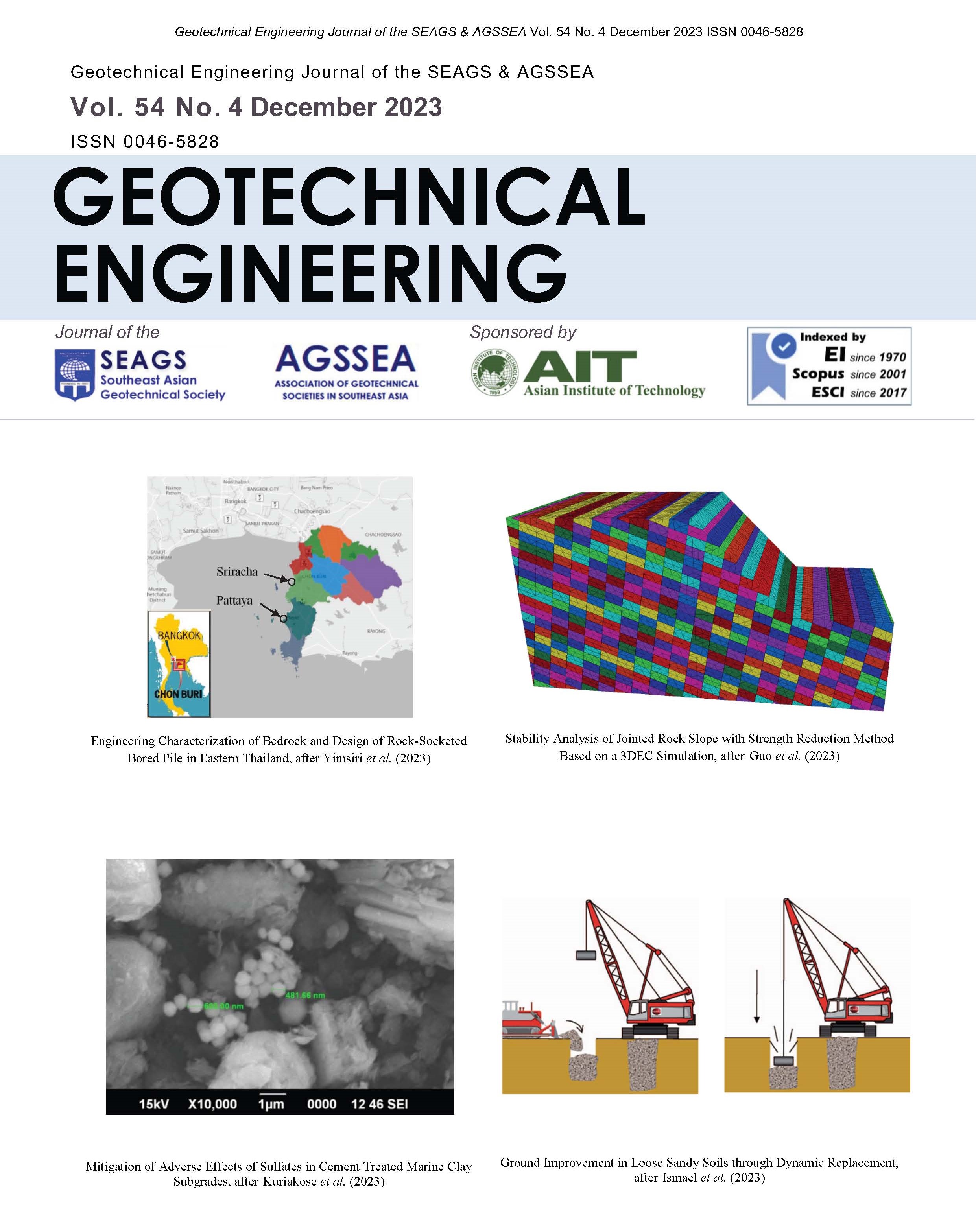
Stability Analysis of Jointed Rock Slope with Strength Reduction Method Based on a 3DEC Simulation
Main Article Content
Abstract
To investigate the application of strength reduction method in the stability analysis of rock slope, a rock slope model with two sets of joints is established in the 3D discrete element code (3DEC) software. Different strength reduction algorithms are used to solve the slope safety factor and the slope failure form in critical condition. Results indicate that it is more reasonable to adopt the coordinated reduction method for the unjointed slope model. However, for the slope model with two groups of joints, the slope is stable when only the rock block parameters are reduced, resulting in a small amount of toppling deformation. The numerical results of only reducing the structural plane parameters are consistent with those of reducing all parameters. The safety factor of the rock slope model with two groups of joints is 1.30, and tensile shear failure occurs along the structural plane. Taking the convergence of the displacement of the monitoring points on the slope surface as the criterion of slope instability, the reduction factor when the slope is in a critical state can be obtained from the displacement curve. The reduction of structural plane parameters should be mainly considered when the discrete element strength reduction method is used to calculate the safety factor of rock slope.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Copyright © 2019 Association of Geotechnical Societies in Southeast Asia (AGSSEA) - Southeast Asian Geotechnical Society (SEAGS).