Enhancement of band gap and electrical conductivity properties of TiO2 nanowire by Ni with hydrothermal method
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.55674/jmsae.v11i1.240634Keywords:
TiO2(B) nanowire, Hydrothermal, Ni doped TiO2Abstract
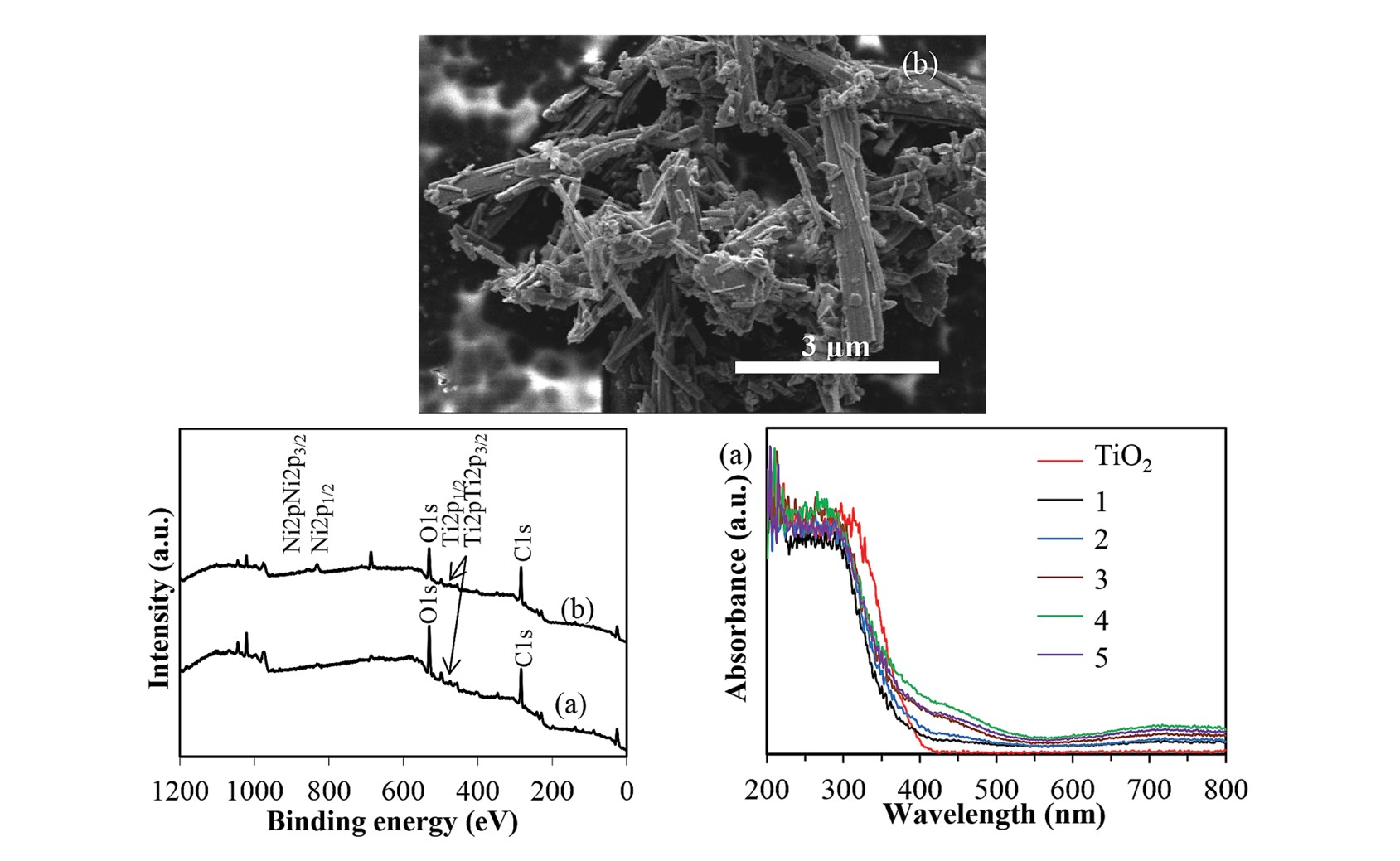
Nickel doped Titanium dioxide phase B nanowires (Ni/TiO2(B) NWs) were successfully fabricated by a hydrothermal method and characterized by XRD, FE-SEM, UV-vis and XPS spectroscopy. The FE-SEM images of the surface morphology showed that the size of nickel doped TiO2(B) phase crystal was small (19 – 29 nm). The results indicated that the uniform Ni doped TiO2(B) nanowires with a length of about 5 µm and an average diameter of about ∼204.80 nm were produced. The result also showed composite with 4 mol% Ni doped TiO2(B) NWs phase exhibited optimum photocatalytic activity for the synergeric effects of electrical conductivity and band gap energy. The properties study of Ni/TiO2(B) NWs leading to a new applications of high-performance materials as solar cells, electronics batteries and many other applications.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2021 Journal of Materials Science and Applied Energy

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.







