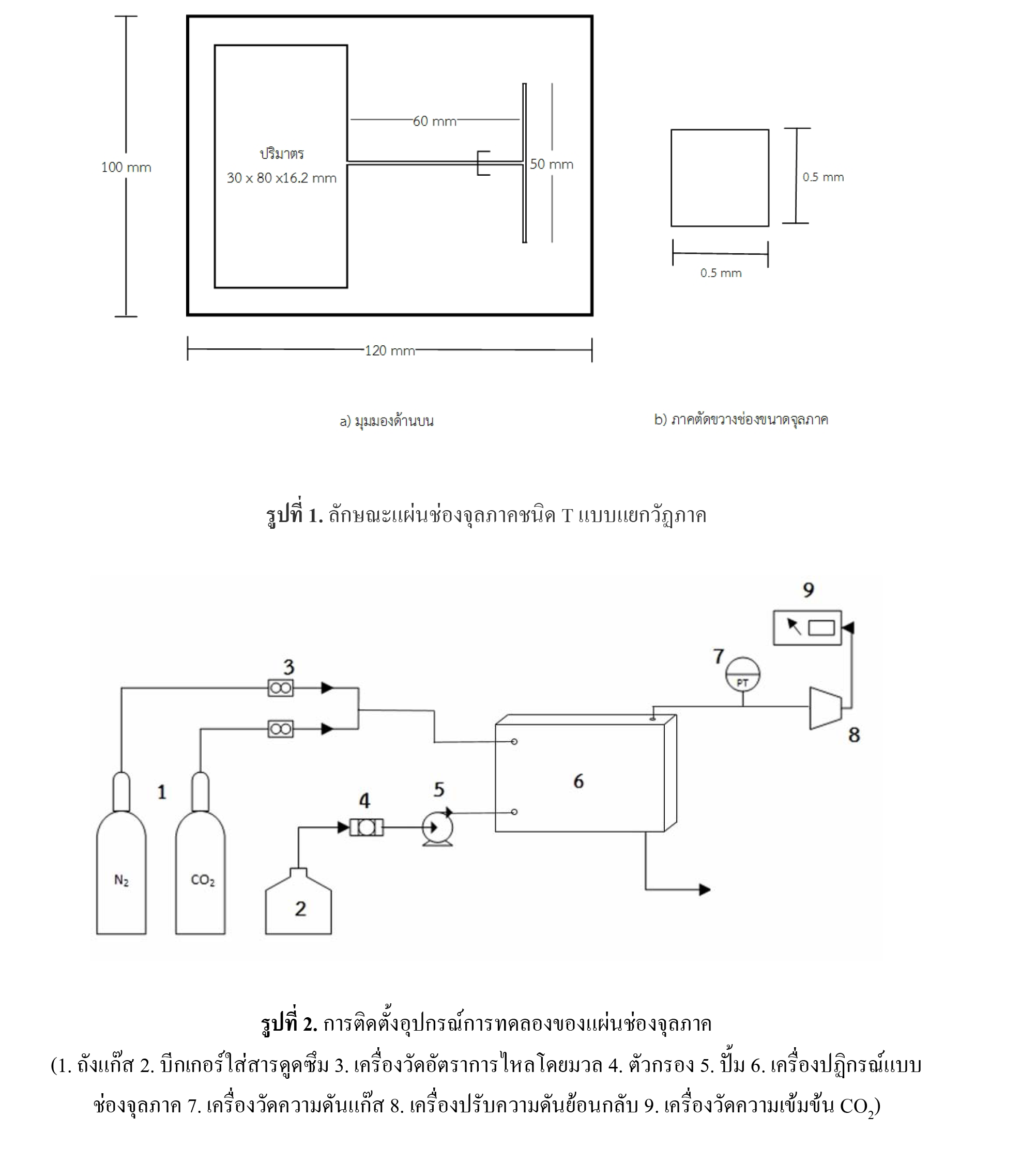
Carbon dioxide capture using monoethanolamine in a microchannel
Keywords:
carbon dioxide, microchannel, monoethanolamineAbstract
Carbondioxide (CO2) capture has considerably gained the interest from industry and research. To reduce CO2 emission and utilize the purified CO2, many processes have been developed such as packed-bed, bubble column etc. This work applied micro-technology for the absorption of CO2 by using monoethanolamine (MEA). Factors for the investigation include pressure (1-3 atm) molar ratio between MEA and CO2 (2:1 - 4:1) and volumetric flow rate of liquid phase (3-5 ml/min). The variation of liquid phase volumetric flow rate while keeping the molar ratio constant did not significantly affect the CO2 absorption efficiency. For atmospheric pressure, increasing the molar ratio slightly improved the performance. Increasing the operating pressure caused this effect to markedly decrease the log-mean CO2 concentration. By comparing the mass transfer coefficient obtained from different types of unit operation, microchannel exhibited high potential due to the high value of L
ka .