Forecasting Model for Pneumonia Cases in 13 Health Districts in Thailand
Keywords:
pneumonia patient, decomposition, moothing, Box-Jenkins, combined forecastingAbstract
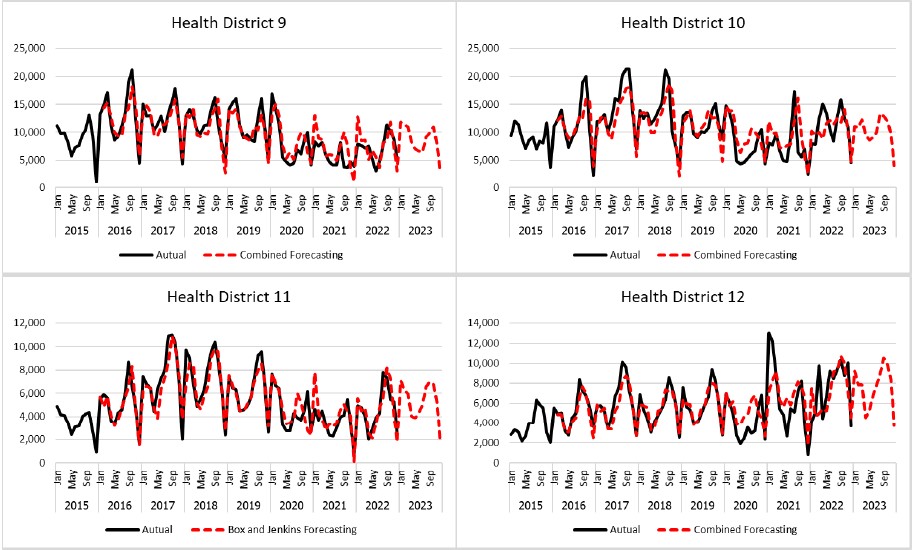
The objective of this research is to evaluate a proposed forecasting model for predicting pneumonia cases across all 13 health districts in Thailand. Monthly time series data from January 2015 to December 2022, obtained from the Health Data Center of the Ministry of Public Health, were utilized. Each health district utilized a varying number of data points depending on data completeness. The data were categorized into two sets: a training dataset for model construction and a test dataset for assessing model accuracy. The forecasting models were evaluated using the symmetric mean absolute percentage error (sMAPE). The results revealed that the combined forecasting approach using regression analysis demonstrated advantages over other methods for health districts 1 to 6, 8, 9, 10, 12, and 13. For health district 7, the most appropriate model was the decomposition model with trend and seasonal components in a multiplicative form. Similarly, for health district 11, the Box-Jenkins model was found to be the most suitable.
References
Armstrong, J. S. (1985). Long-range Forecasting: From Crystal Ball to Computer, 2nded.Wiley.
Box, G. E. P., Jenkins, G. M.,& Reinsel,G. C. (1994). Time Series Analysis: Forecasting and Control, 3rded. New Jersey: Prentice Hall.
Bureau of Epidemiology, Department of Disease Control, Ministry of Public Health. (2015). Annual Epidemiological Surveillance Report 2015. Bangkok, Thailand: The Agricultural Co-operative Federation of Thailand., Ltd. Publisher. Retrieved May 3, 2023, from https://apps-doe.moph.go.th/boeeng/annual/Annual/AESR2015/(in Thai)
Charupronprasit, R., Sirirat,B.,& Sumtip,J. (2017). Statistical Thailand 2017. Nontaburi, Bureau of Policy and Strategy, Ministry of Public Health. Retrieved May 3, 2023, from http: / /digital.nlt.go.th/dlib/items/show/10642(in Thai)
Charupronprasit, R., Suthiart, A., Sirirat,B.,& Dumrongchat,B. (2016). Statistical Thailand 2016. Nontaburi, Bureau of Policy and Strategy, Ministry of Public Health. Retrieved May 3, 2023, from http://digital.nlt.go.th/dlib/items/show/10640(in Thai)
Ekachampaka, P., Sriprayoon, P.,& Thammachart, S. (2018). Thailand Regional Health Profile 2012 -2017. Strategy and Planning Division of Office of the Permanent Secretary Ministryof Public Health, Bangkok:Chinauksorn Printing. (In Thai)
Flores, B. E. (1986) . A pragmatic view of accuracy measurement in forecasting. Omega, 14(2), 93–98.
Health Data Center, Ministry of Public Health. (2023). Rates of Pneumonia Cases.Retrieved May 3, 2023, from https: / /hdcservice.moph.go.th/hdc/main/index.php
Hewamalage, H., Bergmeir, C., & Bandara, K. (2021). Recurrent neural networks for time series forecasting: Current status and future directions. International Journal of Forecasting, 37(1), 388-427.
Hyndman, R. J.,& Koehler, A. B. (2006). Another look at measures of forecast accuracy. International Journal of Forecasting, 22(4), 679-688.
Keerativibool, W. (2016). Forecasting model for the number of patients with pneumonia in Thailand. Public Health Journal Burapha University, 11(1), 24-38.(in Thai).
Minsan, P. (2022) . Forecasting model for export condom quantity of Thailand on the COVID-19 situation. The Journal of Applied Science, 21(1),1-21.(in Thai). https://ph01.tci-thaijo.org/index.php/JASCI/article/view/244500
Minsan, W.,& Minsan, P. (2023). Incorporating decomposition and the holt-winters method into the whale optimization algorithm for forecasting monthly government revenue in Thailand. Science& Technology Asia, 28(4), 38-53. https://ph02.tci-thaijo.org/index.php/SciTechAsia/article/view/250335
Minsan, W., Saengngammuang, N., Taninpong, P., & Thumronglaohapun, S. (2021).Comparing methods of optimization in solver of excel 2019 and whale optimization algorithm.UTK Journal,15(2),107-120. (in Thai). https://ph02.tci-thaijo.org/index.php/rmutk/article/view/245178
Montgomery, D.C., Peck, E.A.,& Vining, G.G. (2006). Introduction to Linear Regression Analysis, 4thed.New York:Wiley.
Nakunthod,I.,& Khamkhod,K. (2018). Time series modeling for the pneumonia rate of patients in Lampang province. In: Proceeding of the 18th Graduate Studies of Northern Rajabhat, University Network Conference and the 4th Lampang Research, 20 July 2018, pp.340-358. Lampang, Thailand. (in Thai)
Persons,W. (1919). Indices of business conditions. Review of Economics and Statistics, 1, 5-110.
Saeying, J., Minsan, W.,& Taninpong, P. (2023). Forecasting model for the amount of water flowing into the reservoirs of the electricity generating authority of Thailand (EGAT).RMUTSV Research Journal, 15(2),494-510. (in Thai). https://li01.tci-thaijo.org/index.php/rmutsvrj/article/view/252100
Taesombat, S. (2006) . Quantitative Forecasting. Bangkok:Kasetsart University Press. (in Thai)
Tunkaew,T., Minsan, P., Nontapa, C., & Minsan, W.(2023). A suitable forecasting model for exchange rates of the top 10 foreign currencies most preferred by Thai tourists compared to the Thai baht. Thai Science and Technology Journal, 31(3),1-21.(in Thai) https://li01.tci-thaijo.org/index.php/tstj/article/view/258445
Downloads
Published
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Journal of Applied Science and Emerging Technology

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.

