Demethylcurcumin analogs, the highly potent compounds for antioxidation in G6PD normal and deficient subjects
Keywords:
antioxidant, curcuminoids, curcumin analog, red blood cell, G6PD deficiencyAbstract
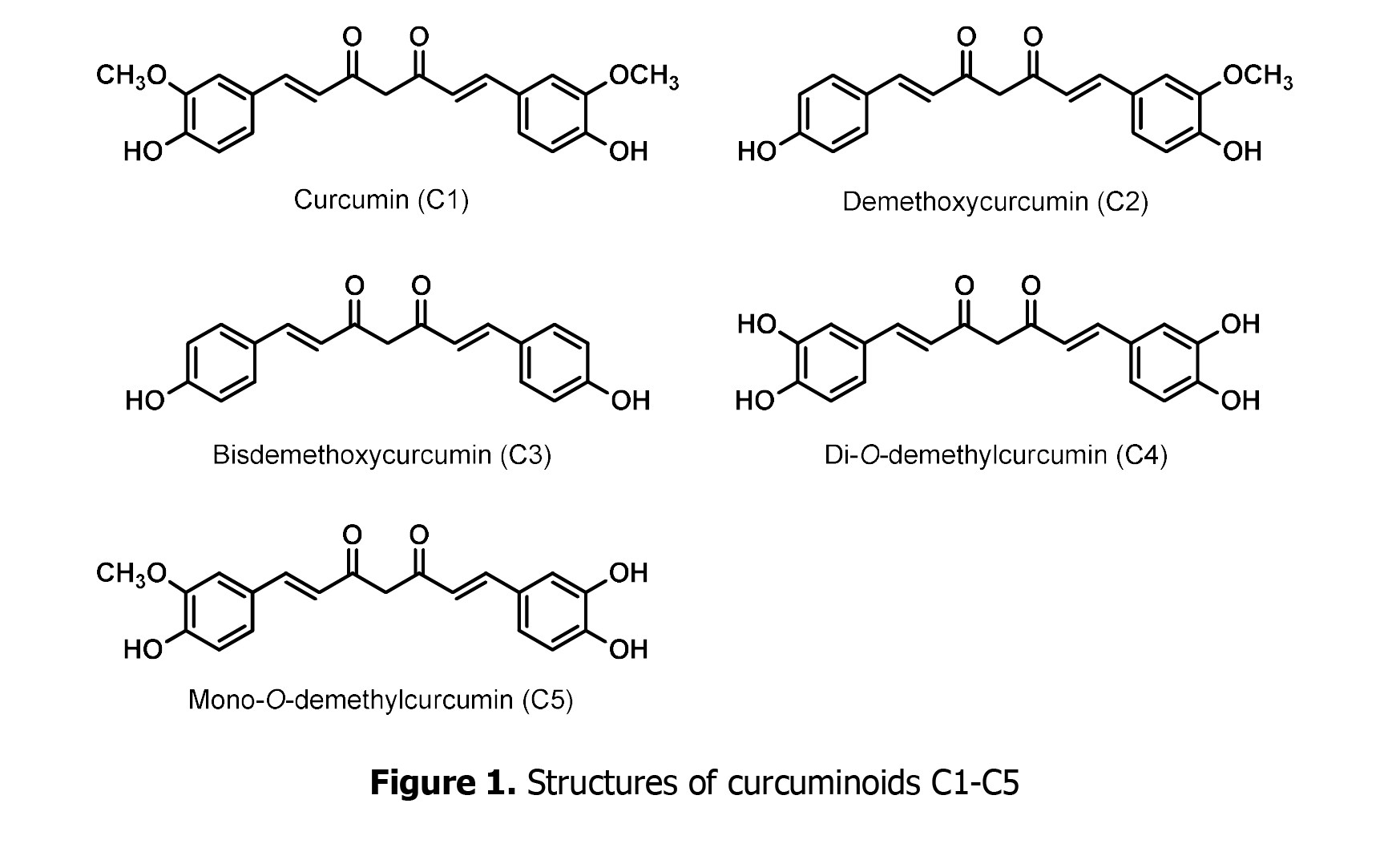
Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency can cause hemolytic anemia in response to oxidative stress. This study was undertaken to study the protective effect of natural curcuminoids (curcumin, demethoxycurcumin, bisdemethoxycurcumin) with curcuminoid analogs (di-O-demethylcurcumin and mono-O-demethylcurcumin) in healthy and G6PDdeficient red blood cells. After pretreatment blood with the test compounds, 0.75 mM sodium nitrite-oxidized hemolysate was determined for methemoglobin (metHb) formation. Concurrently, the released hemoglobin from 2,2'-azobis(2-amidinopropane) dihydrochloride (AAPH)-challenged cells was measured for hemolysis. We found that most of the compounds reduced metHb formation and oxidative hemolysis in red cells. After pretreatment with curcuminoid analogs, the oxidized hemoglobins were lower than treated with natural compounds. Furthermore, this study showed that demethylcurcumin analogs certainly protect AAPH-induced red cell lysis. This study can be concluded that curcuminoid analogs with different phenol rings possibly have higher antioxidant activity in order to protect the oxidative stress condition, especially in G6PD deficiency.