Efficient Violence Recognition in Video Streams using ResDLCNN-GRU Attention Network
Main Article Content
Abstract
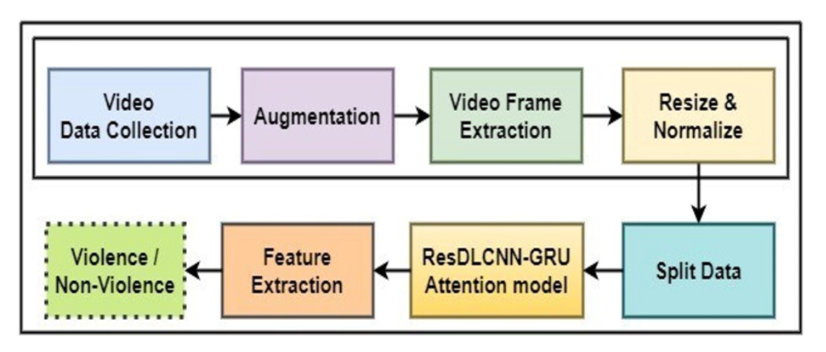
Detecting Violence in video streams is essential for public safety and security due to the rising frequency of violent incidents. Despite the extensive deployment of CCTV for surveillance, the available human monitoring resources still need to catch up with the need for vigilant supervision. This research presents a new lightweight model to address this gap by accurately identifying and categorizing violent behaviors in various scenarios, including CCTV footage. The proposed method leverages optical flow and RGB data to capture spatiotemporal features in the Violence data. Built on a Residual DLCNN architecture integrated with the Attention mechanism and GRU components, the model effectively handles high-dimensional video data, enhancing accuracy by prioritizing crucial frames containing violent and nonviolent instances. The proposed model's performance was validated on the Hockey Fights (HF), Movie Fights, and SCVD datasets, achieving impressive accuracies of 98.38%, 99.62%, and 90.57%, respectively. Here, we developed the Extended Automatic Violence Detection Dataset (EAVDD), featuring 1530 videos of violent scenes in movies, public spaces, social media, and sports. Testing the model with top fight scenes in rated movies yielded outstanding results. This research supports surveillance systems and advances short video analysis and understanding with applications in public safety, social media, sports, and law enforcement.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
References
H. Yao and X. Hu, “A survey of video Violence detection,” Cyber-Physical Systems, pp. 1–24, Jun. 2021.
G. Kaur and S. Singh, “Revisiting vision-based violence detection in videos: A critical analysis,” Neurocomputing, vol. 597, 2024,
I. Serrano, O. Deniz, J. L. Espinosa-Aranda and G. Bueno, “Fight Recognition in Video Using Hough Forests and 2D Convolutional Neural Network,” IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, vol. 27, no. 10, pp. 4787-4797, 2018.
A. S. Keceli and A. Kaya, “Violent activity classification with transferred deep features and 3dCnn,” Signal, Image and Video Processing, 2023.
Q. Dai Pet al., “Fudan-Huawei at MediaEval 2015: Detecting Violent Scenes and Affective Impact in Movies with Deep Learning,” in MediaEval, vol. 1436, 2015.
Naz Du ̈ndar, Ali Seydi Kec ̧eli, A. Kaya, and H. Sever, “A shallow 3D convolutional neural network for Violence detection in videos,” Egyptian Informatics Journal, vol. 26, 2024.
P. Zhang, L. Dong, X. Zhao, W. Lei, and W. Zhang, “An end-to-end framework for real-time violent behavior detection based on 2D CNNs,” Journal of real-time image processing, vol. 21, no. 2, 2024.
J. Mahmoodi and Hossein Nezamabadi-pour, “A spatio-temporal model for Violence detection based on spatial and temporal attention modules and 2D CNNs,” Pattern Analysis and Applications, vol. 27, no. 2, 2024.
