A study in thermoelectric effect of Eu2O3 substitution on Al2O3 in CuAl(100−x)Eu(x)O2
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.55674/ias.v12i3.251500Keywords:
Solid-state reaction, Seebeck coefficient, Power factorAbstract
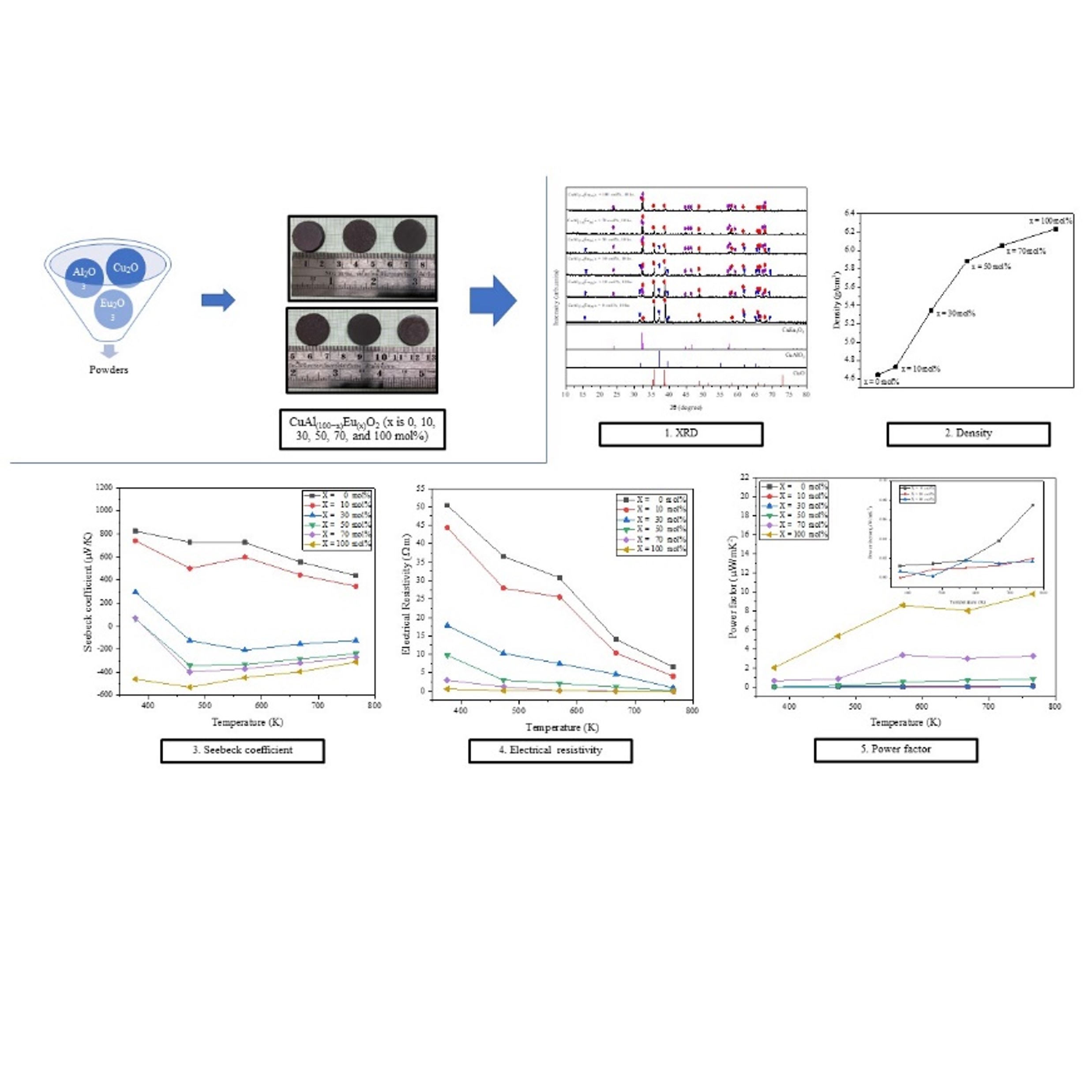
The effects of Eu2O3 substitution on Al2O3 in CuAl(100−x) Eu(x)O2 (x = 0, 10, 30, 50, 70, and 100 mol%) were considered. In this study, all samples with a diameter of 20 mm were sintered by using solid-state reaction method. The structural analysis with XRD investigation shows that it had a hexagonal CuAlO2 structure at x = 0, 10, 30, and 50 mol%. Tetragonal CuEu2O4 structures were reported at x = 10, 30, 50, 70, and 100 mol%. The ZEM-3 instrument measures thermoelectric characteristics like the Seebeck coefficient, electrical resistivity, and power factor throughout the temperature range of 350 − 800 K. According to the investigation, the electrical resistivity value tended to continue to decrease as measurement temperature increased. The Seebeck coefficient shows a positive value. However, when Al2O3 was substituted for Eu2O3 in large amounts, the Seebeck coefficient value became negative. The power factor increases as the mole ratio of Eu2O3 increase, exhibited the highest value of around 9.50 µW mK−2 at 775 K.
