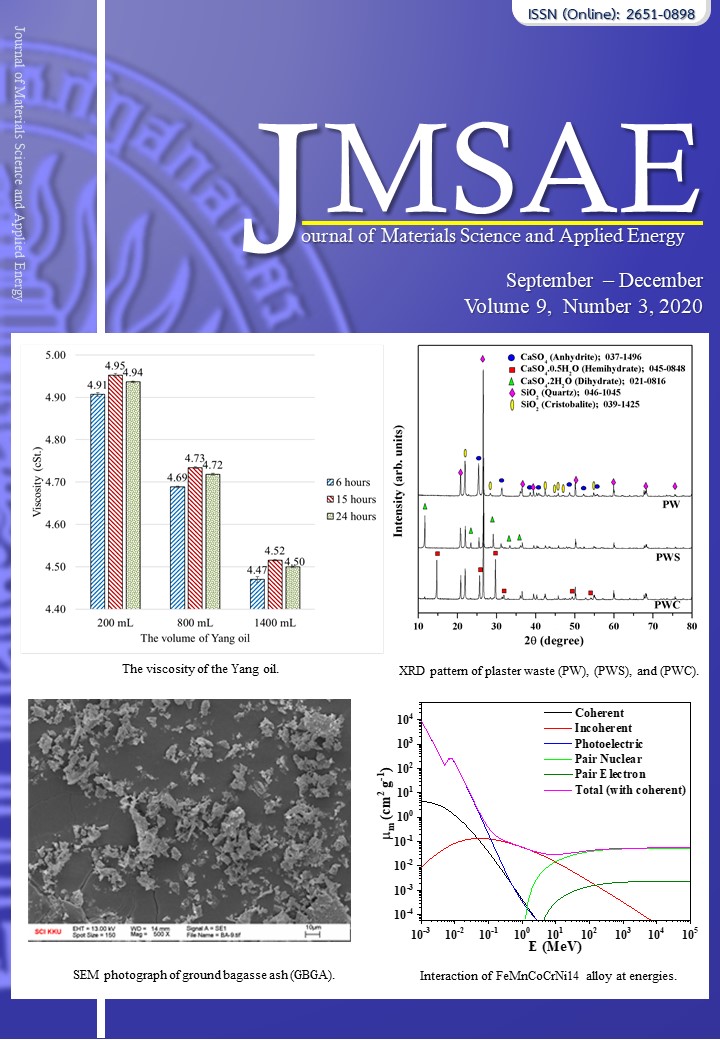
Effect of Curing and Sodium Silicate to Sodium Hydroxide Ratio on Physical Properties of Bagasse ash Based-Geopolymer Material
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.55674/ias.v9i3.240300Keywords:
Bagasse ash, Compressive strength, Geopolymer material, Mortar, Waste materialAbstract
For this research, bagasse ash from landfills was used as a raw material in producing geopolymer mortar to decrease negative environmental to dispose of waste material. The paper reports a study of the compressive strength and porosity of geopolymer mortar containing ground bagasse ash (GBGA). GBGA based-geopolymer mortar with sodium hydroxide (NaOH) of 15 M, constant liquid to GBGA ratio, and similar flow were used for the tests. Extra water was used to improve the workability of geopolymer mortar GBGA. Sodium silicate (Na2SiO3) and sodium hydroxide (NaOH) ratio were used as alkali activator solutions. The effects of the temperature of curing and alkali activator solutions on compressive strength and porosity were investigated. Test results indicate that extra water was needed for all mixes. The geopolymer mortars GBGA with good strengths were obtained with the alkali activator solutions ratio by weight of 2.50. At curing of 75 °C, the reasonable compressive strengths of 21 MPa were obtained. At curing of 75 °C, the reasonable compressive strengths of 6 ̶ 21 MPa and porosity of 10 ̶ 24 % were obtained.