A mathematical model of melioidosis transmission in humans and animals with the effect of a rainfall factor
Keywords:
melioidosis, mathematical model, equilibrium points, basic reproductive number, rainfallAbstract
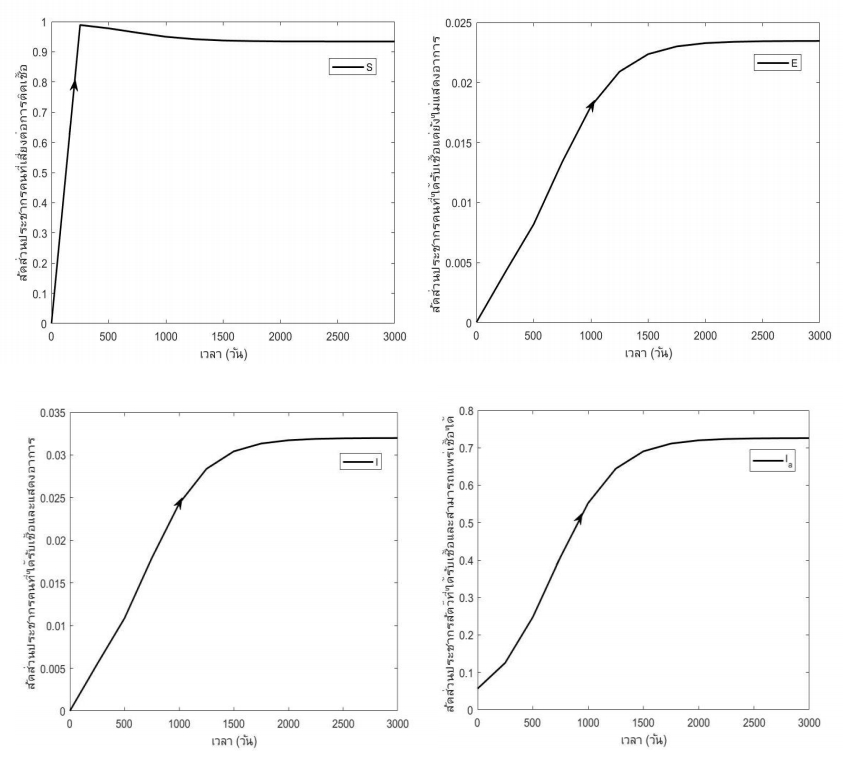
Melioidosis disease is caused by Burkholderia pseudomallei which can infect to humans and animals. Human can get infected from exposure to animal secretions. The bacteria are found contaminated soil or water and usually spread during the rainy season. This research formulating mathematical model of melioidosis transmission in human and animal. Adding rainfall factor to analyze effect of the epidemic with proportion of population infectious and symptomatic. We conducted to find the disease – free and endemic equilibrium points, basic reproductive number and analysis stabilities. The stabilities results disease – free equilibrium points has locally asymptotically stable whereas
and endemic equilibrium points has locally asymptotically stable whereas
. The numerical results the rainfall on simulated by 0.001, 0.01, 0.1 which effect with proportion of population infectious and symptomatic are 0.0320, 0.2008, 0.4253 respectively. Therefore, rainfall has an effect on transmission melioidosis disease to human.