanotubes and nanorods. J. Phys. Chem. C. 111 (2007) 6143 − 6148.
V. Gangaraju, M. Shastri, K. Shetty, N.R. Marilingaiah, K.S. Anantharaju, P.D. Shivaramu, D. Rangappa, In-situ preparation of silk-cocoon derived carbon and LiFePO4 nanocomposite as cathode material for Li-ion battery, Ceram. Int. 48 (2022) 35657 − 35665.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Journal of Materials Science and Applied Energy

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.







