A Priority-based Data Transmission for Energy Efficiency MAC Protocol with Wireless Body Area Networks
Main Article Content
Abstract
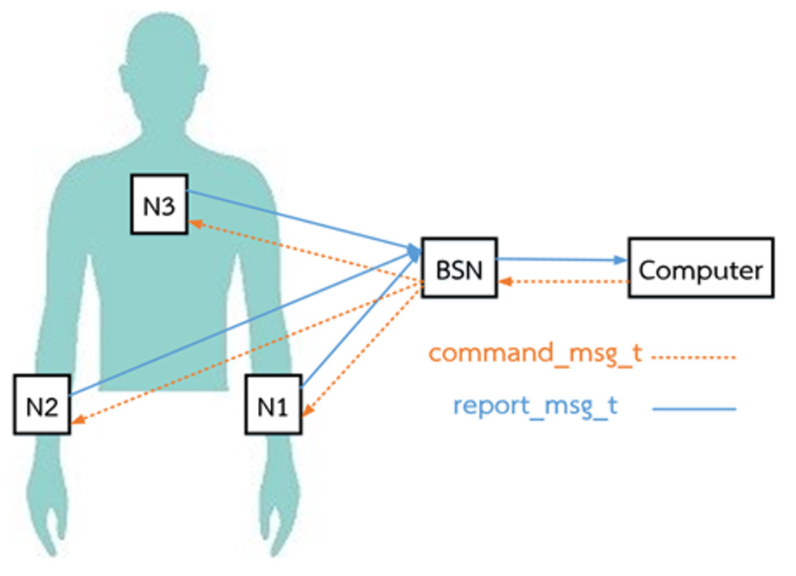
Wireless Body Area Networks (WBANs) are a collection of vital and electrical signals measured from various body parts to help analyze therapeutic approaches for patients using wireless data transmission. The significant data has to communicate with collision avoidance to obtain high throughput. In this paper, a hybrid MAC layer communication is implemented between CSMA/CA and TDMA. CSMA/CA communication has been introduced to manage the TDMA sequence of transmissions without a central node. The experimental results in this system implement real wireless devices, TelosB, with the IEEE 802.15.4 standard. We studied the convergence speed of transmission sequence allocation, which was measured in the CSMA/CA period. When the number of nodes is small, the convergence time is slower than a large number of nodes. However, the number of nodes does not affect the number of rounds entering the transmission period. This parameter has been evaluated for the network and energy efficiency in WBANs. Packet delivery ratio, packet numbers, and energy consumption are examined for the different priority-based nodes in the TDMA period. The energy consumption can reduce to 40% for no priority when compared with high priority in the case of a priority-based node.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
References
D. D. Olatinwo, A. M. Abu-Mahfouz, and G. P. Hancke, “A Hybrid Multi-Class MAC Protocol for IoT-Enabled WBAN Systems,” in IEEE Sensors Journal, vol. 21, no. 5, pp. 6761 - 6774, 2021.
B. Liu, Z. Yan, and C. W. Chen, “CA-MAC: A hybrid context-aware MAC protocol for wireless body area networks,” 2011 IEEE 13th International Conference on e-Health Networking, Applications and Services, Columbia, MO, USA, pp. 213–216, 2011.
J. Wang, Y. Xie, and Q. Yi, “An All Dynamic MAC Protocol for Wireless Body Area Network,” 11th International Conference on Wireless Communications, Networking and Mobile Computing (WiCOM 2015), Shanghai, pp. 1-6, 2015.
X. Yang, L. Wang, and Z. Zhang, “Wireless Body Area Networks MAC Protocol for Energy Efficiency and Extending Lifetime,” in IEEE Sensors Letters, vol. 2, no. 1, pp. 1–4, 2018.
D. Buranapanichkit, and Y. Andreopoulos, “Distributed Time-Frequency Division Multiple Access Protocol for Wireless Sensor Networks,” in IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, vol. 1, no. 5, pp. 440-443, 2012.
F. F. Forouzandeh, O. A. Mohamed, M. Sawan, and F. Awwad, “TBCD-TDM: Novel ultra-low energy protocol for implantable wireless body sensor networks,” GLOBECOM 2009 2009 IEEE Global Telecommunications Conference, Honolulu, HI, USA, pp. 1–6, 2009.
S. Marinkovic, C. Spagnol, and E. Popovici, “Energy-Efficient TDMA-Based MAC Protocol for Wireless Body Area Networks,” 2009 Third International Conference on Sensor Technologies and Applications, Athens, Greece, pp. 604-609, 2009.
T. v. Dam, and K. Langendoen, “An Adaptive Energy Efficient MAC Protocol for Wireless Sensor Networks,” SenSys ’03: Proceedings of the 1st international conference on Embedded networked sensor systems, pp. 171-180, 2003.
B. Liu, Z. Yan and C. W. Chen, “CA-MAC: A hybrid context-aware MAC protocol for wireless body area networks,” 2011 IEEE 13th International Conference on e-Health Networking, Applications and Services, Columbia, MO, USA, pp. 213–216, 2011.
C. Li, J. Li, B. Zhen, H. B. Li and R. Kohno, “Hybrid Unified-slot Access protocol for wireless body area networks,” International Journal of Wireless Information Networks, vol. 17, no. 3–4, pp. 150–161, 2010.
S. Bhandari and S. Moh, “A priority-based adaptive MAC protocol for wireless body area networks,” Sensors, vol. 16, no. 3, pp. 401(16), 2016.
A. Alsiddiky, W. Awwad, H. Fouad, A. S. Hassanein and A. M. Soliman, “Priority-based data transmission using selective decision modes in wearable sensor based healthcare applications,” Computer Communications, vol. 160, pp. 43-51, 2020.