References
D.M. Rowe, CRC Handbook of Thermoelectrics, first ed., Boca Raton, New York, 1995.
L.D. Zhao, G. Tan, S. Hao, J. He, Y. Pei, H. Chi, H. Wang, S. Gong, H. Xu, V.P. Dravid, C. Uher, G.J. Snyder, C. Wolverton, M.G. Kanatzidis, Ultrahigh power factor and thermoelectric performance in hole-doped single-crystal SnSe, Science, 351 (2015) 1 − 7.
A.T. Duong, V.Q. Nguyen, G. Duvjir, V.T. Duong, S. Kwon, J.Y. Song, J.K. Lee, J.E. Lee, S. Park, T. Min, J. Lee, J. Kim, S. Cho, Achieving ZT=2.2 with Bi-doped n-type SnSe single crystals, Nature Com. 7 (2016) 1 − 6.
T. Fu, X. Yue, H. Wu, C. Fu, T. Zhu, X. Liu, L. Hu, P. Ying, J. He, X. Zhao, Enhanced thermoelectric performance of PbTe bulk materials with figure of merit ZT >2 by multi-functional alloying, J Materiomics. 2 (2016) 141 – 149.
J.P. Heremans, V. Jovovic, E.S. Toberer, A. Saramat, K. Kurosaki, A. Charoenphakdee, S. Yamanaka, G.J. Snyder, Enhancement of thermoelectric efficiency in PbTe by distortion of the electronic density of states, Science. 321 (2008) 554 − 557.
B. Poudel, Q. Hao, Y. Ma, Y. Lan, A. Minnich, B. Yu, X. Yan, D. Wang, A. Muto, D. Vashaee, X. Chen, J. Liu, M. Dresselhaus, G. Chen, Z. Ren, High-thermoelectric performance of nanostructured bismuth antimony telluride bulk alloys, Science. 320 (2008) 634 − 638.
W. Xie, X. Tang, Y. Yan, Q. Zhang, T.M. Tritt, Unique nanostructures and enhanced thermoelectric performance of melt-spun BiSbTe alloys, Appl. Phys. Lett. 94 (2009) 102111.
I. Terasaki, Large thermoelectric power in NaCo2O4 single crystals, Physical review b, 56(20) (1997) R12685 – R12687.
I. Terasaki, Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Thermoelectrics International Thermoelectric Society, 1999, pp. 569.
Y. Masuda, D. Nagahama, H. Itahara, T. Tani, W. S. Seo and K. Koumoto, Thermoelectric performance of Bi- and Na-substituted Ca3Co4O9 improved through ceramic texturing, J. Mater. Chem. 13(5) (2003) 1094 – 1099.
Gaojie Xu, R. Funahashi, M. Shikano, Q. Pu, Biao Liu, High temperature transport properties of Ca3-xNaxCo4O9 system, Solid State Commun. 124(3) (2002) 73 – 76.
K. Park, K.Y. Ko, H -C. Kwon, S. Nahm, Improvement in thermoelectric properties of CuAlO2 by adding Fe2O3, J. Alloys Compd. 437 (2007) 1 − 6.
C. Liu, D.T. Morelli, Thermoelectric properties of hot-pressed and PECS-Sintered Magnesium doped copper aluminum oxide, J. Electron. Mater. 40 (2011) 678 − 681.
A.N. Banerjee, R. Maity, P.K. Ghosh, K.K. Chattopadhyay, Thermoelectric properties and electrical characteristics of sputter-deposited p-CuAlO2 thin films, Thin Solid Films. 474 (2005) 261 − 266.
Abanti Nag, V. Shubha, Oxide Thermoelectric Materials: A Structure–Property Relationship, J. Electron. Mater. 43(4) (2014) 962 − 977.
H. Liu, X. Shi, F. Xu, L. Zhang, W. Zhang, L. Chen, Q. Li, C. Uher, T. Day, G. Snyder Jeffrey, G.J. Snyder, Copper ion liquid-like thermoelectrics, Nat. Mater. 11 (2012) 422 − 425.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Journal of Materials Science and Applied Energy

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.







