Evaluation of mineral barriers against acid rock drainage
Main Article Content
Abstract
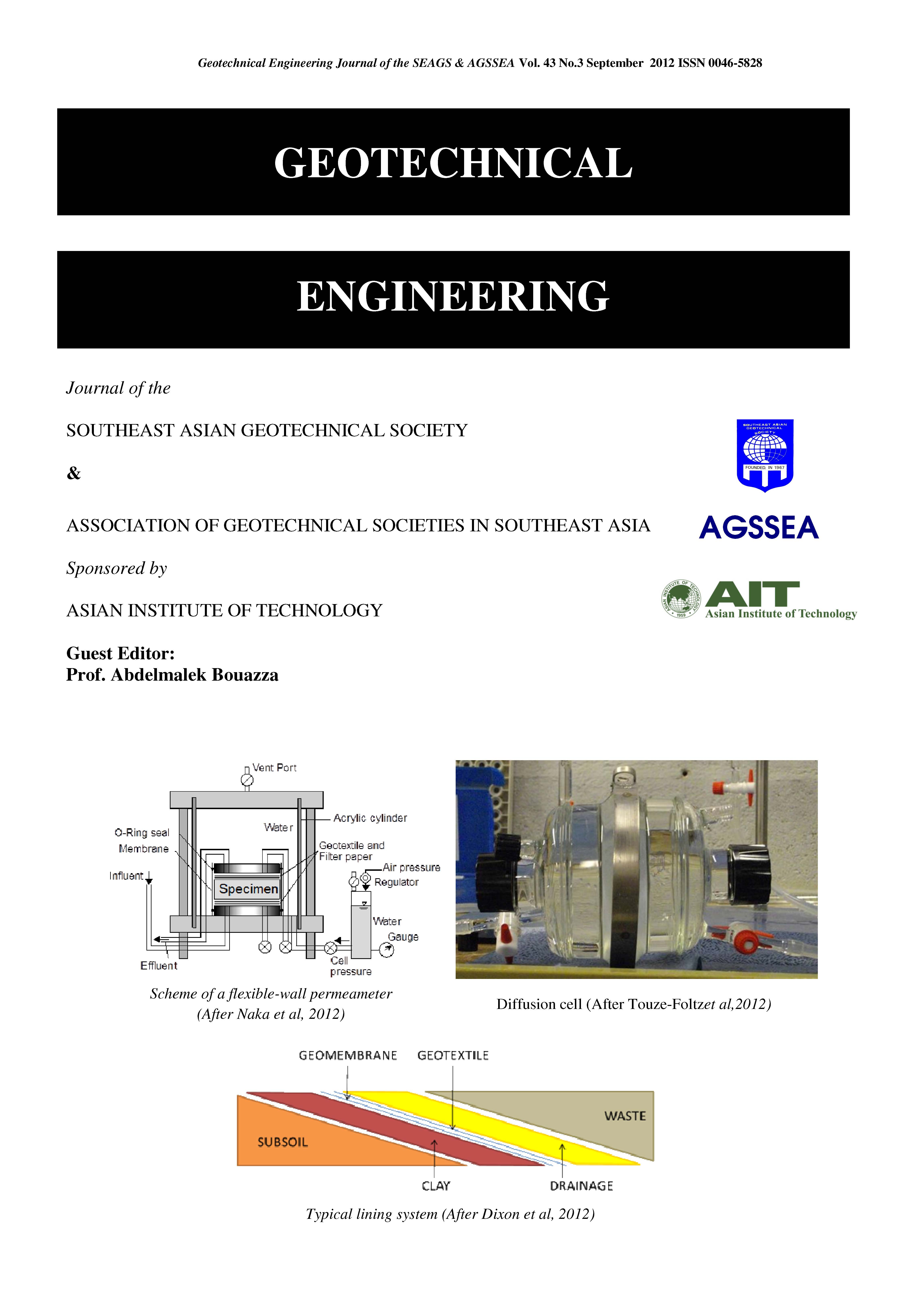
The barrier performance of geosynthetic clay liners (GCLs) containing Na-bentonite, zeolite, and ferrihydrate against acid rock drainage (ARD) was evaluated through hydraulic conductivity and sorption tests in order to determine their applicability as adsorption layers in waste rock containment facilities. The hydraulic conductivity (k) of GCL permeated with water was 1.4×10-11 m/s and this increased by one order of magnitude with ARDpermeation (k= 5.0×10-10 m/s). The k of zeolite permeated with water was 3.0×10-10 m/s and this also increased with ARDpermeation (k = 1.4×10-9 m/s). The k value of ferrihydrate was 7.3×10-9 m/s when permeated with water and this remained constant after ARD permeation (k= 8.6×10-9 m/s). Metal sorption of bentonite, zeolite, and ferrihydrate were different in terms of sorption capacity and selectivity, which can be summarized as follows: bentonite: Cu>Fe>Zn>Al>As>Pb, zeolite: Cu>Fe>Zn>Pb Al As, and ferrihydrate: Cu>Zn>Al>As>Pb. According to experimental results, the tree minerals appear to be good candidates for ARD mitigation.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Copyright © 2019 Association of Geotechnical Societies in Southeast Asia (AGSSEA) - Southeast Asian Geotechnical Society (SEAGS).