S. M. Mohtavipour et al., “A multistream CNN for deep Violence detection in video sequences using handcrafted features,” The Visual Computer, vol. 38, no. 6, pp. 2057-2072, 2022.
V. D. Huszar et al., “Toward Fast and Accurate Violence Detection for Automated Video Surveillance Applications,” IEEE Access, vol. 11, pp. 18772-18793, 2023.
T. Zhenhua et al., “FTCF: Full temporal cross fusion network for Violence detection in videos,” Applied Intelligence, vol. 53, no. 4, pp. 4218-4230, 2023.
G. Garcia-Cobo and J. C. SanMiguel, “Human skeletons and change detection for efficient Violence detection in surveillance videos,” Computer Vision and Image Understanding, vol. 233, p. 103739, 2023.
J. H. Park et al., “Conv3D-Based Video Violence Detection Network Using Optical Flow and RGB Data,” Sensors, vol. 24, no. 2, p. 317, 2024.
K. Chaturvedi et al., “Fight detection with spatial and channel wise attention-based ConvLSTM model,” Expert Systems, vol. 41, no. 1, p. e13474, 2024.
A. Dey, S. Biswas, and L. Abualigah, “Umpire’s Signal Recognition in Cricket Using an Attention based DC-GRU Network,” International Journal of Engineering, vol. 37, no. 4, pp. 662–674, 2024.
S. Sudhakaran and O. Lanz, “Learning to detect violent videos using convolutional long shortterm memory,” 2017 14th IEEE International Conference on Advanced Video and Signal Based Surveillance (AVSS), Lecce, Italy, 2017, pp. 1-6.
C. Li, X. Yang, and G. Liang, “Keyframe-guided Video Swin Transformer with Multi-path Excitation for Violence Detection,” The Computer Journal, vol. 67, no. 5, pp. 1826-1837, 2024.
A. Dey, S. Biswas, and D.-N. Le, “Recognition of Human Interactions in Still Images using AdaptiveDRNet with Multi-level Attention,” International Journal of Advanced Computer Science and Applications, vol. 14, no. 10, 2023.
N. Alabid, “Interpretation of Spatial Relationships by Objects Tracking in a Complex Streaming Video,” ECTI Transactions on Computer and Information Technology (ECTI-CIT), vol. 15, no. 2, pp. 245-257, 2021.
S. Mekruksavanich and A. Jitpattanakul, “FallNeXt: A Deep Residual Model based on Multi-Branch Aggregation for Sensor-based Fall Detection,” ECTI Transactions on Computer and Information Technology (ECTI-CIT), vol. 16, no. 4, pp. 352–364, 2022.
F. J. Rendo ́n-Segador, J. A. A ́lvarez-Garc ́ıa, F. Enr ́ıquez, and O. Deniz, “ViolenceNet: Dense Multi-Head Self-Attention with Bidirectional Convolutional LSTM for Detecting Violence,” Electronics, vol. 10, no. 13, p. 1601, 2021.
J. Li, X. Jiang, T. Sun and K. Xu, “Efficient Violence Detection Using 3D Convolutional Neural Networks,” 2019 16th IEEE International Conference on Advanced Video and Signal Based Surveillance (AVSS), Taipei, Taiwan, 2019, pp. 1-8.
Y. Tang, Y. Chen, Sagar A.S.M. Sharifuzzaman, and T. Li, “An automatic fine-grained Violence detection system for animation based on modified faster R-CNN,” Expert systems with applications, vol. 237, 2024.
S. Accattoli et al., “Violence detection in videos by combining 3D convolutional neural networks and support vector machines,” Applied Artificial Intelligence, vol. 34, no. 4, pp. 329-344, 2020.
F. U. M. Ullah et al., “Violence detection using spatiotemporal features with 3D convolutional neural network,” Sensors, vol. 19, no. 11, p. 2472, 2019.
