Thermal stability of zinc oxide - polystyrene composite thin film
Keywords:
dewetting, nanoparticles, thin filmAbstract
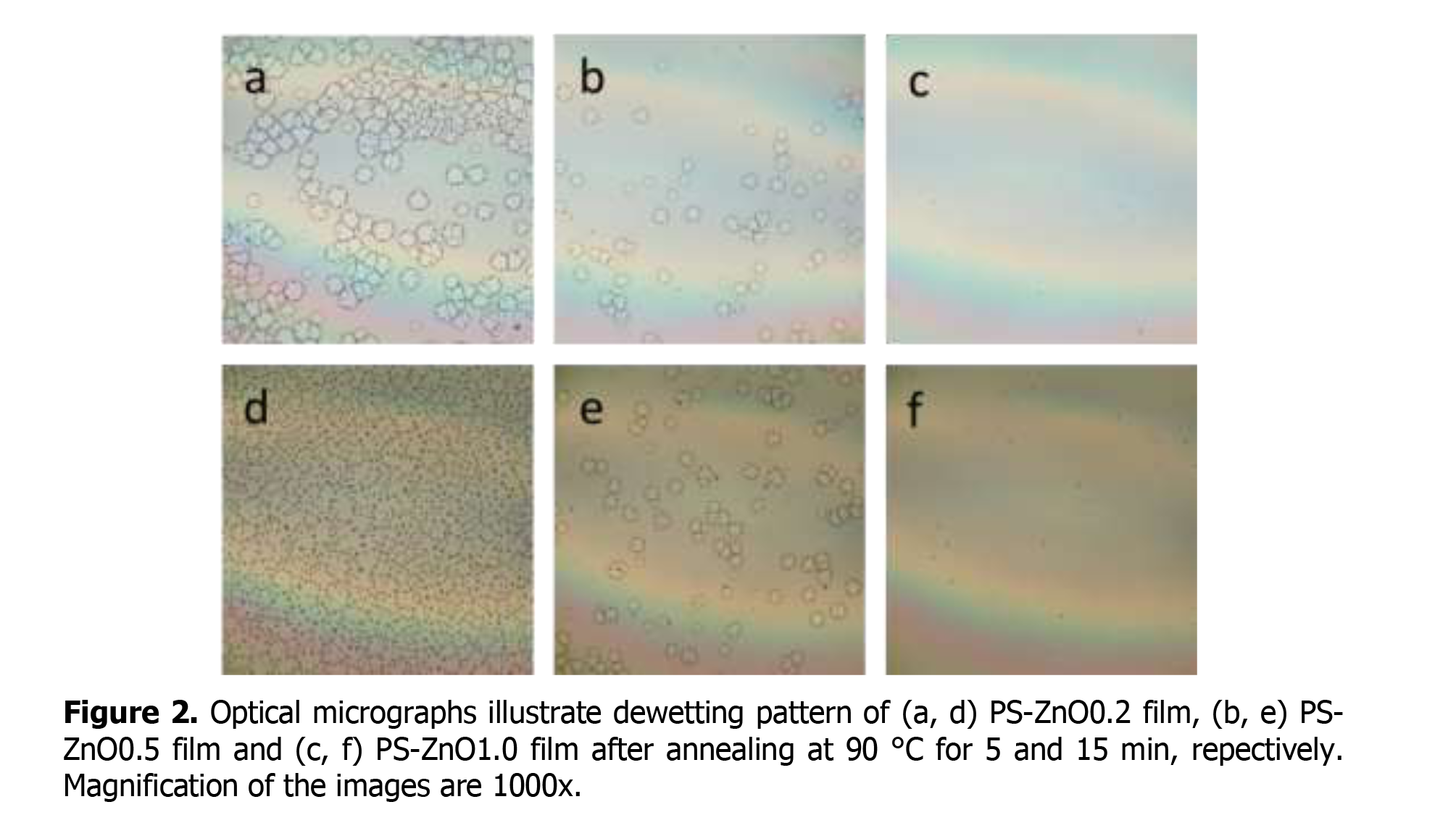
Thin polymer films need to be stable on solid substrates while processing application to preserve their properties. Increasing temperature causes polymer thin films lost their stability. From classical knowledge, the existence of impurity in polymer thin film usually induces dewetting behavior. However, addition of small amount of nano-fillers enhanced thermal stability of polymer thin film. In this research, thermal stability of composite film was investigated by adding zinc oxide nanoparticle into polystyrene thin film. The concentrations of zinc oxide nanoparticles were 0, 0.1, 0.2, 0.5 and 1.0 wt% in polystyrene (MW = 35,000 g/mol). After annealing the composite films at 90 °C for various times, the film morphology was studied by using optical microscope. Contact angle and surface energy of films were calculated by using contact angle measurement. Dewetting area was observed and considered to compare the percentages of each samples. From these results, we found that addition of zinc oxide nanoparticles can retard dewetting behavior of polystyrene film and increasing amount of nanoparticles increases thermal stability of composite films.