Factors influencing the mortality of COVID-19 patients
Keywords:
Covid-19, Comorbidity, ROC-curve, Logistic regressionAbstract
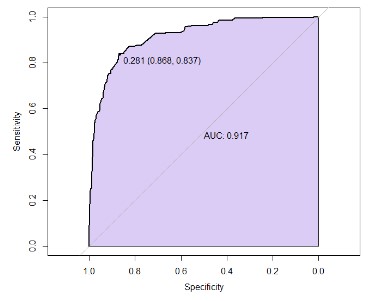
COVID-19 has spread quickly throughout the world. The public health system has been significantly impacted by this pandamic. For people infected with COVID-19 who have comorbidity, this increases the severity of symptoms and increases the risk of mortality. The objective of this research was to characterize the COVID-19 patient and find the influence factors for the mortality of COVID-19 patients. The study population included COVID-19 cases collected between 14 February and 31 April 2020. Real-time data were collected from open-source COVID-19 repositories which collected data on 481,289 COVID-19 cases from 141 countries with a sample size of 1,143 people with complete data. The data were analyzed using descriptive statistics and inferential statistics. The Chi-square test or Fisher's exact test and multivariable logistic regression were used for identifying the factors associated with mortality in patients with COVID-19 and constructed ROC curves to determine the appropriate cut-off point to predict the chance of mortality in patients with COVID-19. The results found that five factors: Gender (OR=2.262 ; 95%CI= 1.519-3.367), Age (OR= 1.118 ; 95%CI= 1.102 - 1.134), Malignancy (OR= 0.193 ; 95%CI=0.039 - 0.949), Pneumonia (OR= 7.173 ; 95%CI= 2.818 - 18.254), and ARDS (OR=11.488 ; 95%CI=4.105 - 32.148) influenced the mortality of COVID-19 patients with percentage of correct predictions of 86%. Moreover, the sensitivity by ROC curve also showed very high accuracy.
References
Aktar, S., Talukder, A., Ahamad, M. M., Kamal, A. H. M., Khan, J. R., Protikuzzaman, M., Hossain, N., Azad, A. K. M., Quinn, J. M. W., Summers, M. A., Liaw, T., Eapen, V., & Moni, M. A. (2021). Machine learning approaches to identify patient comorbidities and symptoms that increased risk of mortality in COVID-19. Diagnostics, 11(8), 1383. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11081383
Alali, A. S., Alshehri, A. O., Assiri, A., Khan, S., Alkathiri, M. A., Almohammed, O. A., Badoghaish, W., AlQahtani, S. M., Alshammari, M. A., Mohany, M., Alamri, F. F., AlRuthia, Y., & Alqahtani, F. (2021). Demographics, comorbidities, and outcomes among young and middle-aged COVID-19 patients in Saudi Arabia. Saudi Pharmaceutical Journal, 29(8), 833–842. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsps.2021.06.005
Badedi, M., Makrami, A., & Alnami, A. (2021). Co-morbidity and blood group type risk in coronavirus disease 2019 patients: A case–control study. Journal of Infection and Public Health, 14(4), 550–554. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiph.2020.12.035
Djaharuddin, I., Munawwarah, S., Nurulita, A., Ilyas, M., Tabri, N. A., & Lihawa, N. (2021). Comorbidities and mortality in COVID-19 patients. Gaceta Sanitaria, 35(S2), S530–S532. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gaceta.2021.10.085
Emami, A., Akbari, A.,Basirat, A., Zare, H., Javanmardi, F., Falahati, F., & Rezaei, A. (2021). The role of comorbidities on mortality of COVID-19 in patients with diabetes. Obesity Medicine, 25, 100352. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.obmed.2021.100352
Fachri, M., Hatta, M., Widowati, E., Akaputra, R., Dwiyanti, R., Syukri, A., Junita, A. R., Febrianti, A., & Primaguna, M. R. (2022). Correlations between comorbidities, chest x-ray findings, and C-Reactive protein level in patients with COVID-19. Annals of Medicine and Surgery, 77(5), 103553. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amsu.2022.103553