M. Khan, A. E. Saddik, W. Gueaieb, G. De Masi and F. Karray, “VD-Net: An Edge Vision-Based Surveillance System for Violence Detection,” IEEE Access, vol. 12, pp. 43796-43808, 2024.
M. Bianculli et al., “A dataset for automatic Violence detection in videos,” Data in brief, vol. 33, 2020.
T. Hassner et al., ”Violent flows: real-time detection of violent crowd behavior,” 2012 IEEE Computer Society Conf. on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), Rhode Island, USA, June 2012.
E. Bermejo Nievas, O. Deniz Suarez, G. Bueno Garc ́ıa,andR.Sukthankar, “ViolenceDetection in Video Using Computer Vision Techniques,” Computer Analysis of Images and Patterns, pp. 332–339, 2011.
G. Kaur and S. Singh, “An ensemble based approach for Violence detection in videos using deep transfer learning,” Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2024.
Toluwani Aremu, L. Zhiyuan, Reem Alameeri, M. Khan, and Abdulmotaleb El Saddik, “SSIVD-Net: A Novel Salient Super Image Classification and Detection Technique for Weaponized Violence,” Lecture notes in networks and systems, pp. 16–35, 2024.
W. Dai et al., “Two-stream convolution neural network with video-stream for action recognition,” 2019 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), pp. 1-8, July 2019.
N. Honarjoo, A. Abdari, and A. Mansouri, “Violence detection in compressed video,” Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2024.
S. Akti, G. A. Tataroglu, and H. K. Ekenel, “Vision-based Fight Detection from Surveillance Cameras,” 2019 Ninth International Conference on Image Processing Theory, Tools and Applications (IPTA), Nov. 2019.
S. U. Khan, I. U. Haq, S. Rho, S. W. Baik, and M. Y. Lee, “Cover the Violence: A Novel Deep-Learning-Based Approach Towards Violence-Detection in Movies,” Applied Sciences, vol. 9, no. 22, 2019.
J. Wang, D. Zhao, H. Li, and D. Wang, “Lightweight Violence Detection Model Based on 2D CNN with Bi-Directional Motion Attention,” Applied Sciences, vol. 14, no. 11, 2024.
Z. Zhang, Z. Lv, C. Gan, and Q. Zhu, “Human action recognition using convolutional LSTM and fully-connected LSTM with different attentions,” Neurocomputing, vol. 410, pp. 304-316, 2020.
A. Dey, S. Biswas, and D.-N. Le, “Workout Action Recognition in Video Streams Using an Attention Driven Residual DC-GRU Network,” Computers, Materials & Continua, vol. 79, no. 2, pp. 3067-3087, 2024.
Top Fight Scenes in Movies [Online Available]: https://www.timeout.com/film/greatest-fights-in-movies.
M. Qaraqe et al., “PublicVision: A Secure Smart Surveillance System for Crowd Behavior Recognition,” IEEE Access, vol. 12, pp. 26474-26491, 2024.
Muhammad Shahroz Nadeem, Fatih Kurugollu, H. F. Atlam, and Virginia N.L. Franqueira, “Weapon Violence Dataset 2.0: A synthetic dataset for violence detection,” Data in Brief, 2024.
T. Marteau, Sitou Afanon, D. Sodoyer, and Sebastien Ambellouis, “Violence detection in railway environment with modern deep learning approaches and small dataset,” Transportation research procedia, vol. 72, pp. 87–92, 2023.
E. Perseghin and Gian Luca Foresti, “A Shallow System Prototype for Violent Action Detection in Italian Public Schools,” Information, vol. 14, no. 4, 2023.
J. Lei, W. Sun, Y. Fang, N. Ye, S. Yang, and J. Wu, “A Model for Detecting Abnormal Elevator Passenger Behavior Based on Video Classification,” Electronics, vol. 13, no. 13, 2024.
T. Santos, H. Oliveira, and A. Cunha, “Systematic review on weapon detection in surveillance footage through deep learning,” Computer science review, vol. 51, 2024.