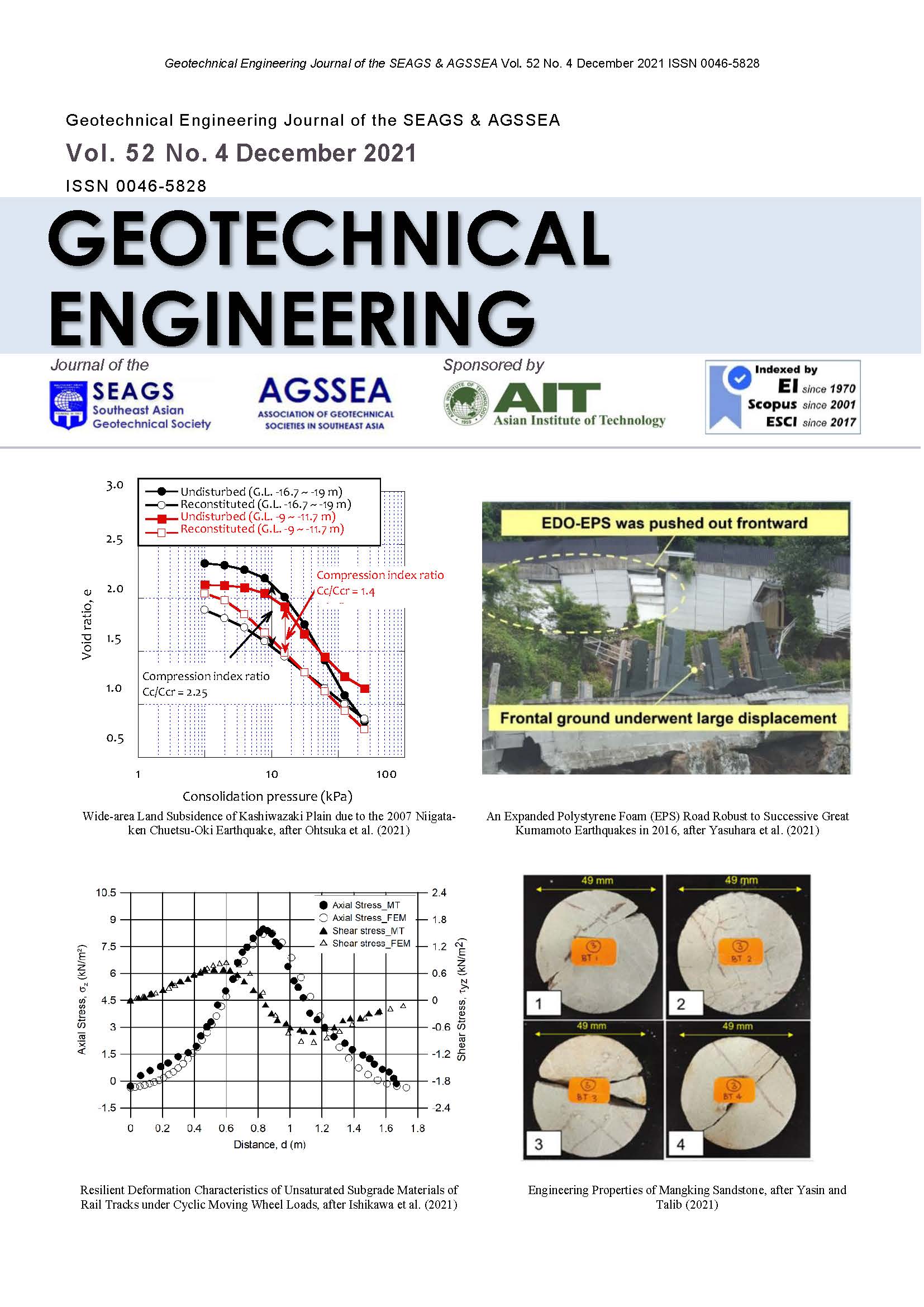
Wide-area Land Subsidence of Kashiwazaki Plain due to the 2007 Niigata-ken Chuetsu-Oki Earthquake
Main Article Content
Abstract
Wide-area land subsidence occurred across the Kashiwazaki Plain, Niigata, Japan after the 2007 Niigata-ken Chuetsu-Oki Earthquake. The stratified ground subsidence meter clearly showed that a thick clayey layer had caused this subsidence after the earthquake. To examine the ground conditions, a boring survey was conducted at the site and the physical and mechanical properties of the ground were tested. Although leveling surveys are insufficient for surveying the behavior of the ground, the measurement data obtained at various points from these surveys are meritorious for grasping the spatial distribution and the time-dependent property of the land subsidence. In this study, by analyzing the instantaneous and the long-term amounts of land subsidence at each point from the time-series observation data, the correlation between geology and topography is reported and the cause of the land subsidence of the clayey soils after the earthquake is discussed. It is clarified that the existence of a marine clay layer greatly affected the long-term subsidence of the land.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Copyright © 2019 Association of Geotechnical Societies in Southeast Asia (AGSSEA) - Southeast Asian Geotechnical Society (SEAGS).