Surface Hardening of SKD61 Steel using Low-Temperature Plasma Nitriding
Keywords:
Low-temperature plasma nitriding, Tool steel, SKD61Abstract
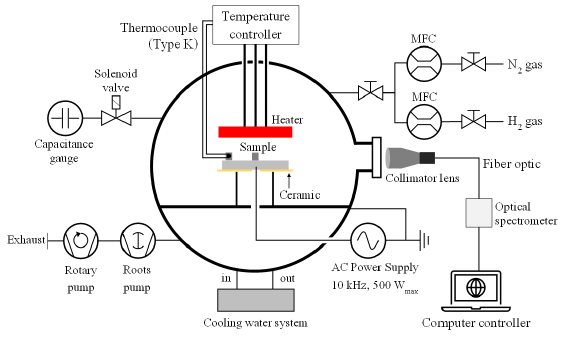
In this research, a nitride layer on tool steel was synthesized using a plasma-assisted nitriding process at low temperatures. Before nitriding, the SKD61 tool steel was cleaned with a hydrogen plasma for half an hour. Then, it was heated in a vacuum with 450 oC for half an hour and followed by plasma nitriding for 4 hours. The nitrogen flow rate was kept at 1000 sccm and mixed with the hydrogen as a different flow rate of 0, 300, and 500 sccm. The operating pressure was held at 149 Pa. The plasma was generated using a 10 kHz power supply with an average power of 53 W. The optical emission spectra during the plasma nitriding process were analyzed. The atomic nitrogen species were detected at the wavelengths of 427.33 and 585.57 nm. The atomic hydrogens at the wavelengths of 434.05, 486.14, and 656.28 nm also were founded. The energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy was used for the elemental analysis of a sample. The atomic nitrogen concentration decrease with the increase of hydrogen flow rate. The structural property of the nitrided specimens was examined using the X-ray diffraction technique. The -Fe3N phase was found corresponding to the 2
of 41.17, and the
-Fe4N phase was also detected at 47.97 and 70.2. Moreover, the CrN phase arising from the precipitation was identified at 63.30. The thickness of the nitrided layer was estimated from the SEM image. It appears that the nitrogen can diffuse into the specimens up to 184, 93, and 77 mm. The Vicker hardness of the nitrided samples was increased from 5.43±0.63 GPa to 11.36±1.20, 12.17±0.35, and 7.42±0.62 GPa that is corresponding to the hydrogen flow rate of 0, 300, and 500 sccm, respectively.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2021 The Journal of Applied Science

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.

