MAPPING OF RESERVOIR SANDS USING SEISMIC ATTRIBUTES AND POST STACK SEISMIC INVERSION IN NAM CON SON BASIN OFFSHORE VIETNAM
Main Article Content
Abstract
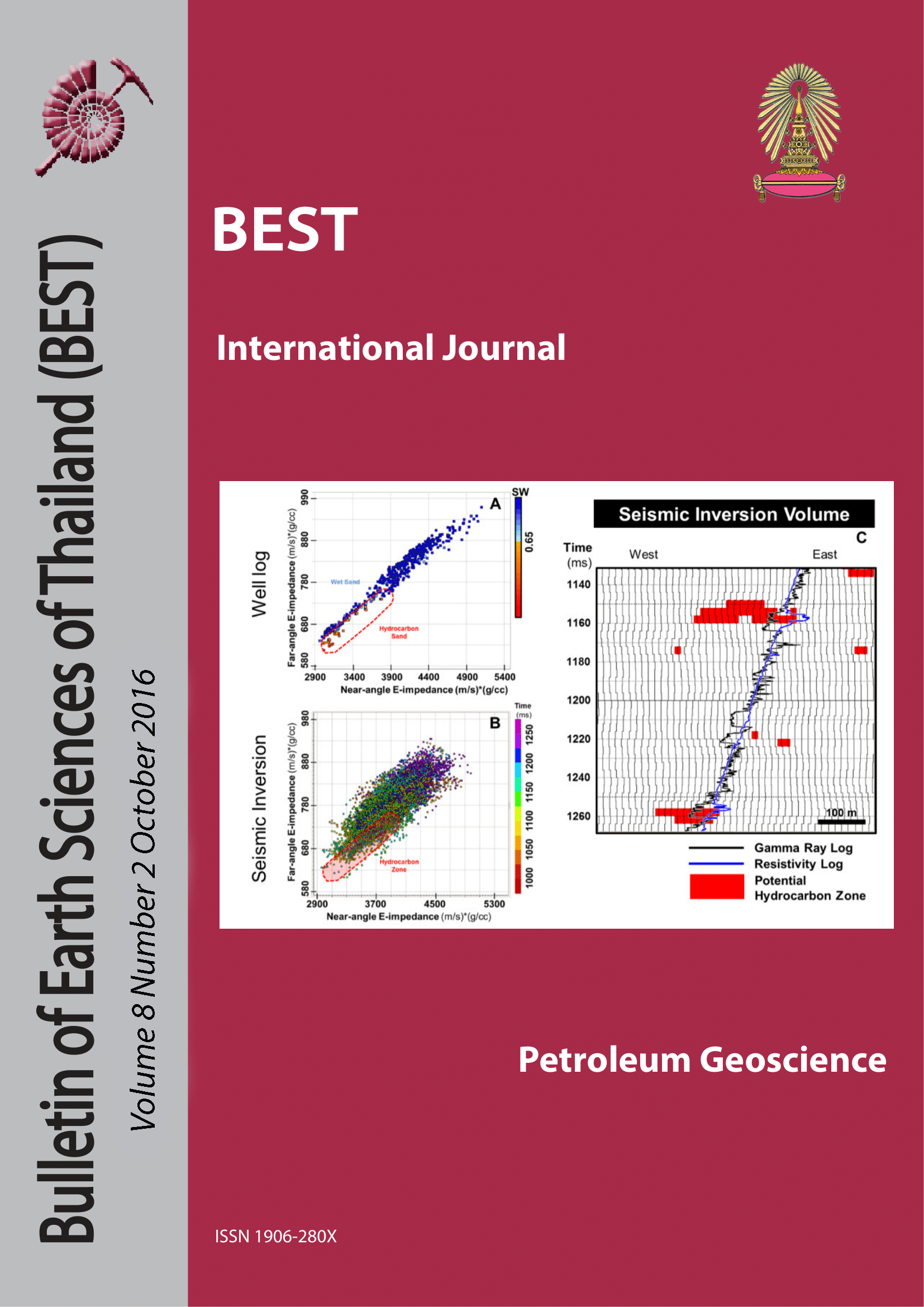
The study area lies within the Nam Con Son Basin located in East Sea offshore Vietnam. The reservoirs in the study area are Middle Miocene clastics of deep marine origin. The reservoirs are heterogeneously distributed and distribution of the reservoirs is further complicated due to complex extensional fault system. Therefore mapping of these reservoirs is difficult based on seismic data. The purpose of this study is to apply rock physic analysis, seismic attributes and post-stack seismic inversion to map sand geometries and hydrocarbon zones. According to rock physics analysis, P-impedance of shale is less than the sand, and the presence of gas within sand reduces the P-impedance. Therefore P-impedance of gas sands and wet sands is different. However, P-impedance of shale and gas sand may partially overlap within the larger interval. Hence, by the analyze P-impedance within the narrow zone of the reservoir we may successfully map the gas sands and differentiate gas sands and wet sands. The extracted P-impedance horizon slice along inverted P-impedance volume successfully mapped the gas sand distribution. RMS attribute shows high amplitude along gas saturation zone. Low-frequency amplitude anomalies obtained from spectral decomposition indicates high value at well with high gas percentage, whereas at the well with a low proportion of gas, it does not show high amplitude. Thus, the combination of spectral decomposition and seismic inversion may successfully map hydrocarbon distribution. The fault blocks which are close to the high structure has relatively more sand. The proposed workflow for mapping sand and gassand can be used forthe furtherwell drilling programs.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Copyright © 2008 Department of Geology, Faculty of Science, Chulalongkorn University. Parts of an article can be photocopied or reproduced without prior written permission from the author(s), but due acknowledgments should be stated or cited accordingly.
References
Ahmad, M. N., 2013. Mapping of fluvial sand systems using rock physics analysis and simultaneous inversion for density: case study from the Gulf of Thailand.
Bouma, A. H., 2002. Geological reservoir characteristics of fine-grained turbidity systems.
Castagna, O., 2003. Instantaneous spectral analysis: Detection of low-frequency shadows associated with hydrocarbons.
Dangprasitthiporn, M., 2015. Lithology prediction using rock physics and acoustic impedance for reservoir distribution in Northern Pattani basin, Gulf of Thailand.M.Sc. Thesis, Chulalongkorn University.
Dubey, A. K., 2012. Reservoir characterization using AVO and seismic inversion techniques.
Gavotti, P. E., 2013. Post-stack inversion of the Hussar low frequency seismic data.
Liem, P. T., 2013. Some comments on the possibility of middle/late miocene-pliocene stratigraphic traps in the centre of nam coson basin.
Priyanto, B., 2012. Lithology prediction using rock physics analysis and seismic inversion within Miocene fluvial reservoir interval in the Songkhla basin, Gulf of Thailand. M.Sc. Thesis, Chulalongkorn University.
Rodriguez, J. M., 2009. Spectral decomposition and inversion: case study of a production area in the cook inlet basin, Alaska, USA.
Rotimi, O. J., Wang, Z., Ako, D.B., 2014. Seismic attribute utilization for structural pattern detection, fault imaging and prospect identification.
Willmore, D., Giao, N., Tin, N.T., Dung, L,V., 1991. Petroleum Geology and Hydrocarbon Potential of Nam Con Son Basin.
Singh, V., 2006. Acoustic to Elastic Impedance –A New Tool for Reservoir Characterization.
Swisi, A., 2009. Post- and Pre-stack attribute analysis and inversion of Blackfoot 3D seismic dataset.
Y, L., 2015. A rock physics model for the characterization of organic rich shale from elastic properties, Petroleum Science.