Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Barringtonia acutangula (L.) Gaertn leaf extract as reducing agent and their antibacterial and antioxidant activity
Keywords:
green synthesis, silver nanoparticles, Barringtonia acutangula (L.) Gaertn, antibacterial activity, antioxidant activityAbstract
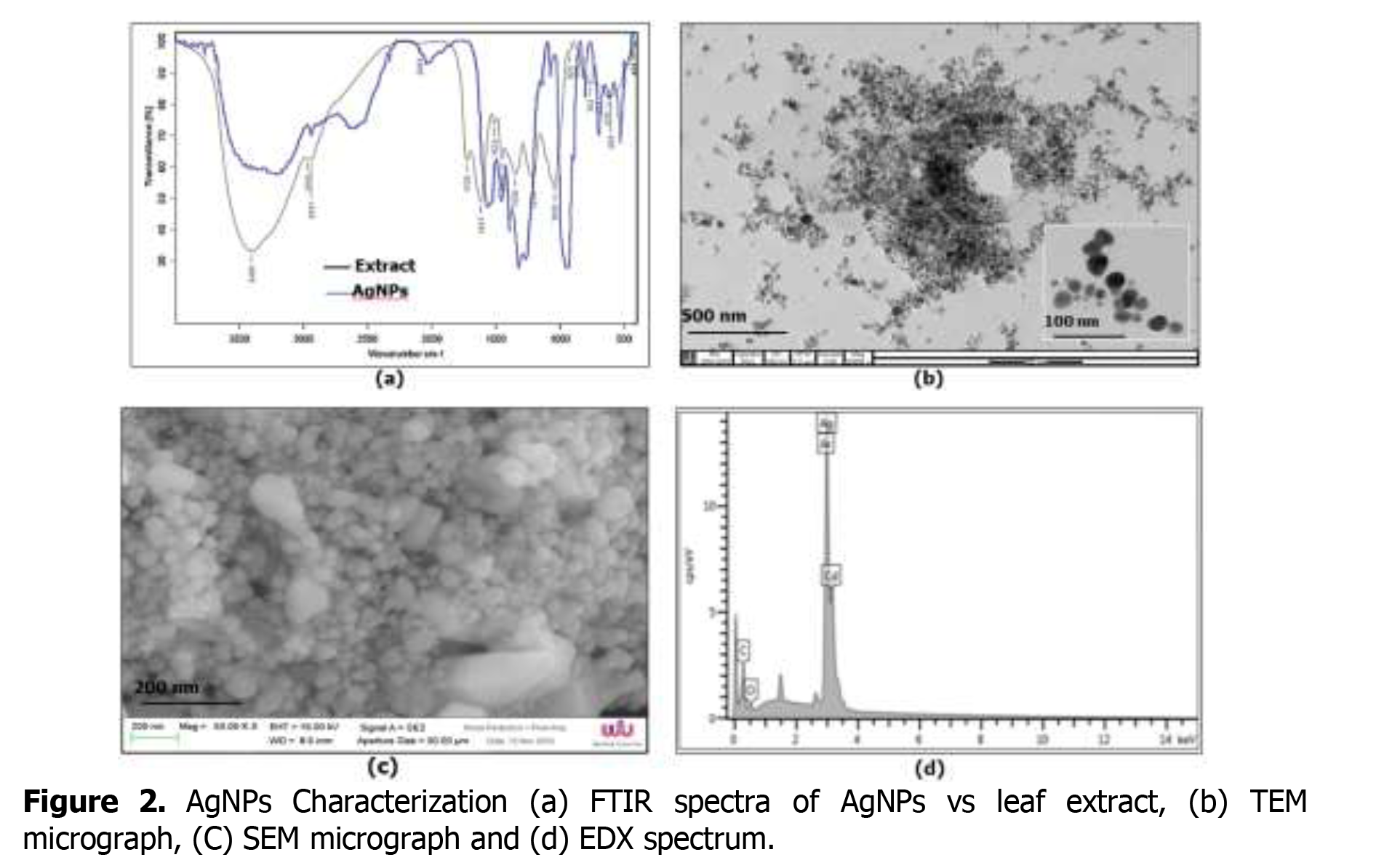
The green synthesis of nanoparticles has been proposed as a cost effective and environmentally benevolent alternative to chemical and physical methods. In this work, a synthesis of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) has been established using leaf extract of Barringtonia acutangula (L.) Gaertn to reduce an aqueous solution. The obtained samples were characterized by various techniques including ultraviolet visible spectroscopy (UV-Vis), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and laser particle size analyzer (LPSA). UV-vis spectra showed maximum absorption peak at 416 nm, which represents the characteristic surface plasmon resonance of the nanosilver. The structure of the particles was spherical and ellipsoidal as observed in TEM. FTIR analysis was carried out to probe the possible functional groups involved in the synthesis of AgNPs. The mean particle size calculated using LPSA was 60 nm. In addition, the synthesized AgNPs were tested for their antibacterial activity against two human pathogens including Escherchia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. The obtained AgNPs showed higher inhibitory activity on both bacterial species than the plant extract and the bare
solution. Moreover, the extract and the synthesized AgNPs were evaluated for the antiradical scavenging activity by 1,1-diphenyl-2-picryl-hydrazyl (DPPH) assay.