Effect of drying temperature on antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of coffee pulp extract
Keywords:
inhibitory effect, pathogenic bacteria, total phenolic compoundsAbstract
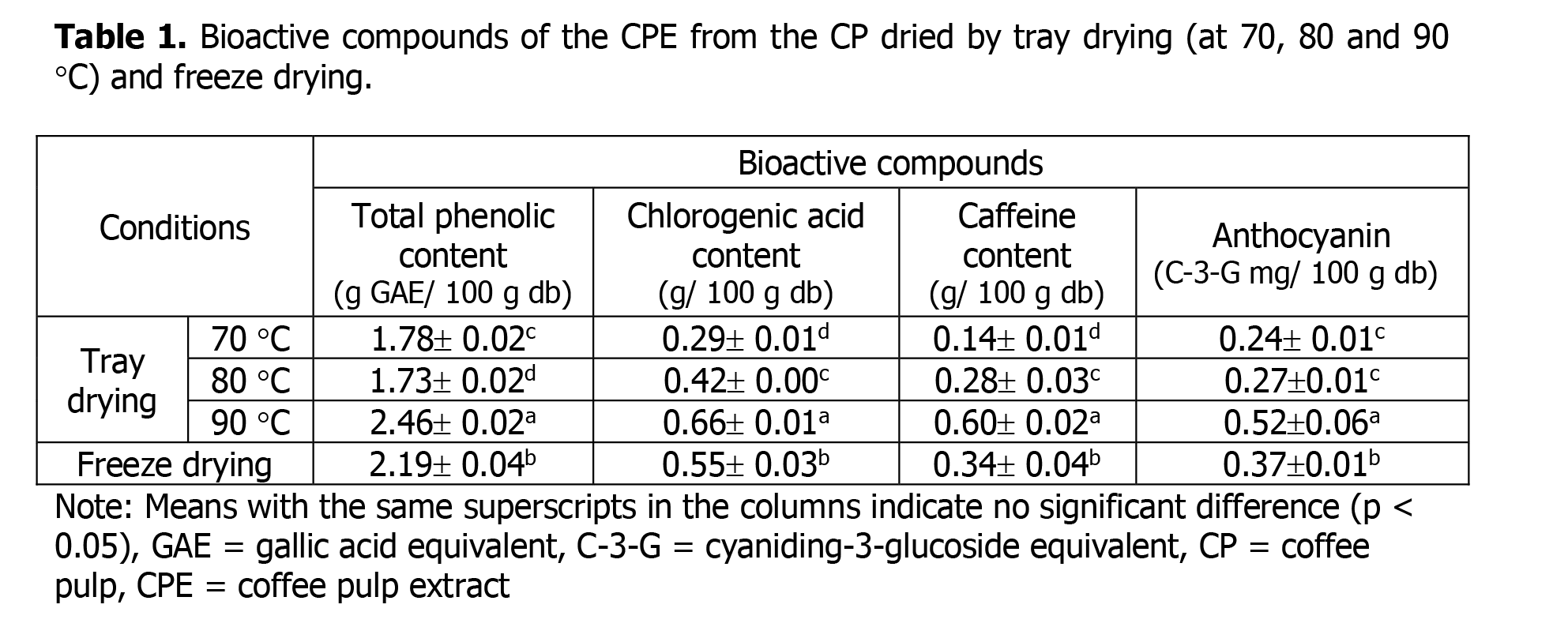
The aim of this study was to investigate the effect of tray drying on antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of coffee pulp extract (CPE). Coffee pulp (CP) was dried at 70 ℃, 80 ℃ and 90 ℃ using tray dryer until the moisture content of sample reached 13 %. Then, the CP was extracted with water to obtain CPE70, CPE80 and CPE90, respectively. Bioactive compounds, antioxidant and antimicrobial activities against some pathogenic bacteria of the CPEs were determined and compared to those of the freeze dried sample (CPEFD). It was found that total phenolic content of the CPE90 (2.46 ± 0.02 gallic acid equivalent (GAE) /100 g CPE db) was higher than that of the CPEFD (2.19 ± 0.04 GAE/ 100 g CPE db), CPE70 (1.78 ± 0.02 GAE/ 100 g CPE db) and CPE80 (1.73 ± 0.02 GAE/100 g CPE db), respectively. The antioxidant activity of CPE90 (1,303.44 ± 56.09 g trolox equivalent (TE)/ 100 g CPE db) was higher than that of the CPEFD (732.69 ± 30.28 g TE /100 g CPE db), CPE80 (688.24 ± 41.10 g TE /100 g CPE db) and CPE70 (548.36 ± 31.93 g TE/ 100 g CPE db), respectively. At 200 mg/ml of CPE solution, it was found that antimicrobial activity of the CPE90 exhibited the highest inhibitory effect against Staphylococcus aureus, followed by CPEFD, CPE80 and CPE70, respectively.