Guan, W., Liang, W., Zhao, Y., Liang, H., Chen, Z., Li, Y., Liu, X., Chen, R., Tang, C., Wang, T., Ou, C., Li, L., Chen, P., Sang, L., Wang, W., Li, J., Li, C., Ou, L., Cheng, B., ... He, J. (2020). Comorbidity and its impact on 1590 patients with COVID-19 in China: A nationwide analysis. European Respiratory Journal, 55(5), 2000547. https://doi.org/10.1183/13993003.00547-2020
Liu, W., Yang, C., Liao, Y., Wan, F., Lin, L., Huang, X., Zhang, B.-H., Yuan, Y., Zhang, P., Zhang, X.-J., She, Z.-G., Wang, L., & Li, H. (2022). Risk factors for COVID-19 progression and mortality in hospitalized patients without pre-existing comorbidities.Journal of infection and public health,15(1), 13-20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiph.2021.11.012
Ma, Y., Zhu, D. S., Chen, R. B., Shi, N. N., et al., (2020). Association of Overlapped and Un-overlapped Comorbidities with COVID-19 Severity and Treatment Outcomes: A Retrospective Cohort Study from Nine Provinces in China. Biomedicaland Environmental Sciences, 33(12), 893–905. https://doi.org/10.3967/bes2020.123
Novelli, L., Raimondi, F., Carioli, G., Carobbio, A., et al., (2023). One-year mortality in COVID-19 is associated with patients’ comorbidities rather than pneumonia severity. Respiratory Medicine and Research, 83(1), 100976. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resmer.2022.100976
Posso, M., Comas, M., Román, M., Domingo, L., Louro, J., González, C., Sala, M., Anglès, A., Cirera, I., Cots, F., Frías, V.-M., Gea, J., Güerri-Fernández, R.,Masclans, J. R., Noguès, X., Vázquez, O., Villar-García, J., Horcajada, J. P., Pascual, J., & Castells, X. (2020). Comorbidities and Mortality in Patients With COVID-19 Aged 60 Years and Older in a University Hospital in Spain. Archivos de Bronconeumología, 56(11), 756–758. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arbres.2020.06.012
Ryan, C., Minc, A., Caceres, J., Balsalobre, A., Dixit, A., KaPik, B., Schmitzberger, F., Syed-Abdul, S., & Fung, C. (2021). Predicting severe outcomes in Covid-19 related illness using onlypatient demographics, comorbidities and symptoms. The American Journal of Emergency Medicine, 45, 378–384. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajem.2020.09.017
Salinas-Aguirre, J. E., Sánchez-García, C., Rodríguez-Sanchez, R., Rodríguez-Muñoz, L., Díaz-Castaño, A., & Bernal-Gómez, R. (2022). Clinical characteristics and comorbidities associated with mortality in patients with COVID-19 in Coahuila (Mexico). Revista Clínica Española (English Edition), 222(5), 288-292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rceng.2020.12.007
WorldHealth Organization. (2022). WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard. https://covid19.who.int
Wu, Z., & McGoogan, J. M. (2020). Characteristics of and Important Lessons from the Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Outbreak in China: Summary of a Report of 72314 Cases From the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention. JAMA, 323(13), 1239–1242. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2020.2648
Wu, Z., & McGoogan, J. M. (2020). Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)outbreak in China: summary of a report of 72 314 cases from the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention. JAMA, 323(13), 1239-1242. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2020.2648
Patipanawat, P. (2565). Factors affecting death of patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), Kalasin Hospital. Journal of Health and Environmental Studies, 7(1), 64-71. (in thai)
Chumcheun, P.,& Buanjunglert, S.(2565). Mortality rate and factors related to deathof COVID-19 patients Damnoen Saduak Hospital, Ratchaburi. Journal of research for promoting health and quality of life, 2(1), 25-37.(in thai)
Downloads
Published
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Journal of Applied Science and Emerging Technology

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.

